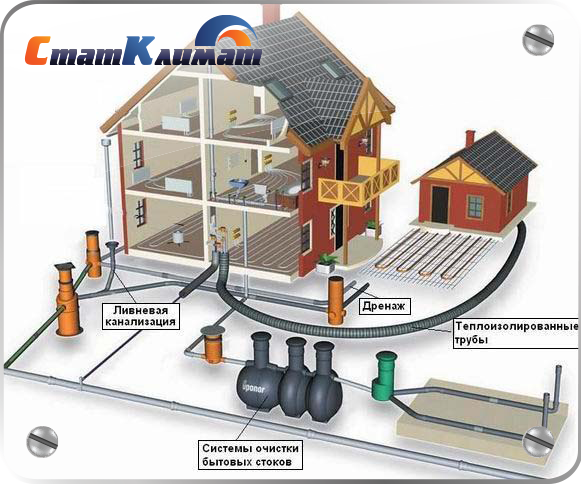
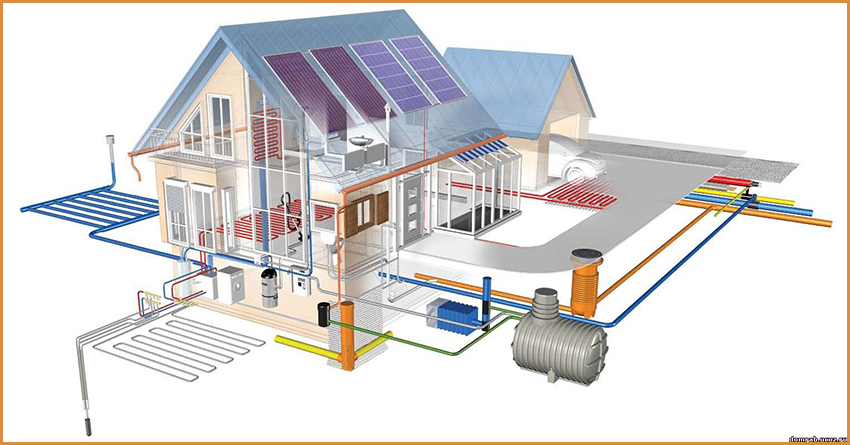
From internal pipelines, drains are transported by external ...

Given the increased popularity of natural wood buildings, a new industry has emerged in the field of house construction, the basis of which is frame technology for building houses.
This technology is considered the most economical in comparison with buildings made of solid wood, therefore it is very common everywhere and is gaining popularity in the CIS countries.
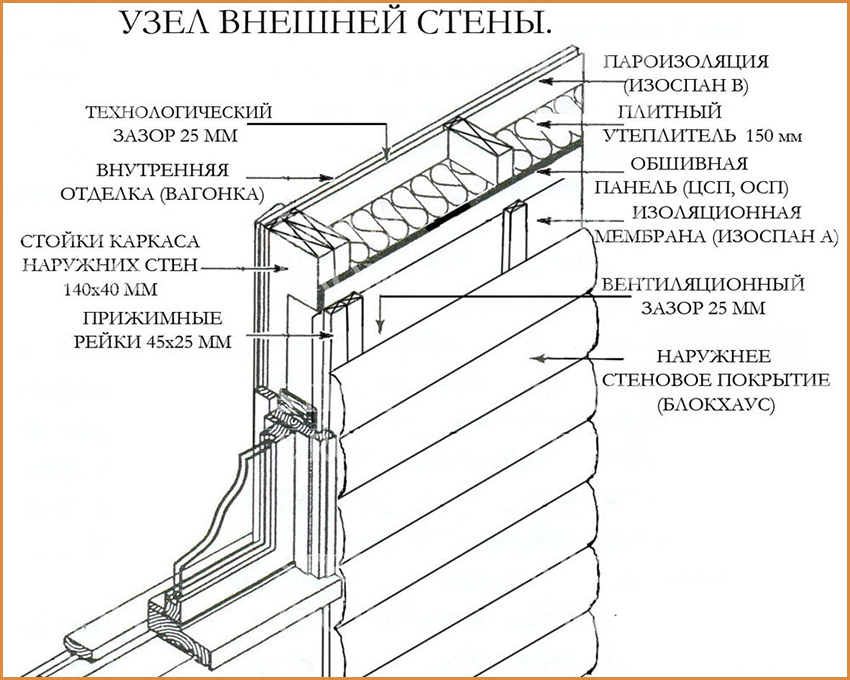
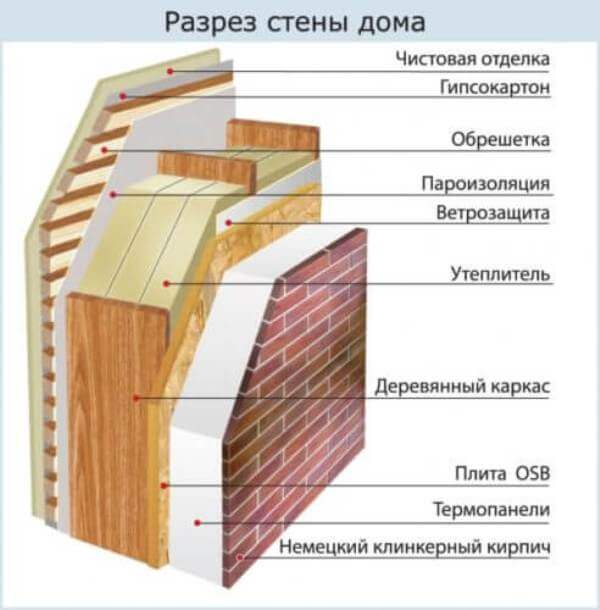
 The frame structure is a structure consisting of a large number of layers. Its frame is formed by wooden posts, separated by a heater, protected by vapor barrier film and hydro-wind insulation.
The frame structure is a structure consisting of a large number of layers. Its frame is formed by wooden posts, separated by a heater, protected by vapor barrier film and hydro-wind insulation.
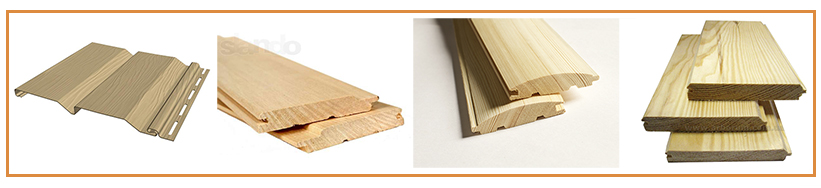 Outside the house is sheathed decoration materials:
siding, lining, blockhouse, raised beam.
Outside the house is sheathed decoration materials:
siding, lining, blockhouse, raised beam.
Frame technology is used in the construction of private cottages, because it is characterized by low cost and impressive construction speed, and in addition - environmental friendliness and reliability of the structure under construction - a complete set of advantages for the construction of a wooden house.

Gained great popularity in the construction of a frame house. Traditions of this technology have arisen in Europe. Similarly, a large half of private cottages in the United States were built. It is in demand in Canada, in Germany, in England, in Sweden, etc.
Many have heard the name “Finnish house”, but few know what is meant. In each region and country, there are certain characteristic features that are taken into account when using available materials for construction, insulation, installation. The most popular are Norwegian, Finnish and Canadian frame buildings.
 The essence of this technology is as follows:
The essence of this technology is as follows:
The Finnish technology differs from the rest by the factory production of constituent parts for the collection of partitions and in that the panels are assembled at the construction site and installed ready for the frame structure.
Advantages of frame construction:
 In the process of erecting a frame house using materials from natural wood, which are characterized by poor thermal conductivity. The walls are small enough in thickness to provide good thermal insulation. In this regard, the frame of the new building is insulated using non-combustible special heat-insulating materials. In addition, they use special roll materials that provide proper hydro- and vapor barrier.
In the process of erecting a frame house using materials from natural wood, which are characterized by poor thermal conductivity. The walls are small enough in thickness to provide good thermal insulation. In this regard, the frame of the new building is insulated using non-combustible special heat-insulating materials. In addition, they use special roll materials that provide proper hydro- and vapor barrier.
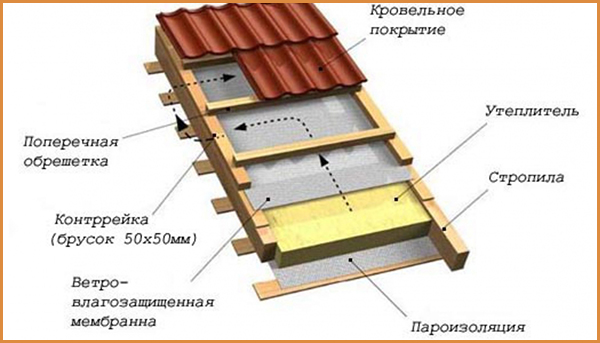 It takes about a week to make the roof covering. Use a metal tile or flexible tile. If the owner wants to save money, then a simple slate is often used.
It takes about a week to make the roof covering. Use a metal tile or flexible tile. If the owner wants to save money, then a simple slate is often used.
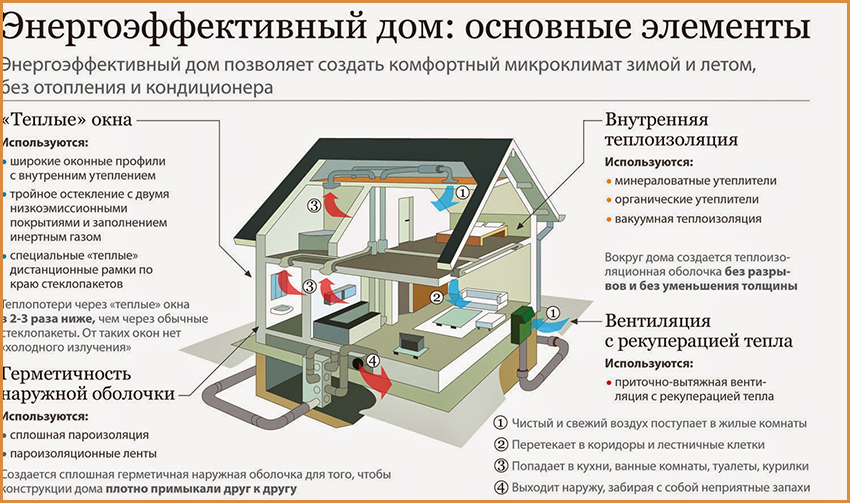
 Passive house is an example of modern high-tech standards in the construction industry. This design is called an energy-passive house. Passive structures are considered to be the warmest, since they are characterized by the lowest heat loss. The climatic conditions outside do not affect temperature condition indoors.
Passive house is an example of modern high-tech standards in the construction industry. This design is called an energy-passive house. Passive structures are considered to be the warmest, since they are characterized by the lowest heat loss. The climatic conditions outside do not affect temperature condition indoors.
The main characteristics of passive structures include:
The “passive structure” standard is a set of building rules, observing which you can create the most comfortable conditions for your home.
 “Passive houses” are carefully insulated, which makes it possible to save on heating and consume significantly less electricity than in standard houses.
“Passive houses” are carefully insulated, which makes it possible to save on heating and consume significantly less electricity than in standard houses.
Due to the strong thermal insulation of the wool, the external walls have a high degree of resistance to temperature changes.
In all cases, the house itself can store heat inside in the winter, and in the summer - cool. Great demand for such houses already exists everywhere.
If we compare a standard house with an energy-passive, then the difference in the consumption of thermal energy is obvious. This effect is created with extremely careful design of the structure.
 Features of the passive cottage:
Features of the passive cottage:
Properly designed and constructed in accordance with the adopted rules, the passive building almost does not require heating. Today, the construction of a house is not suitable from the point of view of appearance or inner luxury, but in terms of quality and characteristics of building materials.
Now the price has completely different quality architectural indicators. Current designers prefer simplicity and the greatest practicality.
Energy-passive houses allow to achieve the following tasks:
 It will be extremely difficult to acquire a fully Finnish project, because all of the above are projects of homebuilders. So they are considered know-how and go as an appendix to a set of firms. The Scandinavians will probably be against the sale of only the project.
It will be extremely difficult to acquire a fully Finnish project, because all of the above are projects of homebuilders. So they are considered know-how and go as an appendix to a set of firms. The Scandinavians will probably be against the sale of only the project.
If you have skills in building a frame house and taking into account the peculiarities of the Scandinavian method, then planning with the dimensions and appearance of the dwelling will already allow you to create, based on the data obtained, a high-quality building project.
Based on this, you can create an exact copy of the Finnish house. This will come out significantly less in price than if you order an original Finnish kit. The level of conformity of the design is determined by the wishes of the customer and his capabilities. In other words, having a “donor” in the form of a layout, facade, appearance - it is possible to place an order for the construction of your own individual constructive project and erect an identical copy of the Finnish project that you liked, having spent significantly less on this.
 Answer how much it costs frame house quite difficult. For starters, due to the fact that there is no such term as a “correct” wireframe project. There is no single and correct scheme for the construction of walls; there is no only correct technology.
Answer how much it costs frame house quite difficult. For starters, due to the fact that there is no such term as a “correct” wireframe project. There is no single and correct scheme for the construction of walls; there is no only correct technology.
The house, which is built in accordance with Finnish frame technology, requires regular inspection. Check the building from base to roof: see if there is fungus or dampness in any places. If such places occur, then it is necessary to eliminate the cause, to carry out additional processing of wood, after it has been thoroughly dried.
Many companies provide ready-made buildings for the Finnish project. You can simply choose a house, and prepare the base on the site. It will be much more expensive in cost, but will have a number of advantages:
Frame housing construction is gaining momentum in the past few years. Among the ads in newspapers, on billboards and on the Internet, one can often see that the company offers construction using Canadian, Finnish or Scandinavian technology. But if you look at the characteristics and equipment of the proposed projects, it becomes unclear what the difference is. The same description of the technology, the same materials, but a different name.
What is the real difference between Finnish, Canadian and Scandinavian houses, and is there a separate Russian technology for frame construction? Let's figure it out.
Most often, in Finland close to us, houses are built using frame technology as in Russia - each in its own area. This determines the characteristics of the material and the stages of work.
The so-called "Finnish houses" have been known to us for a long time, but not everyone could afford them. The erection of the building looks almost like a miracle - the truck delivers a set of materials, including ready-made sections of the walls, with windows, cladding - both internal and external, doors and more. And do not have time to look around, as in a recently still empty place is absolutely finished house. This is the real Finnish skeleton.
![]() Key features of this technology:
Key features of this technology:
Despite the fact that the technology is often called Finnish, it fully complies with the Scandinavian (Sweden, Norway, Denmark) model.
In the USA and Canada, frame construction is widespread. The reason for this is the rapid construction, compliance with the requirements for residential premises and household buildings and a successful combination of materials, guaranteeing a sufficiently long and safe operation of buildings. Canada and the USA have their own nuances of frame construction:
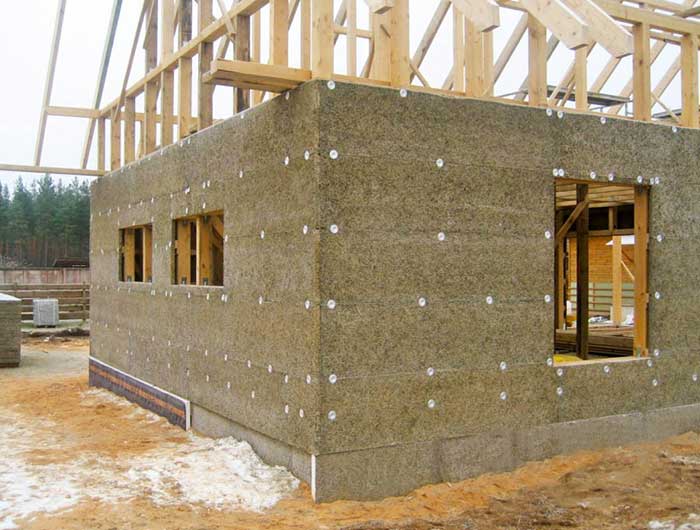 The requirements for lumber, of which the frame is made, in the United States and Canada are much less than those adopted in Europe and, in particular, in Finland. This is due to climatic conditions, air humidity and temperature differences in these countries are much less.
The requirements for lumber, of which the frame is made, in the United States and Canada are much less than those adopted in Europe and, in particular, in Finland. This is due to climatic conditions, air humidity and temperature differences in these countries are much less.
There is a reason determining the development in the USA and Canada by frame structures of a certain area with the use of frame-panel materials of low readiness. Business in economics and taxation in the United States of America. The practice of mass redemption of lands on which the owner builds standard houses on an area of \u200b\u200bseveral tens of hectares is widespread there. In these conditions, it’s easier and more profitable to create construction site production facilities for the preparation of materials (cutting to size, assembly of blocks) than to purchase ready-made block elements.
Scandin technology should not be singled out. It is characterized by the same features as the construction of frame houses in Finland. The only difference between residential properties in Norway, Denmark or Sweden is the layout - characteristic feature is the presence of a living room on the second floor. But the design features of the frame houses of the Scandinavian or Finnish are absolutely identical.
![]() In Russia, frame construction is mainly imitating Finnish or Scandinavian. There are no peculiar features, except that the construction of frame houses and other structures takes place in direct mode, that is, "live". Thus, in Russia frame-panel constructions are a mixture of Canadian and Finnish methods.
In Russia, frame construction is mainly imitating Finnish or Scandinavian. There are no peculiar features, except that the construction of frame houses and other structures takes place in direct mode, that is, "live". Thus, in Russia frame-panel constructions are a mixture of Canadian and Finnish methods.
In Russia, most often they build houses using the frame-shield method. This method is a combination of the real Canadian and European methods, the panels of minimum availability are combined with the assembly of the frame in real time. It is also worth noting that the material for the frame most often becomes a wooden beam, while in Europe and America both wood and metal profile pipes are used.
Features of construction and the advantages of the Finnish technology for building houses - what you need to know in order for the construction to be rational, and the further operation process to be effective?
Each developer in the choice of construction technology tries to identify priorities on the budget issue in the preparation of estimates, the complexity of the process, the availability of material and a number of other criteria. And the construction of buildings using Finnish technology perfectly meets most of these criteria.
 Simplicity of design is one of the main advantages of this technology. Finnish houses are built from wooden beams with a cross section of 245x100 mm and a pitch of their location up to 400 millimeters. They form the actual frame of the building, which is then sheathed with wooden plates.
Simplicity of design is one of the main advantages of this technology. Finnish houses are built from wooden beams with a cross section of 245x100 mm and a pitch of their location up to 400 millimeters. They form the actual frame of the building, which is then sheathed with wooden plates.
The cladding device is precisely the most basic and distinctive parameter of buildings for such projects. Their priority is to ensure the preservation of heat in the house. And it is precisely this advantage that underlies Finnish projects.
 The following primary indicators clearly indicate in favor of the choice of this particular technology by many developers:
The following primary indicators clearly indicate in favor of the choice of this particular technology by many developers:
But at the same time, there are negative episodes in this construction project, for example, - low noise insulation of partitions, very weak strength of slabs for cladding. However, all this can be offset by additional cladding materials with appropriate parameters. But in this case, the estimate will have to be increased, which is also a drawback.
This is not a complete list of the disadvantages of frame houses. On our site there is another article that contains all the pluses and. Forewarned is forearmed!
Read about other types of frame houses for permanent residence. It also has useful information about minimizing costs, planning and much more.
 The choice of materials for the construction of Finnish structures is limited by a small amount, which simplifies the construction process and reduces costs. For the construction you need:
The choice of materials for the construction of Finnish structures is limited by a small amount, which simplifies the construction process and reduces costs. For the construction you need:
Are needed wooden bars having a cross section of 245x100 mm. In seismically unstable regions, the cross section can be selected more. Similarly, it is worth choosing a larger cross-section of the beam for construction in areas with moving soils.
To give the appearance of a greater originality, you can use a profiled beam, the walls of which do not need finishing exterior work.
Also gaining popularity glued beam, which has improved thermal insulation qualities, high strength and sound insulation. Such material is less susceptible to deformation, perfectly resists the action of biological microorganisms, high humidity. And one more advantage of glued beams is fire safety.
The beam is used to create directly the building structure, its load-bearing elements, the basis for the floor, ceiling and wall partitions.
 Plates are used in Finnish technology for cladding internal and external wall surfaces.
Plates are used in Finnish technology for cladding internal and external wall surfaces.
The device of the plates according to Finnish technology is a multilayer structure, the functionality of which is to ensure thermal insulation.
OSB is used for internal cladding, which consists of several layers of shavings bonded with resins and wax. The outer skin is made of fiberboard (fiberboard). To ensure moisture resistance, such a plate should be treated with wax.
As a heater, it is better to use mineral wool.
Roofing, material of the inner lining is chosen at the discretion of the developer.
It does not need massiveness, as the design is lightweight. Therefore, for laying the foundation, you can choose a shallow tape foundation.
 For its installation, it is necessary to prepare a trench up to 50 cm deep - depending on the structure of the soil. Around the perimeter, formwork is made of boards with a thickness of 50 mm. Opposite sides of the formwork are fastened together by transverse bars to avoid squeezing out concrete.
For its installation, it is necessary to prepare a trench up to 50 cm deep - depending on the structure of the soil. Around the perimeter, formwork is made of boards with a thickness of 50 mm. Opposite sides of the formwork are fastened together by transverse bars to avoid squeezing out concrete.
A reinforced mesh of reinforcement with a cross section of 3-5 mm is laid on the bottom along the entire length of the trench to ensure the rigidity of the base.
After preparatory work, pouring concrete of grade not less than 300 is carried out. After hardening, it is necessary to level the basement with cement mortar.
A more cost-effective alternative to the foundation for such houses is the base of bored piles.
 A well is prepared for its device to a depth of not less than 1/3 of the pile height. Not at its bottom is a sand cushion falling over, on top of which small gravel is tamped.
A well is prepared for its device to a depth of not less than 1/3 of the pile height. Not at its bottom is a sand cushion falling over, on top of which small gravel is tamped.
Reinforcement is fixed along the height of the well, after which concrete 300-400 is poured. The upper edges of the pile structures are complemented by reinforcement segments that reinforce the grillage.
A bored type of foundation is more advantageous than the others when using Finnish construction technology in that the building on piles is higher. And considering that the main material in this technology is wood, such a foundation will be able to protect the house from the effects of dampness on the lower part of the structure. A bored foundation is also more promising for financial reasons.
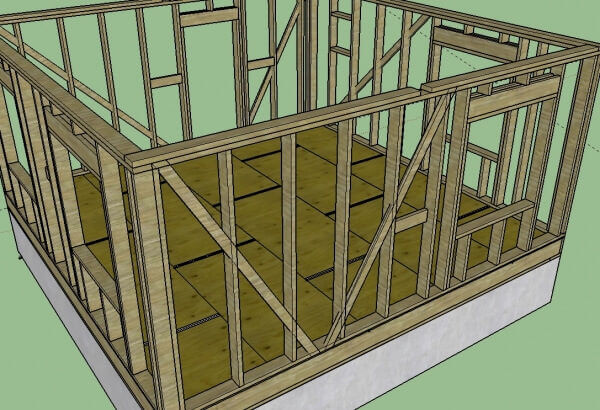
 The construction process begins with the installation of vertical angle bars. All four beams should be proportionally placed relative to each other - the diagonals between two opposite corners should be perfectly equal.
The construction process begins with the installation of vertical angle bars. All four beams should be proportionally placed relative to each other - the diagonals between two opposite corners should be perfectly equal.
In parallel with the corners, vertical posts are fixed in one line, forming the basis for fastening the transverse beams. To connect the individual structural elements, it is necessary to cut the grooves at the junction of the beams and racks.
In order to avoid distortions of the wall area, its entire structure should be additionally strengthened by diagonal jumpers connecting diagonally opposite corners.
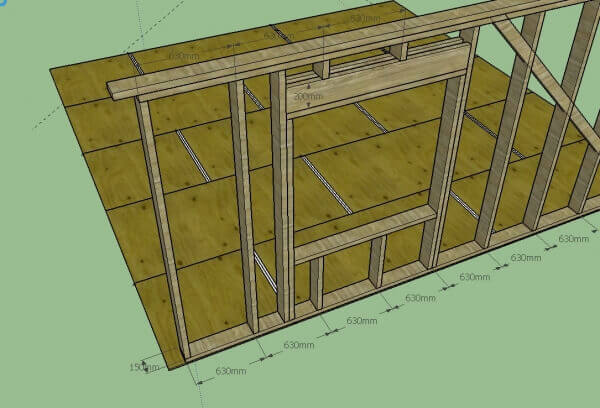
When arranging pepper beams, the location of the window and door openings is left. In these places, short sections of the bars are installed, outlining the format of future openings.
Ready panels are fastened to the finished frame. Or an OSB plate is used, under which a heat insulator is located.
Internal partitions are also attached to the bases of the supporting elements. If the partition passes through the entire length or width of the house, then its horizontal beams are mounted on opposite walls, abutting the edges to the joints of the uprights and beams. If the partition according to the project is only half the length of the house, then a vertical stand is installed at its location. Doorways in partitions are made by analogy with load-bearing walls.
 The floor can be wooden, which is more characteristic of Finnish technology, and can be made as a concrete screed. But the last option does not contribute to the warmth in the house.
The floor can be wooden, which is more characteristic of Finnish technology, and can be made as a concrete screed. But the last option does not contribute to the warmth in the house.
For wooden racks stacked wooden logs aligned on a horizontal level. A floorboard 50 mm thick is mounted on them.
Interfloor overlap is arranged on vertical racks, between which beams are placed. Those, in turn, are also fastened with parallel bars. And already on top of this design the floor is laid, after which the ceiling of the first floor is mounted.
It will help to take the first steps.
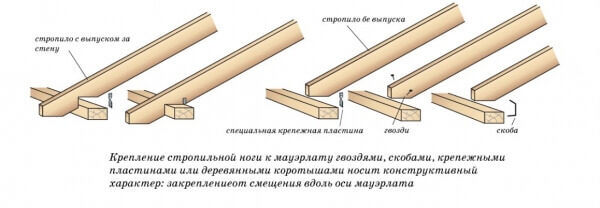
 Roof installation begins with the installation of roof trusses. These are structures of a triangular shape, knocked down at a certain angle and fastened by a transverse beam.
Roof installation begins with the installation of roof trusses. These are structures of a triangular shape, knocked down at a certain angle and fastened by a transverse beam.
Each farm connects to the rest of the beams. On top of the resulting structure, waterproofing with ruberoid or other materials with similar properties is arranged.
Further actions depend on the type of material chosen, which is mounted on top of the waterproofing layer.
The simplicity of construction and the low complexity make it possible to assemble a house using Finnish technology even on their own. The main thing is a strict adherence to the technological scheme and a well-thought-out choice of materials.
In contact with
Classmates
Frame house - one of the most affordable and budget options for suburban construction.
But as soon as it is laid down, an equally responsible stage begins: a device that has its own characteristics in such buildings.
They must be studied before starting construction work in order to avoid in the near future overhaul the whole structure.
![]()
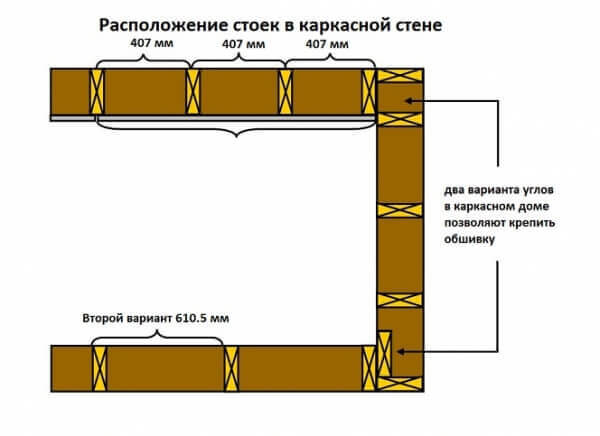
For frame house frame wall structures have only two types:
Reference! Internal partitions intended for zoning of living space are often made of 40x100 timber, since they do not need a thick layer of insulation. For load-bearing walls, materials with a cross section of at least 50x150, and preferably 50x250, are taken in order to be able to increase the thickness of the insulating layer.

What material is used to assemble the walls of frame houses? If you have chosen frame houses for your housing: wall material can be completely different.
It is determined not only by aesthetic properties, but also by the ability to withstand certain loads, climatic and relief features of the site, weight and other characteristics.
For the device of wooden frame walls and partitions mainly use:
Reference! According to one of the innovative technologies, the supporting frame of the structure is completely made of galvanized thermoprofile, and shotcrete or foam concrete serves as the internal insulation. This makes it easy to build a strong and reliable house with the number of floors from 1 to 5.
A frame house can be erected in various ways, since today several effective technologies for creating its walls are known. The most popular among them are: the frame wall construction according to Finnish technology and Canadian. Their differences are that, in accordance with the Scandinavian method, wall panels are assembled directly at the construction site, but construction technologies from Canada involve the installation of a frame from ready-made SIP panels (frame-panel technology).

Finnish is as follows:

When designing a building according to Canadian technology, the work algorithm is as follows:
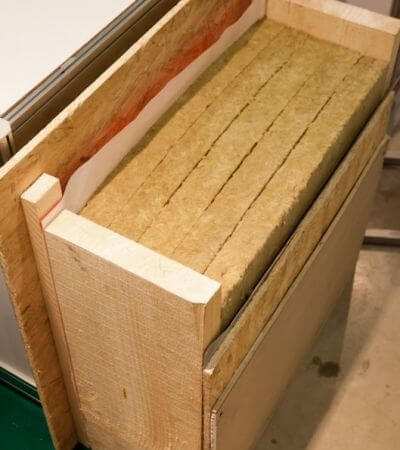

What does the wall of a frame house consist of?
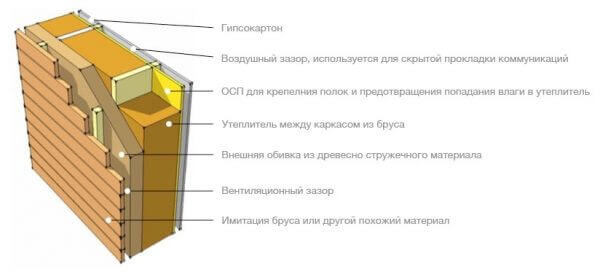
No matter how sophisticated the design of your frame house may be, and what expensive materials have not been used, the design of the frame wall with insulation, especially the carrier, will be almost identical.
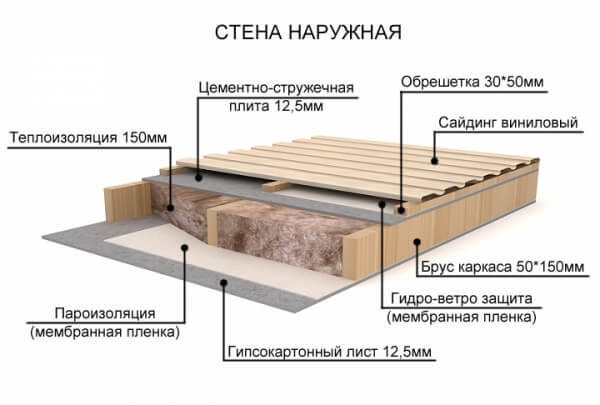
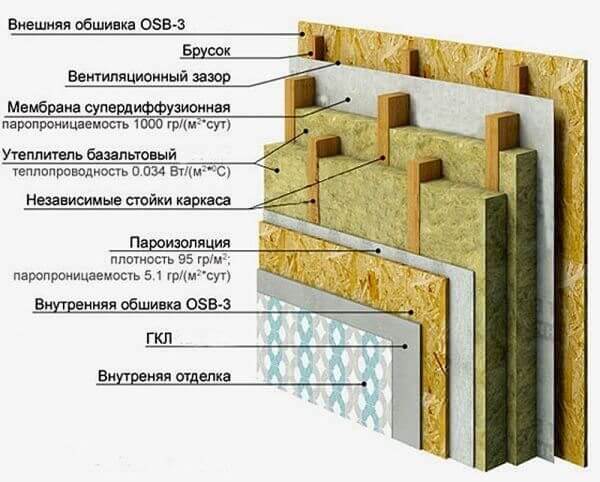
It is multi-layered and is called “sandwich” or “pie” in building jargon.
So, the frame wall: the design consists of layers:
Important! It is much simpler to make the internal partitions of the building: the frame wall diagram contains only the frame posts, a heat-insulating layer, a vapor-insulating membrane installed on both sides, and a drywall or OSB-plate.
The correct pie of the frame wall can be very different and depends on the wishes and financial capabilities of the owner, as well as on the external conditions and internal loads to which the building will be subjected. Consider the structure of the walls of a frame house in detail. The most common options are:
Important! In the above options, "pie" a windproof layer means a layer consisting of waterproofing and wind protection. Since there must be a waterproofing layer on the outside of the wall, which protects the insulation from external moisture.
If you are going to build a frame structure yourself, without a detailed drawing, on which the frame wall in the section will be indicated, can not do.
This will allow you to clearly imagine the location and installation procedure of all supporting structures and internal partitions and to avoid the most common mistakes.
Important! The drawings clearly indicate not only the options for connecting structural elements to each other, but also the layout of the engineering communications.
Largely modern wall drawings of the frame house are made in specialized computer programswhere such parameters as the type and, the location of load-bearing walls and partitions, the number of rooms, external parameters such as humidity, type of soil, average temperature in a given area, etc. are entered.
The diagram and structure of the wall of the frame house necessarily contains the following:
What is a wall unit of a frame house?
The wall of the frame structure consists of the following nodes, the nuances of which you should know:
1. The adjacency of the wall to the floor in the frame house. The frame racks of the wall must be nailed with 3 nails of size 90 mm, and this is done through the rack in the lag. This applies to supporting structures. If the wall is located on the lag harness or jumper, then the third nail is hammered in them. In the case of partitions, a single 90 mm nail hammered into each lag is sufficient.
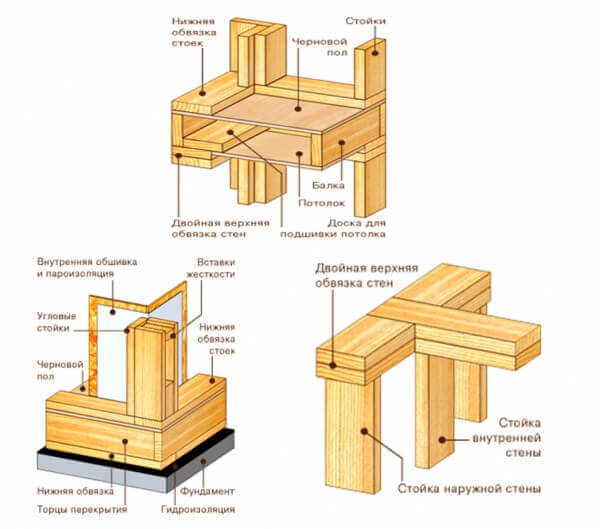
2. The connection of the walls of the frame house.To ensure a reliable connection of the frame walls - to connect the side and front walls of the building, in the side frame it is necessary to make an additional rack deployed perpendicular to the corner rack of the frame structure located on the edge. This will allow you to correctly form the inner corner and simplify the process of finishing with plywood or OSB boards.
3. The angle of the frame wall. Just connecting the bars with a section of 150x150 (or boards with a section of 50x150) in the corner is fraught with its freezing in the winter. Therefore, the angle is made according to the 2 + 1 scheme. To one of the extreme racks of the frame structure, a third is nailed, which is deployed at 90 degrees. You can also strengthen the design by supplementing it with a fourth board.
Two racks are connected parallel to each other or at a small angle by means of 5 90-mm nails with a distance of 6 cm between them. Before finishing the corner, it is necessary to put a heater.
4. Ukosina.This is one of the most important elements of the wall, which gives it spatial rigidity and avoids distortions in the structure. They are cut into both the lower and upper piping strictly at an angle that does not go beyond 45-60 degrees. They must be used if the paneling of the house with plywood or OSB-plates is not planned. It can be wooden with a section of 25x100, 50x150 or metal.
5. Window and doorways.
Important! In Canadian and Finnish technology, they are enhanced a little differently, so these nuances should be taken into account.
In Canadian technology, double racks are used to create them. Under and above the opening, shortened racks are mounted, the distance between which remains the same as between the main racks. A header is placed above the opening made of doubled or tripled boards 10–25 cm high, depending on the width of the opening and beam load. Under the opening, horizontal boards are also mounted, cutting an additional rack in half: they will withstand the weight of the window.
In the case of doorways or the use of Finnish technology, a crossbar is installed instead of the hider - a board placed on the edge, which cuts in front of the lower trim in the upper part of the frame racks both inside and outside. The crossbar can be both single, and built. For it, boards with a size of 50x200 mm are taken.
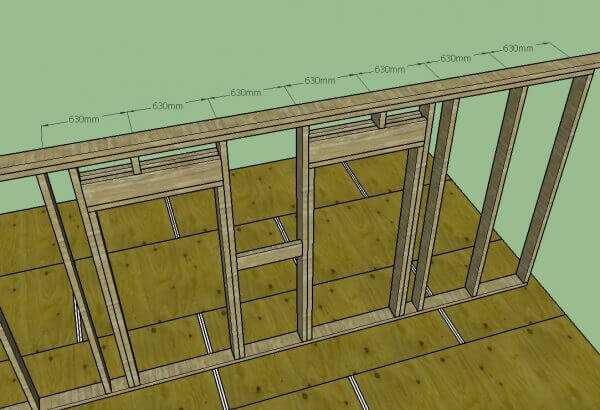
6. The connection of the wall and the roof. Racks are mounted strictly perpendicular to the wall, but can be parallel in partitions or on the pediment of the roof. Beams should be monolithic, and at least 2 posts should be placed in the outer corners of the wall frame.
7. The connection of the wall and floor. Shown above in the figure to paragraph 1.
Sectional wall of a frame house: photos are presented below.
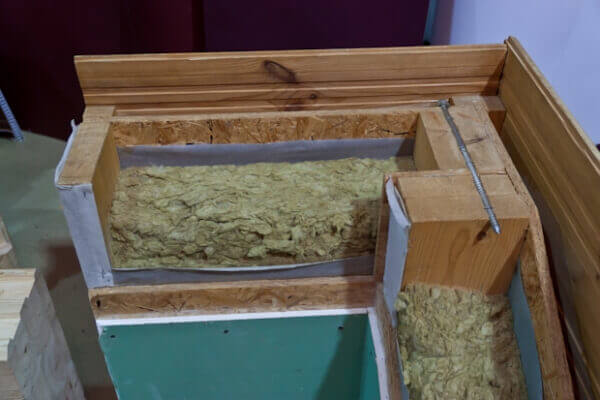

To learn how to make a frame wall cake, see the video below:
The construction of the wall of a frame house is a rather important and painstaking process, but even a lay builder can cope with it without a problem and desire to learn and take into account any nuances.
In contact with
The wooden architecture of the Scandinavian countries is rationality and natural harmony. Russian huts can be safely called the prototype of the Finnish house. However, today the technology of wooden architecture has gone far ahead.
Finnish house building technology has several advantages:
Design stagesIn pursuit of profit and in the fight against competitors, domestic designers are embarking on the development of Scandinavian-style dwellings, but, unfortunately, the output is a low-quality wooden house, overloaded with details and far from the given architectural direction. It is advisable to apply directly to Finnish offices with many years of experience, since they have long and successfully cooperated with Russian-speaking customers. The manufacturer you select is required to specialize specifically in residential wooden housesand not on garden verandas and cottages. It is desirable that the company provides a full cycle, and does not purchase the missing parts from different plants: the more diverse the set, the more difficult the fitting and joining of the elements. Do not chase the low price. You are building a house in which perhaps several generations of your family will live. Right foundationTheoretically, a house can be built on any foundation, which they did before. In the process of evolution, concrete and stone options fell away, leaving two leaders: USP (insulated Swedish plate) and UVF (insulated Finnish foundation). With the right execution at the final stage of the construction of the foundation, you get a ready-made ceiling of the first floor with built-in communications, a drainage system, electrical wiring and a heated floor. A decent contractor often comes from Finland himself to make sure that your foundation meets the requirements of the project and only after that starts delivery for construction. Wall materialThe main thing: the forest should be only winter harvesting. Felled at another time, it undergoes chemical processing and the durability of such a log is in doubt. The highest quality raw materials in the world for designing a Finnish timber house – this is wood of the highest grade “A” from central Finland. The ideal option is when the lamellas are glued from homogeneous rocks. Snow-white spruce is considered the most reliable, but capricious in processing material. Its thermal conductivity is higher than other rocks. For example, a glued spruce beam of 20 cm thickness will provide the same thermal insulation as brickwork of 2 m. Pine houses are called second-rate - it darkens over time, and the knots separate from the wood mass. They also use larch and cedar. Insulation for Finnish housesIn all of Europe, including the Finns, Rockwool basalt mineral wool, which has worked well, is used for these purposes. Basalt is a volcanic rock, completely non-combustible and even prevents the spread of fire. In addition, it is strong, durable, sound-absorbing and thermally insulating; it is not afraid of temperature changes. To isolate horizontal joints along the entire length of the rims, a vapor-permeable Illbruck tape is laid. It contracts under the weight of the upper layer and, expanding, fills all the free space. According to Finnish building regulations, houses made of glued beams with a thickness of at least 180 cm do not even need to be insulated even in severe weather conditions. The fact is that the quality of the assembly and joining of corners rather than the wall thickness is responsible for maintaining the temperature. Natural heat loss goes up through the roof, so special attention should be paid to its design and insulation. The European climate is milder than the Russian one, but there it is customary to put insulation with a thickness of 400 mm, in Russia it is for some reason 150-200 mm. The windows are preferably electrically heated, as Hatrick does. Exterior and interior of finnish housesThe typical Scandinavian dwelling is distinguished by laconicism, its refined simplicity combined with impeccable execution. Log, devoid of decor and extra details, one and a half to two floors, it has a gable roof so that snow does not stagnate. On the ground floor in front front door there is usually a terrace, and above it is a balcony with large windows. Typical colors of the exterior facade are white, light gray, beige, all natural shades of wood. Separately allocated cornices and platbands. The house, as a rule, has two entrances, each with a separate vestibule - a functional element of heat retention. Upon entering, we find ourselves in a spacious hall that leads to the kitchen, guest room, study. The Finnish tradition is to have a large kitchen with a dining table in the middle. On the second floor there is a bedroom under the roof slopes. Often in the house there is a sauna. We offer you to admire a photo of the interior of a Finnish house.
Varieties of constructionSolid timber houseAfter cutting, the tree is sent to the dryer to prevent shrinkage in the future. Then it is profiled and the surface is treated until the lining is smooth. In the cross section, the logs are square or rectangular, with or without a lock profile. The advantages of timber:
Disadvantages:
Finnish glued beam houseThis technology is based on turning logs made of natural wood to perfect geometric dimensions. By processing on special equipment, the bars are expanded using a mini-spike and glued up to 13 meters in length. There is also a D-shaped form of cut, when the inner surface seems to be folded of beams, and the outer - of rounded logs. The profile lock is designed so that its spikes fit perfectly into the grooves, preventing moisture from entering and making the wall unusually strong. Today, this method of building a house is recognized as optimal in Scandinavia and is recommended for the cold Russian climate. Conscientious manufacturers try to use only first-class glue, for example, the Finnish company Kilto, which does not contain harmful substances. Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Frame Finnish houseThere are no clearly established standards for the implementation of the skeleton design, which means that each company has it individually. There are only general requirements for the material - it should be a dry planed board; wooden beams are used extremely rarely. This construction principle is the most easily built and popular throughout the world for more than five hundred years. Home sets are:
Construction technologyThe technology for building a frame house allows you to build it yourself. If the project has already been agreed, then proceed to the foundation. Depending on the weight of the structure and the characteristics of the soil, the most commonly used columns or screw piles. If you have a small house for an average family, then the column foundation will be quite enough:
The screw principle is also very popular precisely because it is valuable to use manual labor. This allows you to strictly monitor the level of drilling. It is important to remember that unscrewing piles is strictly prohibited, as the natural compaction of the soil is disturbed.
Stages of building a Finnish houseDraft floor for a Finnish house
Walls of a Finnish house
Second floor of a Finnish house
Roof of a finnish house
At this stage, it is too early to say that the frame house was built. Now it needs to be carefully insulated inside and out, insert windows and doors, conduct communications and interior decoration. External insulation option
Small but comfortable homeThe Nordic character is calm and loves sophisticated simplicity. At home, many Scandinavians have long gravitated to single-story buildings. Small cottages are another kind of Finnish houses. Here are the facts that speak in their favor:
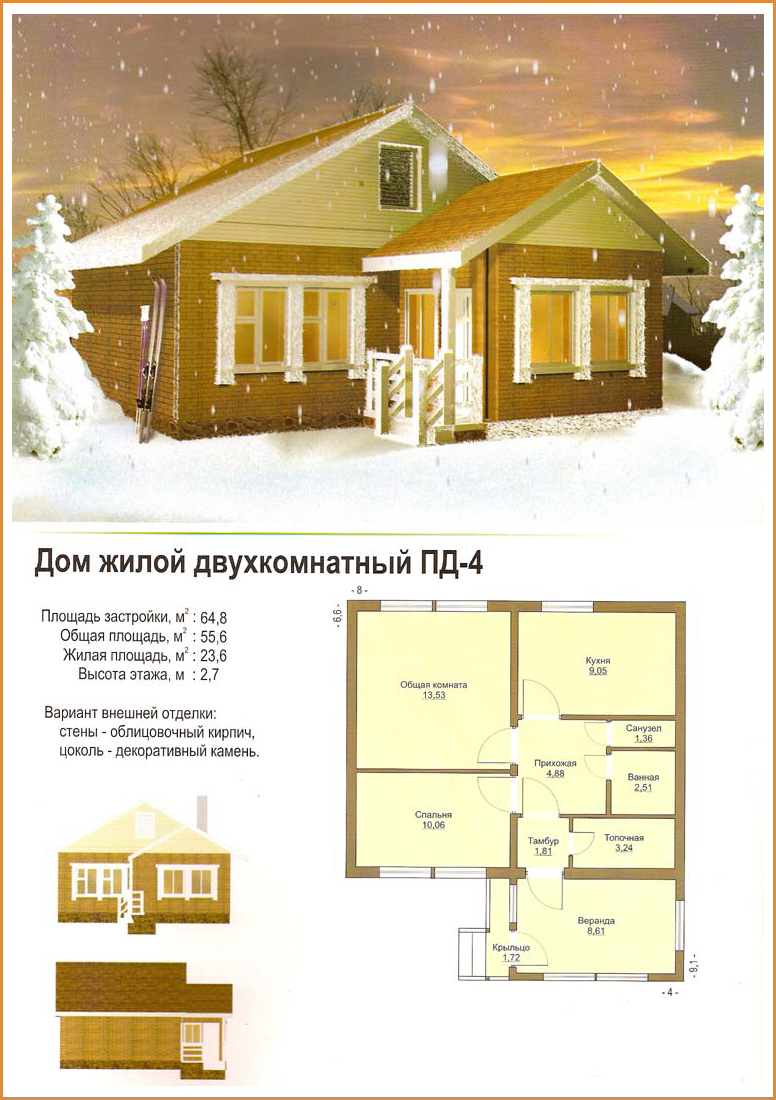
A typical project of a one-story Finnish house includes everything you need: a small living room, one bedroom, a kitchen, a bathroom and a pantry. Average, total area such a cottage - up to 60 m². |