From internal pipelines, drains are transported by external ...

If we speak an accessible language that is not oversaturated with incomprehensible medical terminology, then hypoxia is oxygen starvation, sometimes leading to serious consequences.
Hypoxia is oxygen starvation
There are several types of this fairly common disease:
Further we will learn more about hypoxia and get acquainted in more detail with those species that are most common, and also find out what causes this far from harmless disease. In addition, we determine what symptoms can be considered an alarm, and most importantly - how to treat hypoxia in young children and adults.

Hypoxia in pregnant women is a very common occurrence.
If you are planning a pregnancy or, moreover, are in an interesting position, then you should learn as much as possible about the pitfalls that may appear on the way to happy motherhood. After all, it’s not for nothing that they say: “forewarned — it means armed.”
We sincerely hope that such an unpleasant phenomenon as fetal hypoxia will not affect you. Well, if such an unforeseen situation has already happened and this diagnosis has sounded from the lips of the doctor, do not despair. To get started, read this article to learn more about what the symptoms of fetal hypoxia are hidden behind the words and what are their consequences for the baby.
Hypoxia during pregnancy is a fairly frequent phenomenon, and every year the number of women who experience this disease only increases. By hypoxia of the fetus is meant the processes due to which pathologies begin to appear in the body of a child in the womb. Such processes arise due to insufficient oxygen supply to the fetal organs. But because of such changes, not only the child suffers, but also the mother, since they are a single whole, and everything that is bad for the mother is harmful for the baby. Therefore, it is worth making a small clarification: hypoxia is the result of various disorders in the mother’s body, which, accordingly, leads to various disorders in the child’s body.
Hypoxia during pregnancy is a very alarming bell, especially if it has been observed during all or almost all trimesters of pregnancy. In such cases, hypoxia is called chronic fetal hypoxia. As a result of chronic hypoxia, irreversible pathological processes in organs can begin in the fetus. Therefore, do not take this problem lightly, do not ignore this disease, relying on the fact that everything will pass by itself. It can pass on its own, but time will be lost, and it is not known what problems will arise in the future.

The consequences of hypoxia can affect the further development of the child
Of the causes of hypoxia, there are:
The consequences of hypoxia for the fetus are very deplorable - a lack of oxygen leads to the fact that all the organs of the fetus are laid incorrectly, which is why their underdevelopment is observed. In a child with a high degree of probability, in the prenatal period, malformations appear that can lead to spontaneous miscarriage. As you can see, intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus is far from harmless.
If we talk about the consequences of hypoxia in newborns, then the situation is not happy at all: the baby can be born, firstly, much earlier than the established deadline, which means that the baby will be premature. Secondly, the baby can be born already initially with problems in the development of organs. In the worst case, organ damage resulting from hypoxia may be incompatible with life.

A healthy lifestyle and frequent walks during pregnancy are the best prevention of hypoxia.
In order for a child to be born healthy and hypoxia passed, it is necessary first of all to lead a healthy lifestyle. What is meant by this? For starters, you should give up smoking and alcohol. Secondly, you need to fully eat and breathe fresh air as often as possible. If the future mother has the opportunity to spend some time outside the city, this is very good.
Clean air, nature, birdsong, silence - all this perfectly affects both the mother’s body and the baby’s body, saturating its organs with the necessary amount of oxygen. As you can see, prevention of fetal hypoxia is quite simple. All that is needed is positive emotions, the right lifestyle and regular walks in nature. The importance of the absence of stress should be understood by the relatives of the future mother, so as not to worry her over trifles.
As for the treatment of fetal hypoxia, everything is much more complicated, because in this case the disease is easier to prevent than to treat it. The first thing to do is to diagnose and establish the causes that led to this disease. In mild cases, it is enough to simply adjust the lifestyle of a pregnant woman, prescribe special vitamin preparations.
If hypoxia was raging in earnest, then here it is necessary to fulfill all the doctor's prescriptions, take the pills prescribed by the doctor, and most importantly - do not be nervous! The emotional background of a pregnant woman affects the baby very much, and can aggravate the disease even more.
First of all, the brain suffers from hypoxia, because it reacts very sensitively to oxygen starvation, especially if it lasts long enough. Hypoxia of the brain can occur in both children and adults. Why it happens? If we talk about children, then, as was said above, hypoxia in them manifests itself even in the prenatal period.
It is quite common that a child can earn hypoxia during childbirth, if he is for a long time without normal access of oxygen. As a consequence of this disease, children have a tendency to develop such ailments as encephalopathy, epilepsy and other diseases.
If we talk about adults, then here it is clear - without oxygen in any way. Rather, without enough oxygen. Why does brain hypoxia occur in adults?
Let's try to name the main causes (there are two types of causes - endogenous and exogenous):
- stay in a room that has not been aired for a long period;
- inhalation of toxic substances. Often this does not happen on purpose, for example, by workers at various chemical plants, because even when observing safety standards, harmful fumes are often nevertheless released, albeit in small quantities. It is the lack of good ventilation plus harmful fumes that leads to the appearance of symptoms of hypoxia over time;
- Very often there is hypoxia among climbers when they climb the next peak. This is explained by the fact that the higher you go up, the less air is saturated with oxygen, and this causes unpleasant symptoms that are characteristic of hypoxia;
- unhealthy lifestyle: drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction become the causes of the development of the disease;
- drugs that are not taken according to the instructions can also cause hypoxia;
- diseases such as stroke, heart and lung failure also lead to hypoxia;
- anemia;
- spasms of blood vessels that cause circulatory disorders.

Hypoxia often appears in climbers
Symptoms of brain hypoxia. Now a few words about the symptoms that indicate hypoxia in adults:
- excessive drowsiness, when even after waking up a person feels sleepy and broken;
- fast fatiguability;
- attention is noticeably impaired, it is difficult to concentrate on one thing;
- coordination of movements is fuzzy, in a person with hypoxia, there may be unevenness in movements;
- the headache is pulsating in nature, in most cases it is localized in the frontal part;
- the skin of a person with hypoxia is pale, becomes unhealthy;
- tachycardia;
- breathing too often.
Of course, the presence of these symptoms is not a guarantee that a person will necessarily find hypoxia, but if you observe all or several symptoms at home, this is a good reason to consult a doctor and undergo a diagnosis. In most cases, after examination and clarification of the causes of the onset of the disease, the doctor will suggest adjusting the lifestyle to get rid of hypoxia. But there are times when you need to undergo serious treatment to feel good again and protect yourself from irreversible changes in the body.
There is also such a thing as tissue hypoxia. This type of disease can occur in the fetus, and in children, and in adults. Tissue hypoxia is much less common than brain hypoxia, but nevertheless, many people suffer from this disease. The disease is manifested by oxygen starvation of cells, which can be expressed in membrane damage, vitamin deficiency and a number of other factors. Poisons of cyanides, or rather, poisoning with these poisons and lead to tissue hypoxia.
Hemic hypoxia is another type of hypoxia that can significantly reduce the quality of life. This type of hypoxia is also called blood hypoxia, since there is a decrease in oxygen transport through the blood. If hemic hypoxia is diagnosed, then anemia will be its companion, there is a direct relationship between these diseases.
One of the causes of blood hypoxia is carbon monoxide poisoning. In case of mild poisoning, it is enough to simply transfer the person to fresh air, and over time the symptoms of hypoxia will disappear. If anemia becomes the culprit of the onset of the disease, then here you will have to use drugs that can increase the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin and thereby relieve the disease.

Warty birch sap will help overcome the disease
Traditional medicine has been used since ancient times, because even in ancient times, people knew ways to help overcome the disease. Of course, in many cases you can’t do without medications, but folk remedies should not be written off. Plants such as woodlice, warty birch have proven themselves well in the fight against hypoxia. There are many different recipes that tell you how to brew these herbs in order to achieve the desired effect. You just need to choose which one you find most convenient.
Take a thermos, pour wood lice in it (the grass must be dried) - 1 tbsp. spoon, pour boiling water, then insist 8-10 hours. An infusion of grass is taken before meals, no more than four times a day. The maximum dose at a time is 50 grams. Warty birch sap should be taken every day as much as you want. But not more than one liter.
Before starting treatment folk remedies, be sure to check if you are allergic to these herbs. It is also advisable to consult your doctor, and only if he approves your choice, proceed with the chosen type of treatment.
As for pregnant women, a lot of herbs are contraindicated for them, since some plants have abortive properties. Given this fact, herbal medicine in pregnant women is in many cases contraindicated or, if allowed, should be carried out under the constant supervision of the attending physician.
Any kind of hypoxia develops when oxygen is supplied to the body insufficiently.
- more often to be in the fresh air;
- ventilate the premises as often as possible;
- consume more vitamins or take vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor;
- and for pregnant women, advice is less nervous.
It seems that everything is so simple, but why then so many people get hypoxia? This is because, more often than not, few people pay attention to such trifles. Most modern urban residents lead a sedentary lifestyle: home - car - work - car - home, which minimizes the time spent in the fresh air. The effects of hypoxia are very serious, especially for the fetus or for newborns. So take care of yourself, take care of your kids, and let all ailments bypass you!
The respiratory system provides the body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The ratio of these components in the blood should be such that the body functions at the proper level. Various fluctuations, then down or up one of the indicators lead to different symptoms. One such condition is hypoxia.
What is hypoxia (anoxia, hypoxemia)? This is a condition of the body in which in some areas or in general there is a lack of oxygen in the tissues or a violation of its utilization due to oxidation.
According to the rate of development, hypoxia is shared:
The causes of hypoxia are multiple factors:
According to etiology, the following types are divided:
Symptoms of hypoxia depend on the extent of oxygen starvation within the body. Common signs are considered:
Often, signs of hypoxia are observed in people of large cities who live in a polluted atmosphere, in a regime of constant performance and are exposed to various chemicals and electronic irritants.
In the acute form of hypoxia, signs similar to alcohol intoxication are observed:
In chronic hypoxia, which often develops on hills and in a discharged atmosphere, the following symptoms are distinguished:
The main diagnosis of hypoxia is a general examination of the patient and analysis of the composition of his blood. First of all, the oxygen level is found out, and then the reasons for its absence in normal quantities are already searched.
The main methods of treating hypoxia are medications: antioxidants and antihypoxants. They contribute to the "economical" consumption of oxygen by tissues, better utilization and reduction of hypoxia. Plants with antihypoxic properties are also used. Pharmacological antihypoxants are often used in acute hypoxia, and in plants of chronic origin.
Various instrumental methods of introducing oxygen into the body (oxygen therapy with diacarb, oxygen therapy) and increasing blood pressure are used. Red blood cell transfusion is also used.
As a preventive measure, you should undergo a constant examination by a doctor, and also avoid those places where hypoxia occurs. It is necessary to follow a carbohydrate diet and consume vitamins, timely treat diseases of the respiratory and other systems.
How many people live with hypoxia? It all depends on the body of an individual person. Modern methods of treatment easily remove this syndrome. Life expectancy with hypoxia depends on the condition of the body, its internal reserves and "deterioration." If the body is not able to compensate for the lack of oxygen, then it dies. This can happen both during the day and in a few years.
The prognosis of life is significantly worsened by the fact that oxygen starvation provokes the development of disorders in various body systems. And they, in turn, will lead to the development of other diseases that can be fatal. This makes hypoxia a dangerous syndrome that should be continuously treated in cases of periodic occurrence.
The term "hypoxia" means an abnormal state of an organ that develops when the enrichment of body tissues and cells with oxygen stops, as well as with adverse factors in which oxygen is not absorbed by the tissues. Hypoxia of the brain is a whole chain of circumstances and responses of the body that occurs when the incoming volume of oxygen does not match the needs of the brain cells in it, leading to oxygen starvation of the brain. A state of hypoxia occurs in adults as well as children; an unborn baby is also capable of experiencing a lack of oxygen.
Fetal hypoxia is a very dangerous condition, the reasons for which it develops may be different, but it always leads to serious consequences, which are directly dependent on the time of its occurrence. At the initial stage of pregnancy, this can cause a slowdown in the development and pathology of the fetus, in the later stages it can cause significant disorders in the central nervous system. With placental abruption, acute hypoxia develops, from which the baby can die. Intrauterine hypoxia also leads to delays in the development of the fetus, to difficulties in adapting the child in the postpartum period and to various neurological disorders: restless sleep, poor appetite, moods, and convulsions.
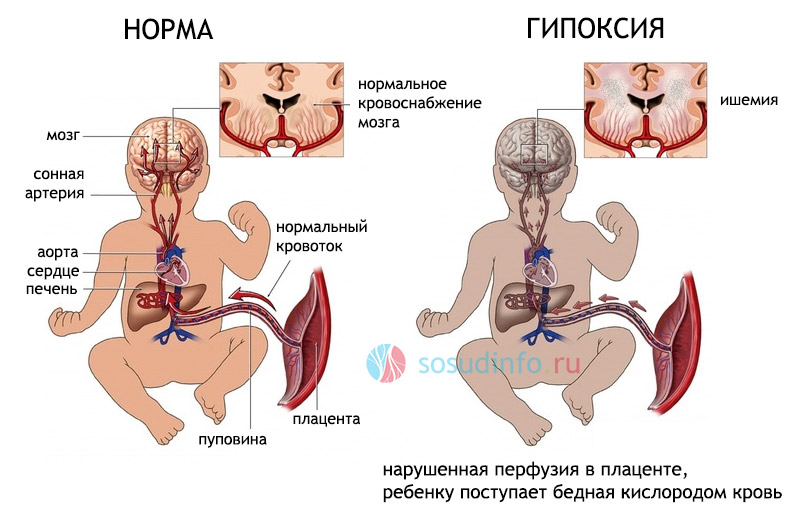
These complications are caused by the fact that the body of an unborn child with hypoxia triggers the action of mechanisms aimed at increased blood supply to vital organs - the heart, adrenal glands, brain tissues, and in the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, lungs, and skin integument, blood flow strength decreases. Therefore, a child with a diagnosis of "Intrauterine hypoxia" may be born with possible impaired functions of these organs. This is manifested in the form of respiratory disorders, fluid retention, frequent spitting up. The next stage, which is characterized by the appearance of signs of oxygen starvation and nervous exhaustion, occurs if oxygen starvation occurs for a long time. In this condition, the heart rate slows down, the tone of the blood vessels decreases, the tissues of the body swell, the brain suffers, nerve cells die, other vital organs are unable to perform their functions, and thereafter there is a danger to the life of the child. During the gestation period, the fetus receives through the placenta all the substances necessary for maintaining vital activity and microelements through it, oxygen enters from the mother’s blood into the fetal tissue. If a pregnant woman suffers from a lack of nutrients, the fetus will also experience inconvenience.
Fetal hypoxia varies in its characteristics, severity of manifestations, the mechanism of its development and the extent of exposure. There are three main types of hypoxia:
This condition can provoke some systemic diseases of a pregnant woman, to which the following reasons can be attributed:
Of great importance in the development of chronic child hypoxia are bad habits of the expectant mother . In no case should a pregnant woman drink alcohol or smoke. All toxins, as well as beneficial substances, enter the baby’s bloodstream and cause negative consequences.
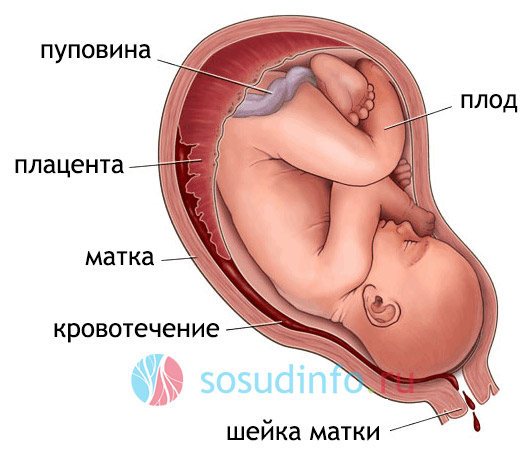
Other good reasons for the development of child hypoxia may be possible abnormalities in the development of the placenta, overeating during pregnancy or an increased uterine tone, other deviations from the normal natural child bearing algorithm, the most frequent and dangerous factor for acute intrauterine hypoxia may be premature detachment of the normally located placenta. Hypoxia of the fetus can cause infection of the fetus in the womb, defects in its development, incompatibility of the fetal blood with the blood of the mother - this condition causes it, it is equally dangerous for the unborn baby and the woman herself. In severe childbirth, hypoxia of the brain of the newborn can occur, caused by a mechanical factor - prolonged squeezing of the head in the birth canal, entanglement around the neck of the umbilical cord, as well as mucus and amniotic fluid in the respiratory tract. This complication of childbirth is called asphyxia and requires resuscitation. The combination of acute and chronic forms of hypoxia is the most unfavorable in predicting the development of complications in a baby at birth.
The first symptom of fetal hypoxia is the child’s active movements.With this, the baby reflexively tries to increase blood supply, increase blood flow. Initially, a woman notes strong and sharp points, rapid movement, it can cause her discomfort and even cause pain. If fetal hypoxia intensifies, its tremors gradually weaken, may disappear altogether. This sign should alert the woman, make her understand that not everything is in order with the baby. In the antenatal clinic, when pregnancy is more than 28 weeks, it is recommended to keep track of fetal activity.
The norm is when a child stirs at least 10 times in 12 hours, if there are fewer of them, you need to urgently seek medical help.
When determining intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus, obstetricians use complex methods designed to assess the condition of the fetus. These methods include listening to fetal heart sounds using an obstetric device - a stethoscope. The doctor assesses the frequency of heart contractions, their tone, rhythm, extraneous noise. But this method cannot be accurate enough, therefore, at the slightest suspicion of hypoxia, cardiotocography should be additionally applied using a special ultrasonic sensor, in this study, the indicators are recorded on paper and the doctor gets the opportunity to analyze the fetal heart rate in different parameters. Another method that allows you to explore to determine deviations in the bloodstream between a woman and the fetus is called. Here, blood circulation is evaluated in all parts of the fetal blood supply chain, the severity of hypoxia and the prognosis for pregnancy depend on the nature of the changes. In addition to the described manipulations, the fetal ECG also provides information on his state of health, and laboratory tests of the mother’s blood are used for the biochemical composition and level of pregnancy hormones.
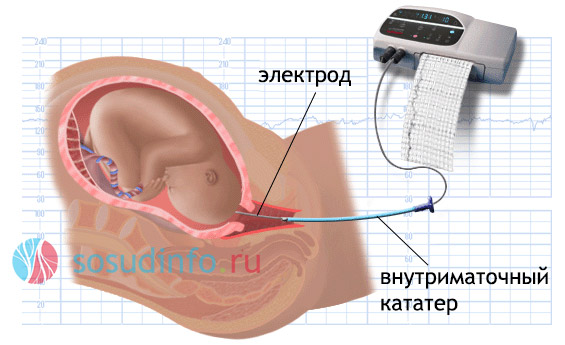
In addition, if intrauterine hypoxia is suspected, the amniotic fluid is analyzed for the presence of meconium - primordial feces. Lack of O 2 provokes relaxation of the muscles of the rectum of the baby and meconium goes into the amniotic fluid. This method of diagnosis is especially important with increasing labor, the whole tactics of the birth process will depend on its results.
If the doctor suggests intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus, the woman is sent to the hospital for additional examinations and necessary therapy. When the condition of the fetus allows it, treatment at home under the supervision of a doctor is possible. A prerequisite for the treatment of hypoxia is the complete rest of a woman.  Treatment with intrauterine hypoxia should be aimed at ensuring normal blood supply to the fetus, will depend on the cause of hypoxia and the degree of pathology detected. In most cases, the expectant mother is prescribed strict bed rest, prescribed drugs that reduce blood viscosity, improve blood supply to the placenta and normalize the metabolism between the mother and the fetus, the preferred position in bed is on the left side. If during the course of the treatment no positive changes are noted, and fetal hypoxia continues to increase, obstetricians may decide to undergo a caesarean section when the period exceeds 28 weeks of pregnancy. To prevent such complications, the expectant mother should give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, not overwork, lead a healthy lifestyle. Great importance should be attached to the prevention of iron deficiency anemia, as one of the main causes of fetal hypoxia. A full balanced diet, early registration in a antenatal clinic and timely visits to a doctor will play a huge role in the prevention of fetal hypoxia and its complications. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with Chronic intrauterine hypoxia, a mandatory cardiomotor monitoring of the fetus is performed during childbirth in order to minimize negative consequences for the baby.
Treatment with intrauterine hypoxia should be aimed at ensuring normal blood supply to the fetus, will depend on the cause of hypoxia and the degree of pathology detected. In most cases, the expectant mother is prescribed strict bed rest, prescribed drugs that reduce blood viscosity, improve blood supply to the placenta and normalize the metabolism between the mother and the fetus, the preferred position in bed is on the left side. If during the course of the treatment no positive changes are noted, and fetal hypoxia continues to increase, obstetricians may decide to undergo a caesarean section when the period exceeds 28 weeks of pregnancy. To prevent such complications, the expectant mother should give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, not overwork, lead a healthy lifestyle. Great importance should be attached to the prevention of iron deficiency anemia, as one of the main causes of fetal hypoxia. A full balanced diet, early registration in a antenatal clinic and timely visits to a doctor will play a huge role in the prevention of fetal hypoxia and its complications. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with Chronic intrauterine hypoxia, a mandatory cardiomotor monitoring of the fetus is performed during childbirth in order to minimize negative consequences for the baby.
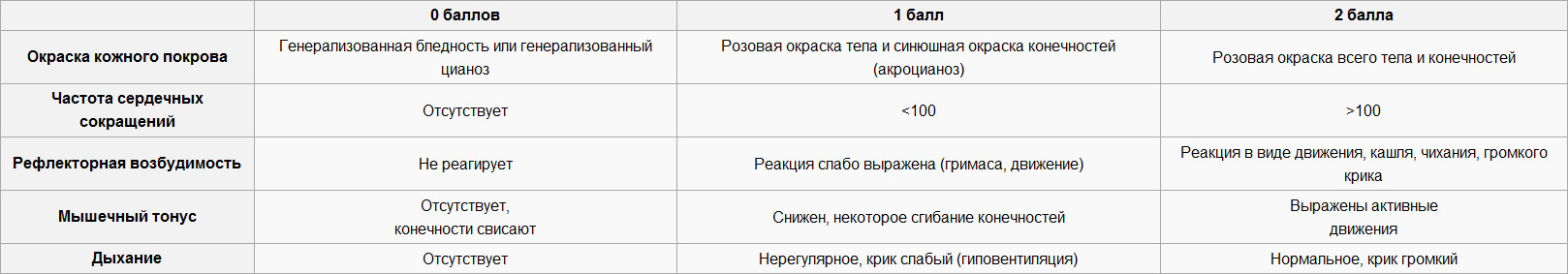
Immediately after birth, the Apgar scale is used to assess the health of the child, according to which the state of the skin, reflex excitability and muscle tone are assessed. Normally, the indicator should be from eight to ten points, an assessment below five points means hypoxia, the less points are assigned, the worse the condition of the child.
(click increase)
With severe hypoxia, the child is pale, muscle tone is reduced, convulsive syndrome, abnormalities in the functioning of the internal organs, possibly up to serious CNS disorders with the formation of blood clots, are possible. At birth, a child with suspected hypoxia should immediately receive medical care aimed at relieving oxygen starvation: the airways are freed from liquid and mucus, warm the baby, and if necessary, resuscitation is taken to improve to a condition that does not pose a threat to life. After stabilization of the baby’s condition, they are placed in a pressure chamber, nutrient solutions are administered, and therapy aimed at relieving the manifestations of hypoxia is carried out. After the first hypoxia, the baby is restless, easily excitable, his muscle tone is increased, which is manifested in involuntary twitches of the arms, legs, chin, are possible. In other cases, lethargy, reluctance to take a chest is possible, he is worried about frequent spitting up. The older the baby becomes, the more these manifestations become less noticeable, however, at 5-6 months, the return of the initial symptoms is possible: convulsions may occur again, muscle tone may increase. This period can last several months or several years, it will depend on the degree of damage to the brain of the baby and its ability to recover. The consequences of fetal and newborn brain hypoxia are very serious, up to the death of the baby, therefore, it is very important to identify this condition in time and take measures to prevent complications in the child’s health in the future.
Further a baby undergoing intrauterine hypoxia should be constantly registered with a neurologistso that the doctor has the opportunity to notice pathologies in physical and mental development on time and prescribe the necessary therapy, since a state of prolonged oxygen starvation can cause various deviations and lags in the development of the baby. To avoid this, you will need to regularly evaluate his health and conduct appropriate treatment if necessary. To help the newborn baby cope with the effects of hypoxia, parents must ensure a calm atmosphere at home, comfortable temperature condition, protect from overheating and hypothermia. It is not necessary to swaddle a baby tightly, you need to give him the opportunity to move more. A big plus is breastfeeding, warm baths with soothing herbs, special massage and gymnastics, which a mother should teach her to use. This should be done daily for 2-3 years.  In complex cases of the course of the disease, as prescribed by the pediatrician, massage should be performed by a specialist who has the skills to treat diseases of the nervous system. It is with the help of massage that you can help restore the nervous system and overcome delays in the development of the child. Reflexotherapy has an intense effect on the central nervous system; it is also used as prescribed by a doctor if hypoxia caused significant impairments in the development of the child. There are various methods of reflexology: acupuncture, laser treatment, etc. If indicated, it is advisable to consult an osteopathic doctor, discuss with him the feasibility of osteopathic treatment. Physiotherapy exercises can also help overcome the consequences of intrauterine hypoxia, this becomes relevant when the development of motor skills is delayed. It should be carried out by a specialist who owns these skills. If there are delays in speech development, you need to contact a speech therapist. All of the above activities should be carried out in a strict system, with a certain sequence and under the obligatory supervision of a physician who is able to track the dynamics of the mental and physical development of the child. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable!With the correct and responsible approach to treatment, in most cases it is possible to overcome the negative residual effects of hypoxia and return the child's condition to normal levels.
In complex cases of the course of the disease, as prescribed by the pediatrician, massage should be performed by a specialist who has the skills to treat diseases of the nervous system. It is with the help of massage that you can help restore the nervous system and overcome delays in the development of the child. Reflexotherapy has an intense effect on the central nervous system; it is also used as prescribed by a doctor if hypoxia caused significant impairments in the development of the child. There are various methods of reflexology: acupuncture, laser treatment, etc. If indicated, it is advisable to consult an osteopathic doctor, discuss with him the feasibility of osteopathic treatment. Physiotherapy exercises can also help overcome the consequences of intrauterine hypoxia, this becomes relevant when the development of motor skills is delayed. It should be carried out by a specialist who owns these skills. If there are delays in speech development, you need to contact a speech therapist. All of the above activities should be carried out in a strict system, with a certain sequence and under the obligatory supervision of a physician who is able to track the dynamics of the mental and physical development of the child. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable!With the correct and responsible approach to treatment, in most cases it is possible to overcome the negative residual effects of hypoxia and return the child's condition to normal levels.
With proper treatment, during the first year of life, the child's health should return to normal, but in some cases, the effects of hypoxia may occur after a fairly long period of time. Children may have a delay in speech development, inability to concentrate, restlessness, constant headaches. In the most complex cases, it is possible to develop progressive lesions of the central nervous system, such as significant impairment of hearing, attention, as well as persistent disorders of the central nervous system, such as epilepsy, other cerebrovascular disorders, including (in rare cases), cerebral venous.
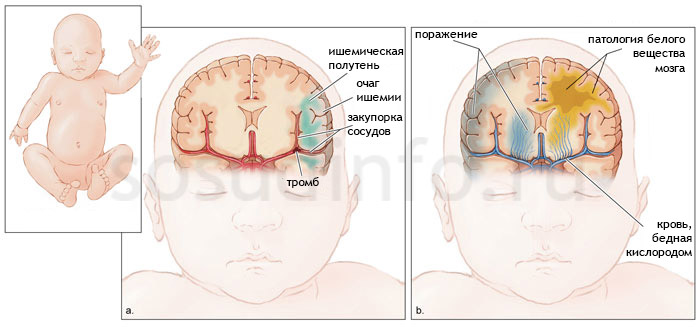
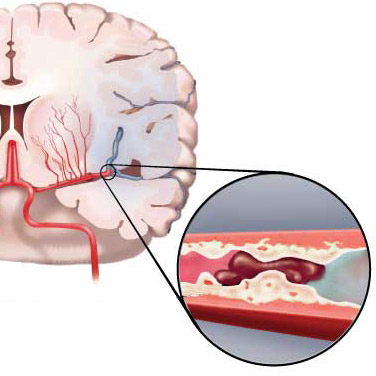
Consequences of hypoxia: stroke (left) and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (right) in a newborn
Not only newborn children can suffer from hypoxia, adults also experience oxygen starvation, the causes of which may be different. As a rule, this condition is caused by chronic diseases.
Hypoxia in adults also leads to disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system, chronic fatigue syndrome, decreased immunity, sleep disturbances, and general deterioration of health. Various methods are used to treat hypoxia in adults. first of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that caused it.
The use of oxygen shakes can help cope with the effects of hypoxia and improve the quality of life. This invention allows you to restore strength during overwork, saturate the cells with oxygen, improve metabolism, increase concentration, attention and reaction, and also has many more positive qualities.  An oxygen cocktail is a thick foam that is completely filled with oxygen molecules. It is prepared on juices, fruit drinks, syrups and enriched with oxygen using special devices, oxygen concentrators. For a long time, oxygen cocktails were available only in medical institutions, but recently compact oxygen cans have been on sale, this allows you to prepare a healthy drink at home. Chronic oxygen deficiency of the brain in adults also leads to negative consequences, the destruction of nerve endings and. In order to prevent this and preserve the quality of life, you should be observed by doctors, monitor your well-being and systematically treat chronic diseases. Delaying the onset of old age and maintaining vigor for many years is quite within the power of all who sincerely desire it. To do this, you need very little - to lead a healthy lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air, relax and value yourself and your health.
An oxygen cocktail is a thick foam that is completely filled with oxygen molecules. It is prepared on juices, fruit drinks, syrups and enriched with oxygen using special devices, oxygen concentrators. For a long time, oxygen cocktails were available only in medical institutions, but recently compact oxygen cans have been on sale, this allows you to prepare a healthy drink at home. Chronic oxygen deficiency of the brain in adults also leads to negative consequences, the destruction of nerve endings and. In order to prevent this and preserve the quality of life, you should be observed by doctors, monitor your well-being and systematically treat chronic diseases. Delaying the onset of old age and maintaining vigor for many years is quite within the power of all who sincerely desire it. To do this, you need very little - to lead a healthy lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air, relax and value yourself and your health.
The term hypoxia refers to the pathological condition of the body due to its oxygen starvation in general or of individual tissues and organs.
Hypoxia can develop with insufficient oxygen in the blood, with a lack of oxygen in the environment, or with biochemical disturbances in the process of tissue respiration.
The adaptation of the body to hypoxia in each person is purely individual and therefore oxygen starvation in patients causes various complications, depending on the state of health of individual organs and the whole organism.
Hypoxia can occur both in acute and in chronic form.
The acute form of hypoxia often has a short-term nature and usually occurs with high physical activity. This type of hypoxia is observed during fitness classes or long runs. The resulting oxygen starvation quickly passes, because the mobilization of a healthy body includes mechanisms for adapting the body to hypoxia.
An acute form of hypoxia can develop during a stay in a stuffy room. Typical signs of hypoxia in this case are drowsiness, lethargy, decreased concentration, yawning. All this takes place when fresh air enters or leaves the room.
But quite often, acute hypoxia is caused by pathological processes in the body. This form may be a consequence of heart failure, pulmonary edema, carbon monoxide poisoning, or airway obstruction.
Acute hypoxia can pass very quickly, but can occur within a few days.
Chronic hypoxia is often observed in diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory system.
The severity of chronic hypoxia depends on the location of the organ suffering from hypoxia, the duration and type of pathology, the characteristics of the body and metabolic processes in it.
Chronic hypoxia is dangerous because it reduces the ability of tissues to absorb oxygen. Thus, a person's chances of recovery are reduced.
This applies to both general and local disease, in which only a certain part of the body is affected. This applies to atherosclerosis, the development of blood clots, embolism, tumors and edema.
Chronic hypoxia can develop and last from several weeks to several months.
When oxygen starvation occurs in the body, a protective mechanism wakes up working in the direction of eliminating or reducing the severity of hypoxia.
These processes appear already in the very early stage of hypoxia. Such adaptive mechanisms are called emergency. If the disease goes into a chronic stage, the process of adaptation of organs to hypoxia becomes more complex and lengthy.
Emergency adaptation is the transport of oxygen and metabolic substrates and the inclusion of tissue metabolism.
Long-term adaptation is formed more slowly and includes the adjustment of pulmonary alveoli functions, pulmonary ventilation blood flow, compensatory myocardial enlargement, bone marrow hyperplasia and hemoglobin accumulation.
The duration and intensity of the course distinguish functional, destructive and metabolic hypoxia.
Destructive hypoxia is a severe form and leads to irreversible changes in the body.
Functional hypoxia occurs when hemodynamics are impaired, i.e. as a result of a violation of blood flow for various reasons, for example, with hypothermia, injuries, burns, etc.
Metabolic hypoxia develops as a result of a violation of the oxygen supply to tissues. At the same time, a change in metabolic processes occurs in them.
Both functional and metabolic hypoxia are reversible. This means that after the necessary treatment or a change in factors causing hypoxia, all processes in the body are restored.
For reasons of occurrence, hypoxia is divided into:
Often found in medical practice, hypoxia of the brain and hypoxia of the newborn.
Hypoxia of the brain disrupts the activity of the whole organism and, first of all, of the central nervous system.
Hypoxia in newborns is quite common in obstetric and gynecological practice and has serious consequences. The main causes of fetal hypoxia are maternal diseases such as diabetes mellitus, anemia, occupational intoxication, heart disease and other diseases.
The causes of chronic fetal hypoxia include a complicated pregnancy caused by a disorder of uteroplacental circulation. In addition, pathological development of the fetus in the form of malnutrition, Rh conflict, infection of the fetus during the breakthrough of protective barriers and multiple pregnancy can also be causes of chronic fetal hypoxia.
 Signs of Hypoxia
Signs of HypoxiaSymptoms of oxygen starvation are expressed by constant fatigue and depression, accompanied by insomnia.
There is a deterioration in hearing and vision, headaches and chest pains appear. An electrocardiogram reveals a sinus. Patients experience shortness of breath, nausea and disorientation in space. Breathing can be heavy and deep.
In the initial stage of development of brain hypoxia, its signs are expressed by high energy, passing into euphoria. Self-control of motor activity is lost. Signs may appear with a shaky gait, palpitations, pallor bordering cyanosis, or vice versa, the skin becomes dark red.
In addition to common to all, signs of cerebral hypoxia, as the disease progresses, are expressed by fainting, cerebral edema, lack of skin sensitivity. Often this condition ends in a coma with a fatal outcome.
Any type of hypoxia requires immediate treatment, based on the elimination of its causes.
With the onset of pregnancy, colossal changes take place in the mother's body, allowing a new life to arise and develop. A unique mother-placenta-fetus system is formed. Normally, this mechanism works very clearly, providing the baby with oxygen and nutrients, removing the products of his life and protecting him from adverse factors.
Even with a normal pregnancy, the fetal blood is less oxygenated than the mother's. This deficiency can be compensated by the enhanced work of the baby’s heart and a special type of hemoglobin - the so-called fetal hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to each cell of the child.
If the blood supply through the placenta is disrupted, then the fetal body cannot compensate for everything. About 3-7% of pregnancies occur in violation of this system. This condition is called fetoplacental insufficiency (FPF), the result of which is intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus. According to statistics, this condition occurs in 10% of all pregnancies and childbirths.
The placenta completes its formation by the 16th week of pregnancy, by this time the placental circulation begins to fully function, that is, deliver oxygen-enriched blood through the umbilical vein to the liver and heart of the unborn baby. From there, blood is distributed to all organs and tissues of the embryo through special compounds - shunts. Any disturbance in the blood circulation or in the structure of the placenta leads to the development of FPI.
The placenta and its predecessors in the course of their development undergo two waves of activity: at 7-9 and 14-17 weeks of pregnancy. It is during these periods that vascular abnormalities occur more often, resulting in FSF. Typically, such disorders are formed against the background of a mother’s illness, improper lifestyle, or pregnancy complications.
In view of the formed FSF, intrauterine hypoxia of the baby develops, which means insufficient intake of oxygen in his body. Synonyms in intrauterine hypoxia are oxygen deficiency or oxygen starvation of the fetus.
It is worth noting that this condition is not a disease. This is a syndrome that develops in an unborn child as a result of exposure to various unfavorable factors on his body.
Oxygen starvation of the fetus can develop for a long time and gradually, as a result of chronic chronic renal failure. Such hypoxia is also called chronic. If the violation of the blood supply to the placenta has developed rapidly and rapidly, then FPI and hypoxia are acute.
Also, fetal hypoxia can develop during pregnancy, then it is called antenatal, and if it occurs during childbirth, they talk about intranatal hypoxia.
Almost every expectant mother is likely to develop hypoxia, but not everyone develops it. The doctor of the antenatal clinic calculates the degree of risk of this condition in the fetus, taking into account the chronic pathology of the mother, endocrine disorders that existed before and appeared during pregnancy and complications of the gestational period:
The causes of intrauterine hypoxia are divided into 2 large groups, depending on whether they contribute to the development of acute or chronic hypoxia.
Chronic oxygen deficiency of the fetus is caused by adverse factors that act for a long time.
During pregnancy, the placenta has a great effect on the heart and blood vessels of a woman. The blood volume is almost doubled, and the peripheral vessels expand, which prevents jumps in blood pressure. Therefore, if the tonometer stubbornly shows values \u200b\u200bgreater than 130 / 80mm RT. pillar, you can think about the malfunctioning of the mother-placenta-fetus.
The classification of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy is presented in the table.
| Disorder | Definition |
| Chronic hypertension | Hypertension is present before pregnancy or is first diagnosed at a gestation period of up to 20 weeks |
| Preeclampsia-Eclampsia |
The first occurrence of hypertension during pregnancy (\u003e 140 mmHg systolic or\u003e 90 mmHg diastolic pressure) and protein in the urine (excretion\u003e 0.3 g at 24 h) after 20 weeks Diabetes and pregnancyDiabetes mellitus is a serious disease that affects mainly the kidneys, blood vessels and nerves. With this pathology, uncontrolled blood sugar levels adversely affect almost all organs and tissues. During pregnancy, diabetes causes fetal hypoxia, endangering the health of the baby and mother. Maternal diabetes risk:
The risk of diabetes for the fetus:
Diabetes Pregnancy Planning
Throughout pregnancy, careful monitoring of fetal health is required, including ultrasound with Doppler, determination of the biophysical profile of the fetus and monitoring of blood glucose in the mother. The optimal delivery period is considered to be 38-40 weeks, mainly independent birth. Thyroid diseaseApproximately 5% of pregnant women have an insufficiently functioning thyroid gland. Some of them suffered before pregnancy, and some of them arose during the period of expectation of the baby. This is due to hormonal changes in the body and increased fetal demand for trace elements. The main symptoms of hypothyroidism before pregnancy:
Among the consequences of hypothyroidism during pregnancy, fetal growth retardation, hypoxia, placental insufficiency, placental abruption, and premature birth are often found. In addition, with hypothyroidism, a newborn without treatment may develop oligophrenia. The standards for the level of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) for each trimester of pregnancy have not yet been studied, average data: from 0.4 to 3.5 mU / l. If the amount of the hormone differs from these values, then it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the gland and prescribe treatment. Hormone replacement drugs are used to treat hypothyroidism. They are prescribed by a doctor, since it is quite difficult to choose the right dose for a woman in position. If hypothyroidism can be compensated for with drugs, then the risk of complications for the baby is minimized. Infectious diseasesInfections alone can cause vascular reactions and worsen uteroplacental blood flow. For example, with influenza, the risk of fetal hypoxia is quite high, since fever is combined with cough and general intoxication. Some infections (toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus, ureaplasmosis and others) can penetrate the placenta, causing inflammation directly in the membranes, placenta and amniotic fluid. In this case, not only FPI and chronic fetal oxygen deficiency develop, but the risk of acute hypoxia and the death of the unborn child also increases. Symptoms that are the reason for visiting a doctor:
Most often, after treatment of the infection, the fetus is stabilized. Among the drugs used are antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs, as well as infusion of intravenous solutions to relieve intoxication. In some cases, it is necessary to apply emergency delivery in case of a threat to the life of the mother and child. Immunological complications during pregnancyRhesus conflict during gestation occurs in the case of Rh-negative maternal blood and Rh-positive blood in the fetus. The risk group for the development of an immunological conflict (blood type) includes future mothers who have the first blood type (O or I), and the future father has any other, but not the first. Due to immunological incompatibility, immunological complications develop, which are caused by the production of antibodies in the maternal body that adversely affect the tissues and organs of the fetus. Ultimately, the unborn child develops oxygen deficiency. Antiphospholipid SyndromeAntiphospholipid syndrome or APS refers to autoimmune diseases in which the production of a large number of antibodies to phospholipids is noted. Phospholipids, in turn, are necessary for the construction of parts of cells. The prevalence of AFS is 5% among all expectant mothers. In a third of cases, APS causes habitual miscarriage. If during pregnancy you do not adhere to certain measures and do not carry out treatment, this syndrome can provoke the occurrence of oxygen starvation and intrauterine growth retardation, placental abruption, severe gestosis, pulmonary embolism in the mother and even the death of the baby (in utero) and mother. Factors that trigger the occurrence of APS
PolyhydramniosExcessive amniotic fluid can provoke gestational arterial hypertension, significantly increases the likelihood of the fetus wrapping (in this case the neck) with the umbilical cord and the formation of true nodes in the umbilical cord (when the umbilical cord is tied into a knot due to the baby’s increased activity). In addition, polyhydramnios leads to metabolic disorders in the fetus and the gradual development of oxygen deficiency, which in turn inhibits fetal growth. Low waterThe lack of amniotic fluid reduces the motor activity of the unborn child, and with severe oligohydramnios can lead to compression of the fetus and the formation of intrauterine anomalies. A small amount of water causes disturbances in oxygen metabolism, which causes chronic hypoxia. Also, with oligohydramnios, often weakness of the birth forces and early postpartum hemorrhages develop (violation of the contractile activity of the uterus). RepottingIf the gestational age exceeds 41 weeks and 3 days, they talk about true nauseation, which can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus and cause its antenatal death. If there is a suspicion and threat of overshoot in the absence of labor, doctors carefully recount the gestational age according to various sources (the first appearance at the antenatal clinic, ultrasound, the last menstruation and the first stir of the fetus). If the diagnosis of true nausea is confirmed, resort to labor excitation and induction of labor. The tactics of managing a pregnant woman is individual and depends on the maturity of the cervix, the state of health of the woman and the indicators of an additional study of the fetus (ultrasound, CT, Dopplerometry). Multiple pregnancyMultiple pregnancy is always a high risk of developing chronic hypoxia of one or more fetuses. This is especially true of monochorionic monoamniotic twins, whose fruits have common fetal membranes and placenta). As a result of this, there is a high risk of an uneven distribution of maternal blood between future babies, which will lead to insufficient oxygen supply to one of the twins. Pelvic presentationWhen the fetus is presented with the pelvic end, the likelihood of pressing the umbilical cord increases when it passes through the birth canal. In addition, pelvic presentation causes various complications in childbirth, which leads to the development of fetal oxygen starvation. Fetal malformationsIn case of intrauterine malformations (abnormalities of the cardiovascular system, neural tube, etc.), chronic oxygen deficiency in the fetus occurs in 100% of cases. To eliminate malformations, biochemical and ultrasound screening is carried out, the subsequent tactics of pregnant and childbirth management depend on the results of these. Bad habitsIf a pregnant woman has not abandoned bad habits (smoking, taking alcohol and psychoactive substances), toxic substances are formed in her body as a result of metabolic disorders, and the vessels are in constant spasm. All this significantly worsens the blood supply in the mother-placenta-fetus system and leads to the development of chronic fetal oxygen starvation. In addition, the regular intake of alcohol during pregnancy causes the formation of fetal alcohol fetopathy, which affects its mental and physical development. What causes acute hypoxiaAcute oxygen deficiency of the fetus can develop at any stage of pregnancy, but most often occurs during childbirth. The only true tactics of doctors with acute hypoxia is immediate delivery, since the count goes on for minutes and the fetus can die. Placental abruptionPlacental abruption is a formidable complication, the main sign of which is severe abdominal pain, which causes the pregnant woman to take a forced position and, as a rule, bleeding from the birth canal of varying intensity (sometimes external bleeding may not occur, for example, with placental abruption in the bottom of the uterus). This complication threatens not only the life of the fetus, but also the woman. With detachment, a “separation” of the placenta from the uterine wall occurs, which leads to rupture of blood vessels and a violation of the flow of oxygen to the fetus. Since detachment occurs prematurely, when the fetus is still in the uterus, the uterine vessels do not have time to shrink and stop the loss of blood. As a result, severe fetal hypoxia occurs, the consequences of which are difficult to predict. A frequent cause of detachment is high blood pressure, and the outflow of a large volume of water, abdominal injury. Since 15% of placental abruptions are accompanied by intrauterine death of the fetus from oxygen starvation, the best solution is immediate delivery Acute cord blood flow disturbanceThe causes of this complication are:
The occurrence of these complications can be suspected during an ultrasound scan at 32 to 36 weeks, especially cord entanglement. But the fetus at the beginning of labor can repeatedly change its location, which will affect the localization of the umbilical cord. Therefore, in childbirth, it is advisable to conduct cardiotocography. The pressing of the umbilical cord is indicated by a decrease in the fetal heart rate in the labor and a slow recovery of the heart rate after the labor. In the case of persistent and increasing bradycardia, caesarean section is indicated. Anomalies of patrimonial forcesViolation of the contractile activity of the uterus in childbirth (weakness of contractions, cervical dystocia, or discoordination of labor forces) delays the process of childbirth, slows down the fetus's progression along the pelvic ring and tires the woman, which causes acute oxygen starvation in the fetus. Prolonged or rapid birthWith prolonged labor, the fetal head is long in the same plane of the small pelvis, as a result of which the blood vessels are compressed and the blood flow is disturbed. With rapid childbirth, the child very quickly passes through all the planes of the small pelvis and does not have time to complete the correct turn to the period of the expulsion of the fetus. Premature discharge of waterThe outflow of water before the onset of labor leads to a prolonged anhydrous period, which is dangerous not only by the development of infectious complications, but also by acute oxygen deficiency in the fetus. Uterine ruptureUterine rupture is an extremely serious and urgent condition, resulting in a sharp cessation of blood supply to the fetus, acute hypoxia and antenatal death. A woman’s life is also at risk, and if an immediate operation is not done, she may die. Predispose to this complication:
Hypotension in womenLow blood pressure in the mother, for example, fainting, leads to a sharp decrease in blood flow to the fetus and oxygen starvation. Rational and nutritious nutrition of a pregnant woman, timely and adequate treatment of anemia during pregnancy, and proper breathing and behavior of women in labor will help prevent the occurrence of fainting. During contractions, a woman breathes shallowly and often, which is not true. Such breathing does not saturate the blood with oxygen, tires the woman in labor and causes hypoxia in the fetus. A woman experiences dizziness, shortness of breath, and a baby's heart rate is quickening. False contractionsFalse or preparatory contractions occur at periods of 22 to 37 weeks and do not lead to structural changes in the cervix. False contractions are characterized by a periodic increase in uterine tone and the occurrence of pulling pains in the lower abdomen. Uterine stress (hypertonicity) can cause fetal oxygen starvation. Drug use in childbirthDuring contractions, narcotic analgesics, such as promedol, are sometimes used. Promedol inhibits the respiratory center of the fetus, which provokes the development of oxygen deficiency. The use of drugs during childbirth should be strictly justified and monitored (monitoring the fetal heartbeat, CTG), and the period of rest is carried out in the presence of a neonatologist. Degrees of hypoxia and placental insufficiencyViolation of blood flow in the placenta does not always entail instant hypoxia. The fetus has a certain margin of "strength" that allows you to compensate for FPN. There are several degrees of FPF and hypoxia:
How is intrauterine hypoxia manifested?Signs of hypoxia and their severity depend on how long the process lasts and the degree of oxygen deficiency. Alarming symptoms:
Terrible signs requiring immediate delivery:
If the violation of placental blood flow was secondary, that is, due to illness of the mother or fetus, these pathologies are manifested in the first place: anemia, eclampsia, renal failure. If a violation of the blood flow of the placenta is primary, then for a long time a woman does not experience any unpleasant symptoms. Sometimes you can note the frequent, erratic and intense movements of the baby. If the treatment is late, then the motor activity decreases until the complete absence of tremors of the child. It is important to remember that with chronic fetal hypoxia, symptoms may not appear until serious complications. Chronic FPF and hypoxia lead to a slowdown in fetal growth. This can be seen by the small size of the abdomen, not corresponding to the gestational age. Ultrasound in this case determines the IUGR - the intrauterine growth retardation of the fetus. If the fetus is smaller than it should be at a given gestational age, then it is more difficult for it to endure the difficult process of childbirth and begin independent breathing. In addition, such children often have neurological disorders and respiratory illnesses. Hypoxia in childbirthDuring normal birth, each uterine contraction (cramping) causes a temporary decrease in blood flow in the placenta. Such short hypoxia is well tolerated by a healthy fetus, and after relaxing the uterus, the blood supply to the fetus is fully restored. If the duration of oxygen starvation during childbirth is increased, then the blood supply to the fetus is severely impaired. Changes in the internal organs begin. If at this time the baby is not born into the world, then his death may occur at the time of birth or immediately after them. Causes of fetal hypoxia during childbirthSigns of fetal hypoxia during childbirth
Signs of asphyxia of the newborn (stopping oxygen supply)Hypoxia of newborns is usually called asphyxia, and its degree (moderate or severe) is determined on the Apgar scale in the first and fifth minutes after birth. Saving 0-3 points on the Apgar scale for 5 minutes or more - severe asphyxiation.
Signs of asphyxiation of the newborn (stopping oxygen supply)Saving 0-3 points on the Apgar scale for 5 minutes or more Disorders of the brain and other organs:
It used to be that an infant can only breathe in the original feces (meconium) only during childbirth. Now there is evidence that with chronic hypoxia there is a risk of meconium aspiration. Moreover, the removal of the original feces from the lungs in the second case brings fewer results, and among the consequences there are disorders of the nervous system and frequent pneumonia.
Signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
It is important to remember that the development of cerebral palsy in a child is often associated with hypoxia. This scenario is possible, but not required. Most children who have undergone perinatal hypoxia and do not suffer from this serious illness. The consequences of intrauterine hypoxia for a childHypoxia of the fetus in one way or another, but almost always, is accompanied by consequences in the child after birth. The lack of oxygen in utero during the period of active growth and development of organs and systems of the fetus primarily affects the state of its nervous system and immune status. After chronic hypoxia
After acute hypoxia
All the consequences for the baby are associated with brain hypoxia and premature birth, since in order to save the life of the child, emergency delivery is often used much earlier than before. Most cases of hypoxia have no consequences if the child successfully survived the first month. Special methods for detecting hypoxiaFor the diagnosis of fetal oxygen deficiency, in addition to studying the anamnesis and complaints of the expectant mother, examination data and instrumental methods are used. During auscultation, the doctor listens to the heart tones of the fetus, evaluates their frequency, rhythm and clarity. CTG - cardiotocographyThe purpose of the examination is the registration of baby's heart contractions, based on the Doppler effect. Additionally, fetal movements are noted (since the heartbeat changes during movements) and contractile activity. The combination of these data helps to determine the condition of the fetus, determine its response to contractions and timely detect hypoxia (see). Signs of the heartbeat of a healthy fetus are:
Signs of fetal oxygen starvation:
During childbirth, CTG should be carried out every 15 minutes, and during a busy period - after each fight. If there are signs of hypoxia, you can try to change the position of the woman's body to eliminate the clamping of the umbilical cord. In recent years, remote CTG devices have appeared. High-risk pregnant women are offered to conduct home recording of a cardiotocogram using a special apparatus. All results are sent via the Internet to the attending physician in real time. This allows you to quickly identify acute hypoxia and save the child. Doppler ultrasoundUsing the Doppler effect on ultrasound, it is possible to determine the state of blood circulation in the mother-placenta-fetus system after 20 weeks of pregnancy. When examining the uterine arteries, it is possible to identify the initial violations of the uteroplacental blood flow and prevent severe fetal hypoxia. Additionally, the structure of the placenta itself and the level of amniotic waters are determined. Counting fetal movementsThis diagnostic method is quite inaccurate, therefore it is mainly used in low-risk pregnant women (without chronic mother diseases, fetal malformations, and placenta pathologies). It allows you to identify the first stages of hypoxia in time, when the child changes his motor activity in response to oxygen starvation. For the test, you need to get comfortable (preferably on your side) and concentrate on the movements of the baby. If less than 10 tangible movements occur in an hour, then you must urgently consult a doctor. Gynecological examinationExamination on a gynecological chair is indicated in case of complaints of the pregnant woman on unusual discharge from the genital tract:
Analysis of blood taken from the pre-existing part of the fetusThis study is new and is based on the determination of the concentration of lactate (lactic acid) in the blood of the unborn baby. The study is possible only with an opened fetal bladder and opening of the cervix by 2 cm or more. Interpretation of results:
How to determine the biophysical profile of the fetusThe method involves evaluating the five main parameters of fetal health. It is carried out during high-risk pregnancy, when there is a high probability of suffering or even intrauterine death of the fetus. Respiratory rateWith a 30-minute ultrasound, the number of episodes of respiratory movements is counted. 2 points are given in a 30-second episode for half an hour of observation. Lack of respiratory movements means 0 points. CTGAssessment of parameters of a 20-minute cardiotocographic study. If during this time 2 or more episodes of increased heart rate were observed, then the test is evaluated at 2 points, the prognosis is favorable. With a "bad" CTG test is rated at 0 points. Muscle tone of the fetusThe episodes of limb flexion in 30 minutes are evaluated. If 2 or more episodes - 2 points, if the limbs all the time in the unbent state - 0 points. Physical activityIf 3 or more active fetal movements are noted on a 30-minute ultrasound, then 2 points are given for the test. If less than 3, then the score is 2 points. If there are no movements - 0 points. Amniotic fluidWith an amniotic fluid index of more than five, 2 points are given. With a lower IAI, the test is rated at 0 points. To assess the biophysical profile of the baby, scores are calculated for all 5 tests. If the amount is 8-10 points, then the fetus is in good condition, you can repeat the study after 3-4 days. If the amount is less than 8 points, then additional examinations are necessary, and sometimes - emergency delivery. Profile assessment is carried out twice a week. This allows you to detect acute and chronic intrauterine hypoxia in time. Often, the complete method is replaced by a shortened one: only CTG and the level of amniotic fluid are evaluated. Treatment of intrauterine hypoxiaWith fetal hypoxia, treatment depends on the duration of pregnancy, the condition of the mother and child, and the concomitant diseases of the pregnant woman. There is still no clear algorithm for eliminating oxygen starvation, since its causes are very diverse. If the condition of the patients allows, then the doctor can try conservative methods.
Due to difficulties in treating fetal hypoxia, it is important to properly plan your pregnancy, get rid of bad habits and monitor your health. After all, to carry out prevention and prevent the disease is always easier than getting rid of it. PreventionHow can a future mother avoid hypoxia in the fetus? The following recommendations will help prevent the development of this condition in the fetus:
Prevention of hypoxia in childbirth is the optimal method of delivery and proper management of labor. Question answerI have a period of 34 weeks, the gynecologist says that the pregnancy is proceeding normally, according to ultrasound, everything is also normal. But lately (about a week) I began to notice that the child moves very often, which makes me uncomfortable. Is this a sign of incipient hypoxia?No, not at all necessary. Many factors influence the motor activity of the fetus (stress of the mother, fear, hunger, stale indoor air and others). And in the third trimester, the size of the baby is already significant and it becomes somewhat cramped in the stomach, so most of the movements can be felt by the mother painfully. It is possible that recently you are very nervous, think about the upcoming birth and neglect a healthy lifestyle. Try to walk more often in the fresh air, adhere to a fractional diet (4 - 5 times a day), avoid hunger and air the bedroom before going to bed. Of course, it is unscheduled to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist who listens to the fetal heartbeat and, if necessary, appoints a CTG. Can I listen to the fetal heartbeat on my own?Obstetricians use a special (wooden) obstetric stethoscope to listen to heart contractions in the unborn baby. It is impossible to independently listen to the fetal heartbeat in this way. But you can buy a portable fetal doppler (such an ultrasound device equipped with headphones, the principle of operation is similar to the CTG apparatus) with which you can control the fetal heartbeat at home. Does it make sense to consume oxygen cocktails for fetal hypoxia?At present, oxygen cocktails are very popular, they are prescribed to pregnant women not only when any obstetric pathology is detected (anemia, early toxicosis, fetal hypoxia), but also to strengthen the immune system and saturate the body with vitamins. Oxygen cocktails are made from natural juices and herbal decoctions and are saturated with oxygen using an oxygen mixer or cocktail and an oxygen cylinder. It is useful for expectant mothers to drink oxygen shakes just to prevent possible pregnancy complications. But there are contraindications for taking such cocktails, so you should first consult your doctor. |