From internal pipelines, drains are transported by external ...
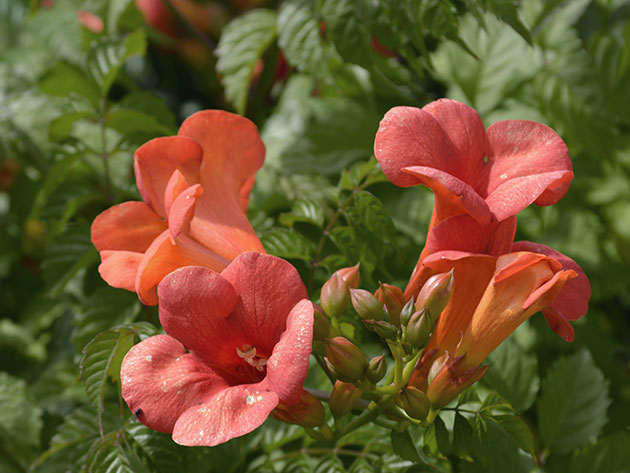

Plant campsis (lat.Campsis), or bignonia - woody deciduous lignum of the Bignoniaceae family, a large heat-loving plant with bright flowers. The campsis flower received its scientific name from the Greek word meaning to twist, bend, bend. Some amateur gardeners believe that kampsis and tekoma, or tekomaria, are the same thing, but this is not so: these plants really belong to the same family, but represent different genera. The genus Kampsis includes only two species, one of which has been cultivated in European parks since the 17th century.
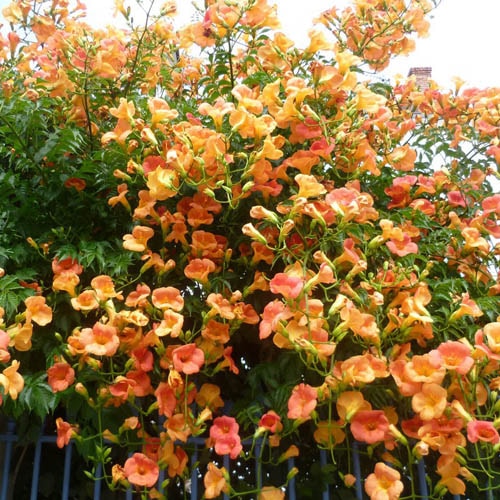
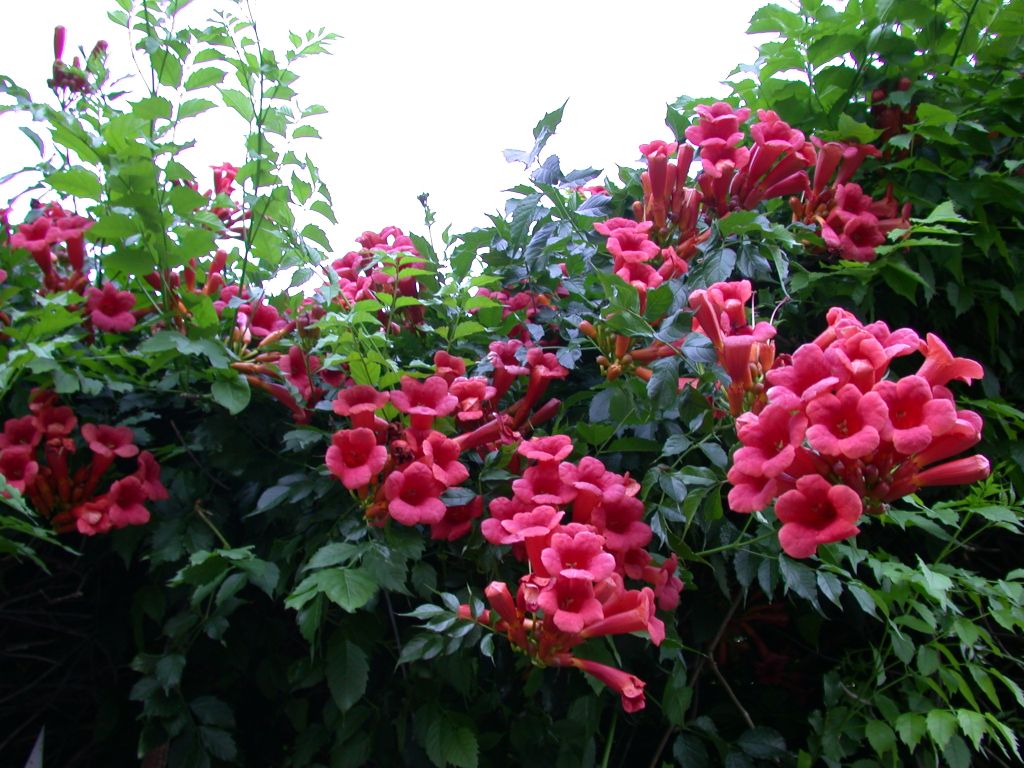
Liana campsis is most often used for vertical gardening - it is fixed on a support by aerial roots. The beautiful complex, pinnate leaves of the campsis, consisting of 7-11 leaflets with serrated edges, are very effective, and its large tubular flowers, odorless and collected in short panicles at the ends of the shoots, reach a length of 9 and 5 cm in diameter. Depending on varieties of flower color can be red-orange, raspberry, red-golden or pink. Campsite blooms in June and lasts until September. The creeper Camppsis is a honey plant that attracts not only bees, but also wasps, ants, and even flies. The fruit of the campsis is a leathery elongated pod 8-10 cm long of two valves, in which a large number of webbed seeds with wings ripen. When ripe, the pod cracks and the winged seeds of the campsis fly around. However, not all campsises bear fruit - apparently, to set the seeds, it is necessary that another clone plant grow nearby.
Despite the fact that the campsis winter hardiness allows it to withstand short-term frosts of up to -20 ºC, campsis in the middle lane can be planted in open ground only in the second half of May. Campsite is planted in the Moscow Region on the southeast or south side of the site, in a place protected from gusts of wind and drafts, but away from the windows of houses, because insects are actively flying to the campsis. The plant is indifferent to the composition of the soil - kampsis grows even in limestone soil, but the soil must be saturated with trace elements and minerals. Camppsis is planted in a pit prepared in the fall of 40x50x50 cm in size.

If you want the kampsis to start blooming already in the second or third year, you need to plant a rooted stem taken from an adult plant, characterized by abundant flowering.
The top layer of soil removed from the pit is thoroughly mixed with 5 kg of compost and 500 g of complete mineral fertilizer, after which a layer of this soil mixture is laid at the bottom of the pit, then the seedling roots are lowered, straightened and gradually the remainder of the fertile soil mixture is added to the hole. The shank should be in the ground at the same depth at which it grew until then. After planting, the surface of the trunk circle is crushed and watered, and after the water is absorbed and the earth dries out slightly, the surface is mulched with compost or peat. Since kampsis is a liana, you need to install a support for the seedling and tie it to it, so that this aggressive plant does not capture more territory than you allocated to it, dig around the root section metal sheets or slate to a depth of about 80 cm.
How to grow campsis? Despite the exotic nature of the plant, the cultivation of campsis and the care of it are even within the reach of a novice grower. Care of the campsis liana consists of watering, loosening the soil and removing weed grass around the plant, fertilizing, protecting against diseases and pests and compulsory pruning of the campsis. In the watering regime, it is important to maintain balance, since the plant does not like both drought and stagnation of moisture in the roots. On wet ground, it is easier to weed and loosen the trunk circle. The shrub kampsis culture is drought-resistant and is unlikely to die if you forget to water it, but timely maintenance is of great importance to maintain a well-groomed and healthy-looking plant. To keep moisture longer in the near-stem circle of the campsite, plant several bushes of low-growing plants in it with similar requirements for the conditions of detention.
Camppsis can grow without fertilizing, but it responds to the application of nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer by abundant flowering throughout the season.
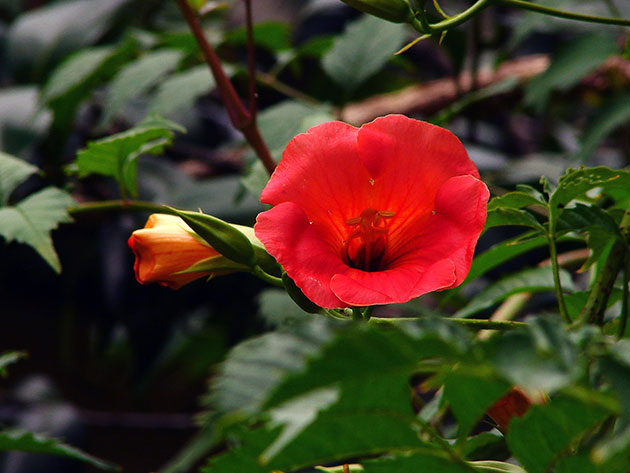

Campsis care requires regular pruning. Campsis formation should begin immediately after planting - all shoots are cut off at a height of 15 cm from the ground. When they begin to grow, leave four or five of the most developed shoots, and remove the rest. The remaining shoots, as they grow, direct along the support, tying them to it if necessary. It will be possible to talk about the formed plant when the skeletal branches reach 4 m in height. This usually takes 2-3 years. As for the lateral shoots, they are annually shortened to 2-3 eyes, and weak, dry, diseased and poorly growing ones are completely removed. In case of severe damage to one of the skeletal branches, remove it and direct in its place the strongest of the formed substitute shoots. To rejuvenate the old plant, all campsis branches are cut at a height of 30 cm. Pruning is best done in early spring, before the buds awaken.
During the growing season, remove wilted flowers and cut off faded shoots for 3-4 eyes - this will ensure a high level of decorativeness of the plant and the duration of its flowering.
Readers sometimes ask us this question. Most often this happens with plants grown from seeds - such a campis blooms only in the fourth or sixth year after emergence, while the rooted cuttings begin to bloom in the third year. The reason that the campsis does not bloom may be sudden late spring frosts or severe drafts, as well as the defeat of the disease or pests. Campsis will not bloom in a cold climate.
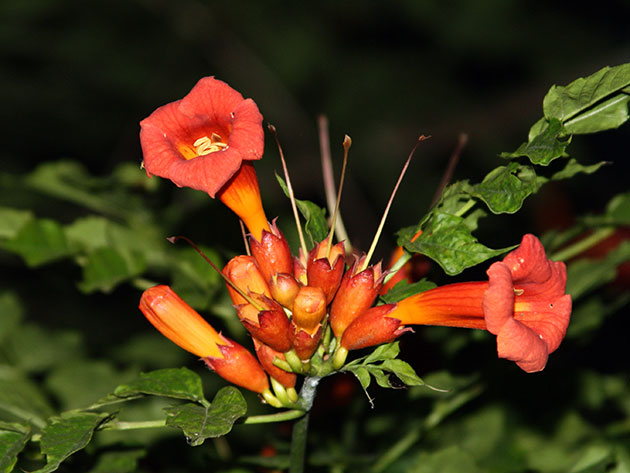

Campsis is very resistant to diseases and pests, but its roots can rot due to excessive watering, and in dry and hot weather the plant attacks aphids. Keep a balance of soil moisture and treat the campsite from aphids with a solution of 10 g tar soap in 10 l of water.
In all other respects, planting a campsite and caring for it is not only not time-consuming, but also a very pleasant process.
Campsis is propagated generatively (by seeds) and vegetatively - by cuttings, lignified and green cuttings and root shoots.
The seed method has the disadvantage that seedlings almost never inherit the varietal qualities of their parents, and these plants bloom much later than those grown by vegetative methods. But on the other hand, this is the most uncomplicated way to get campsis: the seed does not need preliminary stratification and any other treatment and is normally stored at room temperature. In the spring, the seeds of the campsis are sown in a loose permeable substrate with a neutral reaction to a depth of about 5 mm and germinated at a temperature of 25 ºC. Shoots appear in a month. As soon as the seedlings develop 3 pairs of real leaves, they are transplanted to a permanent place.
Green campsis cuttings are cut in June or July from the middle of the shoots. They leave 2-3 upper leaves, shortened by two-thirds, then planted on a bed in partial shade at an angle of 45 º in fertile loose soil, after which the garden is watered and mulched. The rooting rate of green cuttings is about 90%.
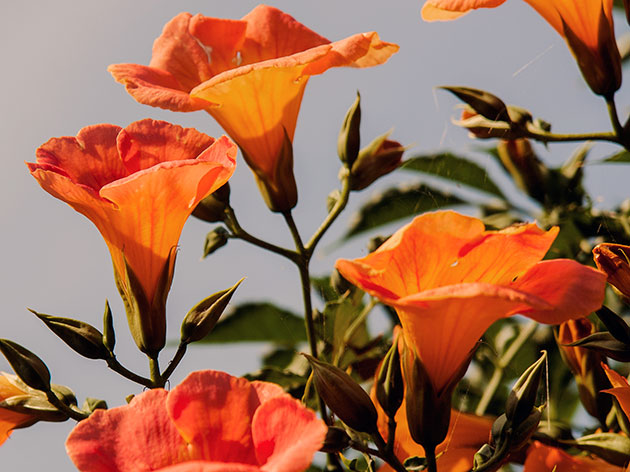

Campsis propagation is possible and lignified cuttings. They are cut in early spring from one-year-old woody shoots and planted immediately at an angle to the ground, since almost all cuttings take root.
Under favorable conditions, kampsis provides abundant root shoots. The basal process is dug up with part of the root and immediately planted in a permanent place. This should be done when the plant is at rest - in early spring or after leaf fall.
In the spring, the campsite shoot, growing close to the soil, is bent and fixed in this position. Throughout the season, the soil around the layer is maintained in a loose and wet state, and then next spring the layers can be separated from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place. Campsis of the layering develops very quickly.
The campsis winter hardiness allows it to endure short-term frosts up to -20 ºC without damage, but in areas with prolonged cold weather the plant should be covered for the winter. Therefore, it is better to use removable supports for the campsite, so that on the eve of winter they can be easily removed, and again quickly installed in the spring. The procedure for preparing the campsis for winter is similar to warming grapes: winding campsis is removed from its support, laid on the ground, covered with leaves, spruce spruce branches or sawdust, and covered with a film on which the spruce branch is again laid.
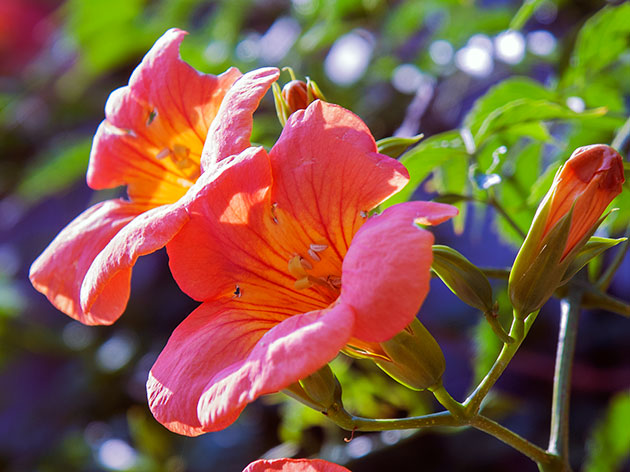

There are only two types of campsis in the genus: the campsis rooting, growing in North America, and the large-flowered campsis, growing in Japan and China. These natural species of campsis gave birth to a third species - the campsis hybrid.
or rooted Bignonia (Bignonia radicans) - a large liana rising to a height of 15 m with the help of numerous aerial roots. Her leaves are unpaired, up to 20 cm long, consisting of 9-11 leaves, on top bare and bright green, below light due to pubescence, which can cover the entire leaf plate, and can only be located along the veins. The flowers are tubular-funnel-shaped, up to 9 in length and up to 5 cm in diameter, with a bright orange corolla and fiery red limb, 10-15 pieces are collected in apical brushes. The duration of flowering is achieved due to the fact that the flowers open sequentially, starting from mid-summer. The fruits of the rooting campsis are flat pod-shaped capsules from 5 to 12 cm long. The species has been in culture since 1640. Campsis rooting is represented by such decorative forms:
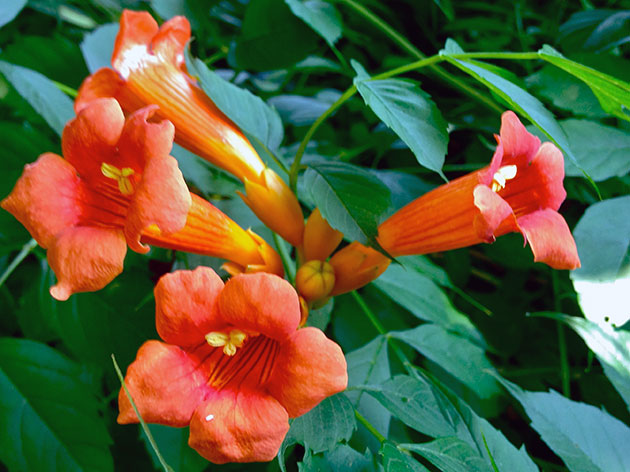

or campsis Chinese or chinese bignonia (Bignonia grandiflora), unlike the campsis rooting, it has no air roots, therefore it is attached to the support by the ends of the shoots. Obviously, for this reason it reaches a lower height, and sometimes even grows in the form of a low bush. The leaves of plants of this species are unpaired, consisting of 7-9 leaves up to 6 cm long, not pubescent on the underside of the plate. The tubular-funnel-shaped flowers of a red-orange hue, larger than the flowers of the rooting campsis - up to 8 cm in diameter - bloom 3 years after the emergence of seedlings. The fruit of the Chinese campsis is a pod-shaped capsule 15-20 cm long. This species is not as hardy as the rooting campsis, but it is brighter and more spectacular. The decorative form of this species, Campsun Thunberg, has orange flowers with short lobes and a short tube. In the culture, campsis is large-flowered since 1800.
Rating 4.42 (19 votes)Five years ago, I was relaxing on the Black Sea coast, and for the first time I saw a chic vine. She impressed me with her beauty, brightness and power. Before leaving, I dug up the root offspring that I brought home.
Soon I found information about this plant, which, as it turned out, had two names - campsys and tekoma. I began to understand the features of its growth and development. I found out that this is a woody deciduous liana, which belongs to the Bignonium family. There are two types of kampsis, which I decided to grow, and Kampsis delights with its flowers, which are collected in a brush and reach 10 cm in length, beautiful and pinnate leaves of the plant.
I placed the liana in a large container and let it winter in her house in an unheated veranda. In the second half of May, she planted a plant on a permanent place near the southern side of the fence in loose fertile soil. In some publications I met information that limestone soil is suitable for the campsite. After transplanting, it abundantly watered and made a support to direct the vine to the fence.
Once in the spring and once in the summer I bring in nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer. I propagate vines with cuttings or undergrowth, it’s more familiar to me, but you can sow seeds.
Campsis is a very thermophilic vine, and there are severe frosts in my area. Therefore, sheltering the plant for the winter is very important. When the cold comes, I try to remove the vine and cover it with spruce branches, and on top with dry foliage. Do this procedure in dry weather.
In winter, I try to throw more snow on the shelter. I spend spring pruning, leaving 3-4 shoots. Once in a dry period, aphids attacked my vine.
I struggled with harmful insects by spraying with a solution of laundry soap. As if I were not in love with this vine, but I still have to admit that it has negative sides. Firstly, insects - both flying and crawling - love the plant very much I do not recommend growing a vine near windows. Secondly, the campisis fully justifies its name - rooted. If grown near a building, the roots cling and grow into a tree, and even into a brick. If you decide to create a green wall with beautiful flowers - it should be for a long time, since it is very difficult to destroy the vines. Campsis also abundantly shoots root shoots, so you need to make sure that it does not conquer the area more than it is allocated to it. Thirdly, the flowers of the vine are very beautiful, but only bloom for a day or two, then fall off, new ones appear in return, therefore almost every day I have to sweep the ground under the vine. It has been four years since I planted the campsis in the ground, and only this year it pleased me with truly abundant flowering. I recently found out that with constant pruning of the vine, it can be grown as a house plant, I want to experiment. About I’ll write about successes or failures. I hope that my recommendations regarding the rooting campis will be useful to readers. Let your plants also have beloved and healthy plants.
Surely, while on vacation, you have ever seen hedges completely covered with a beautifully flowering vine, the flowers of which resemble gramophone finishes. Many amateur flower growers would like to grow a plant at home, but they have lost all interest in the campsis - this is the name of this liana - finding out about its heat-loving disposition.
A plant habitual for the southern regions, if desired, is quite easy to grow in the middle lane. Campsis is an unpretentious plant. Plant it in a sunny, protected from drafts place and abundant flowering is guaranteed.
Kampsis is not afraid of drought, but this does not mean that it does not need to be watered at all. Water it regularly and plentifully. To preserve moisture, soil the soil at the roots of the plant with peat or sawdust.
Campsys does not have special requirements for top dressing. For the longest and brightest flowering, feed the plant twice a month with complex fertilizer with nitrogen and phosphorus. Camping WinteringPerhaps the most crucial moment.
In areas where winters are traditionally mild, there is nothing to worry about. But if the temperature is often and long below -20 degrees, then without shelter it is impossible. This procedure is quite simple. The entire plant is completely covered - both the stems and the roots.
The stems must be removed from the support, laid on the ground and covered with fir spruce branches, sawdust or leaves. Then cover the "hill" with plastic wrap. Every year, the campsis needs cropping and shaping.
A properly formed plant will be more attractive. Regular pruning stimulates abundant flowering, since flowers are formed only on young shoots. From the first years of life, form a campsis skeleton of three four branches.
And young shoots that have grown over the year are ruthlessly removed. Propagate Campisis can be cuttings, layering or seeds. The seed method is quite simple, but not popular, in which case you will have to wait 7-8 years to bloom. It’s pretty easy to propagate the campsis with layering.
Pinch and dig the shoot, growing as close to the ground as possible, and cover the ground above the layer with plastic wrap in order to increase the soil moisture. Next spring, a new plant will be formed from the rooted layer. A young plant can be obtained using the root shoot.
To do this, in the spring, before the onset of the vegetation phase, separate the shoot with the root from the main plant and plant it in a permanent place. For propagation of the campsis, the cuttings are also used. In early spring, last year's cut, well lignified (only not green) cuttings are cut and planted in a permanent, not sunny place.
If the winters in your region are especially frosty, cuttings should be planted in containers that you can easily put in a cool and bright room for the winter. If the winters are really cold and the shelter does not help, the campsis can be “domesticated”. With proper care and regular pruning, a garden plant can become a room vine.
Campsis (Campsis) is a genus of thermophilic perennial deciduous vines from the Bignoniaceae family, which consists of only 2 species: Asia (more precisely: in China and Japan). “Able”, wrapping around the support with the ends of his shoots, approach it to the sky for 6-8 meters. Sometimes takes the guise of a low bush.
Delicious and in a standard form. Bright orange flowers (up to 8 centimeters in diameter, looking like a smooth combination of a wide funnel with an elongated tube) for the first time show on the 2nd or 3rd summer after planting seedlings in open ground.
It tolerates frosts up to minus 18 ° C, but only for a short time. The length of the leaves does not exceed 6 centimeters. Introduced into the culture since 1800; - Campsis rooting (Campsis radicans, or Bignonia radicans), also known as Tecoma rooting (Tecomaria radicans), comes from North America.
Sucking to a support (even to a window pane) by dozens of aerial roots produced by stems, it rises to a height of 15 meters (leaves correspond to such “guard” growth - their length reaches 20 centimeters). A skilled gardener can be shaped like an upright tree.
Equally “fiery” flowers (with a diameter of up to 5 centimeters, a length of up to 9 centimeters) with a scarlet limb are combined 10-15 pieces into the apical brushes, not all are revealed at once, but sequentially (therefore, flowering is very long and plentiful). Withstands short-term temperature drops to minus 20 ° C.
Cultivated in Europe since 1640. And from 1883, the hybrid of these two species, Campsis Tagliba (Campsis - hybrida \u003d Campsis - tagliabuana \u003d Tecoma tagliabuana), began to gain wide fame. It is often a shrub, and with sprawling branches.
The size of the flowers is similar to Campsis grandiflora, and the degree of cold hardiness is similar to Campsis radicans. The foreign GRIN website (for more details see the Sheffler article) mentions the third species in the list for the Kampsis genus - Campsis fortunei (\u003d Paulownia fortunei), however, it immediately refers to the family Paulowniaceae (not Bignoniaceae) .Tekoma (Tecoma) or Tecomaria (Tecomaria) - synonyms of a different kind (covering about 40 different species) from the Bignoniaceae family - are often used as Camppsys names, which, strictly speaking, is a mistake. The spoken version of Tykom generally sounds rude.
Do not repeat these mistakes, please. Much better are the nicknames "Trumpeter" and "Trumpeter", which are among amateurs. “Virgin Jasmine” is beautiful ... and, alas, not very correct, because the Campsys do not radiate the fragrance accessible to human smell. (Their smell is quite accessible and attractive for bee and ant smells.) In their genus there are varieties with a different color of flowers: scarlet (purple), purple, yellow, classically orange, red-orange or bright red.
Dark green, non-pinnate, opposite leaves, consisting of 7-11 leaflets with serrated (toothed) edges, effectively looking against the background of walls and other elements of garden structures, enhance decorativeness. Do not bother about erecting a trivial support elongated along the vertical like a flagpole. Instead, try to make a figured structure in the middle of the lawn, which Kampsis rooting, braiding, will turn into a ball, into a prism or cylinder cut obliquely, into a truncated cone or pyramid with a peak hidden in the ground.
Try to use this plant as a groundcover. Secrets of the successful cultivation of Kampsis It is photophilous (and along with insolation, the sum of summer temperatures is also important for good flowering). It prefers light, loose soil (“agrees” to loam). It will develop confidently and quickly if it is endowed with wealth (fertility) and moderate humidity.
Therefore, top-dressing and regular watering are necessary (especially during flowering: at Kampsis Chinese, it unfolds in August-September, at Kampsis rooting - from June to October frosts). The list of breeding methods begins with the line “seeds”. They are placed in the seedling box in March.
After 20-25 days, seedlings appear, which in May can be moved to normal soil. If sowing is carried out in autumn, then preliminary stratification of the seeds will be required (see the article “Kandyk” about it), and they will germinate in 60-100 days. Alternative animated materials: - root shoot; - cuttings; - cuttings from year-old shoots, rooted in the sand.
From the rooted cuttings at the start of the first growing season break off all the shoots, except for 2-4 the strongest. They should make up the "skeleton" of the specimen, that is, by the end of the growing season, reach 250-300 centimeters in length and solidly lignify.
Perhaps for the sake of this, young Campsis will have to live a whole summer in a container. In winter, the container will be demolished in a cold basement. If “skeletal” stems have not acquired the necessary conditions over the year, growth in the container continues.
If you get it, in the spring it is planted in the intended place under the sun. In the southern regions (on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus, for example), grafting by the cuttings is acceptable. Planning to get a standardized form, the “Chinese” is grafted about 10 centimeters above the ground onto the trunk of a tree from the Catalpa family, also belonging to the Bignonian family. Camppsis pruning (he transfers it without suffering) is a multi-purpose and multiphase procedure.
Firstly, it determines the decent appearance of the plant (remove small side shoots, keep them “skeletal”). Secondly, annually in the spring, shorten last year's shoots by 2-3 buds, since inflorescences are formed at the ends of only those shoots that are released by matted stems in the current year.
Thirdly, for the sake of rejuvenation, cut all the shoots almost to the base every 5-6 years (do not expose the lowest tier). In the complex of cosmetic measures also include tying. : it rots) and sprinkle with earth. For the “guardsman”, you can organize wintering in another way: transfer to a cool greenhouse, continue watering moderately, cut flowered branches in February. Kampsis is not susceptible to diseases or insect pests. When covering it before winter, come up with and provide reliable protection against small rodents. If you do not comb out the wilted flowers from the hands (and they wilt no more than 50 hours after they bloom), then in a couple of weeks, the Campsis rooting will become like a garbage heap. If the "guard" lash falls on the wet substrate, then after a few days to tear it off without damage, do not dream. (But you need to rip it off if you don’t want to spread to the entire lawn.) If you dig out Campsis without thoroughness, then in its place new shoots will soon “shoot” from the ground (thanks to the super-duper survivability of the root system). Glyphosate (a herbicide famous for its brands “Roundup” and “Hurricane”) does not help in such situations. The lazy owners are inclined to declare the plant aggressive, for which it can “eat through” the foundation, break through the floor, squeeze out the windows, fill the attic, and drop the roof, and from the nostrils to grumble ... However, he really does not recommend Campsis should be planted in close proximity to wells, basins, artesian wells, for, having sensed water, he will penetrate his roots even through reinforced concrete in an effort to reach it.
Campsis (tekoma) - deciduous vine of the Bignonius family, homeland - China and North America. This fast-growing liana forms airy sucker roots clinging to a support and can climb up to a height of 15 m. Campsis is very decorative, resistant to urban conditions, smoke and gas resistant.
However, the thermophilicity of this plant prevents its widespread use in regions with cold winters. Kampsis grows well and blooms profusely in a mild climate, in more severe conditions, this thermophilic vine requires shelter for the winter.
The main decorative effect of this liana is given by large tubular-funnel-shaped flowers, 8–9 cm long and 5 cm in diameter. Depending on the variety, the campsite flowers are orange, pink, red-golden, raspberry.
The first flowers begin to bloom in mid-June, flowering continues until September. Types and varieties of campsis: - Campsis rooting (Campsis radicans) is a native of North America. It reaches 7-9 m in height.
Rooted Campsis is a large vine with numerous aerial roots on stems, with the help of which it rises along a support. The leaves consist of 9-11 leaves with a characteristic pubescence on the lower side (solid or only along the veins).
Large, tubular flowers reach 6 cm in length and form apical brushes of 10-15 flowers. Flowers with a bright orange corolla and a bright red limb. Heat-loving, but can withstand a short-term drop in temperature to -20 ° C. Varieties of this type:
- Campsis large-flowered, or Chinese (Campsis grandiflora) in nature grows in China and Japan. Unlike the campsis, the rooting one has no aerial roots and wraps itself around the support with the ends of the shoots.
Unpaired leaves carry 7-9 leaves up to b cm long, without lowering from the bottom. But the tubular-funnel-shaped flowers of this species are much larger, up to 8 cm, than that of the campsis rooting, bright, fiery-orange color.
It reaches a lower height, sometimes grows even in the form of a low bush. At the time of flowering comes in 2-3 years. Less frost-resistant, tolerates short-term frosts up to -18 ° C without damage.
More colorful than the campsis rooting due to larger flowers and plentiful flowering. - Campsis Tagliabuan (Campsis tagliabuana) is a hybrid species resembling Campsis grandiflora. Camplis tagliabuan reaches 4-6 m in height.
Growing, it forms a bush. This hybrid rises worse on supports. By its decorative qualities, it is closer to the large-flowered campsis, and by winter-hardiness - to the rooting one. The variety of this type:
The location. Campsis photophilous, requires a secure location. It is unpretentious to soils and can grow even on heavy loams, but grows better and blooms profusely on fertile soil.
Demanding on stable moisture supply and substrate fertility. With sufficient nitrogen-phosphorus nutrition, flowering increases and increases. Old faded stems are best trimmed at the end of winter.
Like most vines, kampsis is tolerant of pruning, so you can give the plant any shape if desired.
It should be remembered that the flowers near the campsis appear on the shoots of the current year, growing from perennial stems, which must be correctly formed. Typically, a plant is formed into two to four main shoots.
They will make up the skeleton and bear the main burden during flowering. Too many shoots are formed at the base of the aboveground part, they must be cut out as they will interfere with the development of the main part.
Small side shoots need to be removed from the bush, taking care only of the "skeletal" branches. If the climate in your area is quite severe in winter (air temperature below -20 ° C), you should take care of sheltering the campus for the winter. For this, the support for the plant must be made removable, for example, from a synthetic cord.
Before the onset of frost, the whips are removed together with the support and laid on the ground. They are covered with spruce branches, dry plant residues. Reproduction. Easily propagated by seeds, root shoots, cuttings and layering. Seeds rarely propagated.
- Propagation of campsis by seeds rarely used - mainly in cases where vegetative propagation is difficult. A plant grown from seeds will bloom only in the seventh to eighth year. - Root planting - The fastest and most effective way to propagate campsis.
Root shoots are processes that form abundantly around adult plants. Such a process is cut off together with a piece of root, when the plant has not yet entered the phase of active growth, and is planted in a permanent place.
- Propagation by green cuttings produced in June-July. Cuttings are cut from the central part of the shoots, on which 2-3 leaves are left and planted obliquely in loose, fertile soil in partial shade.
It is advisable to mulch the soil with a thin layer of leaves to reduce evaporation of moisture. The survival rate of the green campsis cuttings is quite high, reaching 90%.
- Lignified campsis cuttings cut in early spring from the shoots of last year’s growth, planted obliquely. You can immediately plant it in a permanent place, since the survival rate of campsis winter cuttings is almost 100%.
- Campsis propagation by layering should be used for shoots located low above the ground. The lignified or green shoots of the campsis are enough to pin to the ground.
But it is necessary to ensure that the soil is constantly moist during rooting of the shoots, then the shoots of the campsis root during the season. In the spring of next year they are separated from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place.
Campsys propagated by layering develops very quickly. Using. For vertical gardening of fences and facades of houses, and also grown in a low-punch form in the form of a small tree.
|
In childhood, we christened the plant an orange gramophone. This flower - tekoma liana (campsys). Planting, care, cultivation, reproduction deserve attention, since it has an extraordinary decorative effect (photo), it is able to close unsightly fences and walls, is unpretentious, frost-resistant. How many names does this flower have - campsis, tekoma, tube flower, but one thing can be said - this is a perennial plant that tolerates frost well (sometimes still needs shelter), deciduous. The stalk spirals around the support. Therefore, sometimes the stems, intertwined, form bizarre forms. And the tekoma liana near the ground resembles a trunk of a fancy tree. Above it is crowned with a magnificent cap of dark green feathery leaves up to 40 cm long and tubular bright orange flowers collected in drooping brushes. Why not the crown of a tree. It blooms all summer. As you can see, the brush has discolourations, open flowers, and many buds. So the gramophone players will please us for a long time, decorating the flower garden with bright spots. But then the look will be elegant, since long boxes will be tied in place of flowers, which can hang for a long time, even sometimes all winter. The most common can be called rooting campsis. The vine is up to 3 meters long, the shoots are brownish, up to 5 cm thick. Although often the rooted tequana vine can reach 10-15 meters, taking possession of trellises, climbing onto the roof, covering a low house with a hat. When planting tekoma is not demanding on the soil, but nevertheless, for more decorativeness, select either fertile places or carefully prepare the landing pit. After all, you will have to grow in one place for many years. Choose sunny places, there will also be better growth and flowering. Camppsis is planted in spring in pits prepared since autumn. Size 40 * 50 * 50. Add 500 grams of full mineral fertilizer, 5 kg of humus. Hurry, the best survival rate can be provided in the time before budding. For reproduction, you can use seeds. There are a lot of them in the boxes. But before landing it is necessary to carry out stratification. This is for spring sowing. If the seeds are dried, then their germination is reduced. Therefore, it is better to use vegetative methods - layering, root and green cuttings, root offspring. As already mentioned, one of the most common types is the campsis rooting. Reproduction is simple, comes from the name itself. Take a closer look, on the shoots you will see small sleeping aerial roots. Take and just pin any shoot to the ground (can be laid in a small hole). The soil in this place must be kept moist. By the spring of next year, it will already be possible to separate a new plant. But not everyone may like this rooting ability. Since the roots are able to penetrate into the masonry of walls, and in wooden window structures. Therefore, it is better to use specially designed supports, and not just throw a liana on the wall. Flower campsis care is practically not required. You don’t even need to fertilize. The plant is able to penetrate to a great depth in the ground. Of course, especially after planting, you need to water. If there is a drought, then pour 3 times during the season, giving 30 liters under the bush. Loosen the earth, get rid of weeds. And if you feed it, for example, with an extract from ash or plants, then the flowering will be even more magnificent. Often form 2-4 shoots of the main. A trifle growing close to the ground is cut off. Thus, several skeletal shoots are obtained. Often, faded shoots are cut into 3 eyes. But nevertheless, tecom grows well both after pruning and after freezing. So boldly with the help of a secateurs give it different shapes, create green hedges or keep within the size of the bush. Using special designs, you can get a cube, a ball in your flower garden, some bizarre shape braided by liana. He copes with diseases and pests very well, until they have noticed. But in the spring, do not be alarmed. At first, it may seem to you that the liana has dried up, it just does not manifest itself early. Small hedgehogs of greenery will begin to appear, in bunches. Little by little, little by little, and then once and for all growth will go in a stormy wave. Campsis flower photo (click-to-enlarge) |
Campsis is a blooming deciduous liana with bright flowers, similar to small pipes from the first gramophones. Liana has become popular due to its magnificent decorativeness and unpretentious character.
This plant has amazing abilities to use supports; campsis can climb the wall of a house or any other structure to a height of more than 10 meters. The aprons help the kampsis to climb up the supports, the air roots-suckers and the twisting ends of the shoots.
Large red scarlet or orange flowers and sprawling branches with large leaves give the plant its beauty. Camppsis flowers are odorless, but contain a lot of nectar, attracting a lot of flying insects and ants.
Kampsis is a perennial perennial plant for which the ideal conditions are sun, heat and the absence of drafts. Campsis belongs to the genus of woody vignets of the bignonia family, therefore it is also called bignonia, and there is another name - tecom.
Despite its southern origin, the campsis was liked by gardeners of the Middle Strip who successfully grow it in their garden plots, enjoying flowering from June to September.
Campsis is not too picky about the soil, but it demonstrates better decorativeness on loose fertile soil. The plant feels very good on the south side of the building, for example, for planting a campsite, the south side of the house is suitable, which gives additional heat to the plant from the wall heated in the sun.

Given that kampsis provides many root shoots, it is advisable to enclose the space reserved for this plant with slate or sheet iron, by digging them into the ground to a depth of 70 cm.
A pit for planting a seedling needs to be dug about half a meter from the wall of the building and it is best to do this in advance, in the fall. The size of the pit should be approximately two times larger than the lump of the seedling with a closed root system.
Seedlings are planted in spring, in the second half of May, when all spring frosts pass. The empty space in the pit is filled with excavated soil mixed with organic and mineral fertilizers.

For drainage, sand or gravel should be poured into the bottom of the pit. The seedling in the pit is placed at an angle to the wall and tied to a trellis. Next, the plant is watered, and the trunk circle is mulched with compost or peat.
Bignonia can also be grown by seeds, which are planted in moist soil in March, constantly keeping the soil moist. The first shoots appear after 3-4 weeks, after which the box with seedlings is exposed to the sun.
At the end of May, when several leaves appear, the plant is transplanted into the open ground or continues to be grown at home: in the room or on the balcony, adjusting the size of the plant by cropping.
The method of growing tecoma seeds is not very popular, since the plant begins to bloom only after a few years (usually after 5 - 7 years).
The fastest and most effective way to propagate campsis with the help of shoots of rhizomes that grow around plants. Root processes along with the root are separated from the main rhizome and planted in a permanent place.

It is easy to grow campsis, because the plant does not require any special conditions for growth. Since it is thermophilic, it needs sun and moisture, and the plant does not like waterlogging and stagnation of water.
In the middle lane in winter, the plant needs to be covered with non-woven material, spruce branches and sprinkled with snow. At the end of the season, it is necessary to cut off faded shoots for 3-4 eyes. This will improve flowering next year. Bignonia can sometimes be affected by aphids. In this case, the plant is treated with a solution of laundry soap.
There are two species and one hybrid in the campus genus:
The name of the species itself speaks of the properties of these plants. The hybrid is called "Campsis tagliabuan" and is positioned as a separate species of this plant. It combines the properties of both species. The most famous and lush-flowering variety of this hybrid is "Madame Galen" with orange-red flowers.
Kampsis is a blooming deciduous liana that quickly greens a wall of a house, a trellis or a pergola, with its help you can create a thick green wall and divide the space of the garden.
Video: Campsis - flowering deciduous liana
Camppsis (lat. Campsis) is a genus of woody vines of the Bignoniaceae family. The genus name has Greek etymology and literally means “kamptein” - to bend, twist or bend, in the shape of a long winding trunk.
Campsis has been known in culture since the 17th century. Representatives of this genus are also called Tecoma, or Tecomaria, but Tecoma (syn. Tecomaria) is a separate, albeit similar, genus of plants from the tribe Tecomeae of the same Bignoniaceae family.
Perennial deciduous woody vines up to 12 meters long, sometimes branching. Campsis, as a rule, rises along trees, shrubs, poles, using aerial roots, in the absence of vertical support, the plant stretches over the whole earth. Young shoots are greenish-brown, with time become woody and darken.
Pairs of opposite odd-leafed leaves grow along the entire length of the vine, consist of 7-11 separate ovoid or elliptic petiolate leaves with roughly serrated edges, their upper surface is shiny and glabrous, and the lower is often pubescent along the main veins.
Inflorescences of 2-8 large (up to 8 cm) flowers of elongated funnel shape are located on the tops of the shoots of the current year. The corolla is elongated, funnel-shaped, reddish veins stretch along its inner surface, which play the role of a conductor of insects to nectar. The leathery five-lobed calyx is much smaller than the corolla. The flowering period falls in the summer and lasts for 2 months.
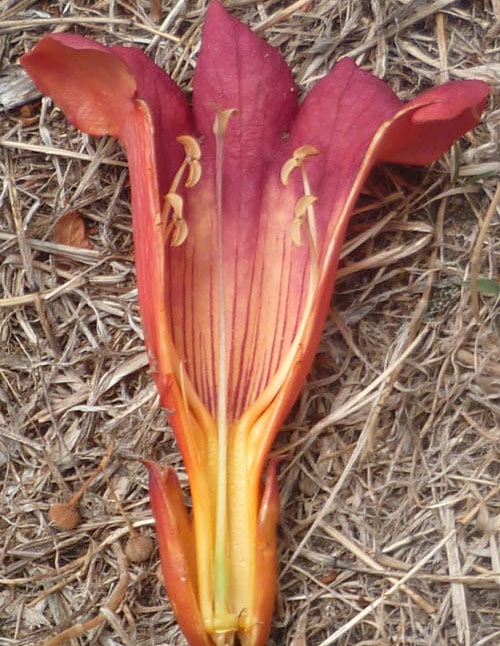

Campsis flower structure
The abundance of colors varies depending on the species. Each flower is replaced by an elongated seed box of a pod-shaped shape up to 15 cm long, which after ripening breaks up into two lobes and releases flat seeds with webbed wings.
The genus Campsis is represented by only two species and their hybrid, which is classified as a separate species.
K. rooted (lat. C. radicans) - grows in southeastern North America and on the Gulf of Mexico along fences and on the outskirts of forests. These are fast-growing deciduous tree creepers. Aerial roots spaced along the stem help the campsis gain a foothold on any vertical surface, so the plant does not need special support. After the liana rises to a certain height, it grows horizontally.
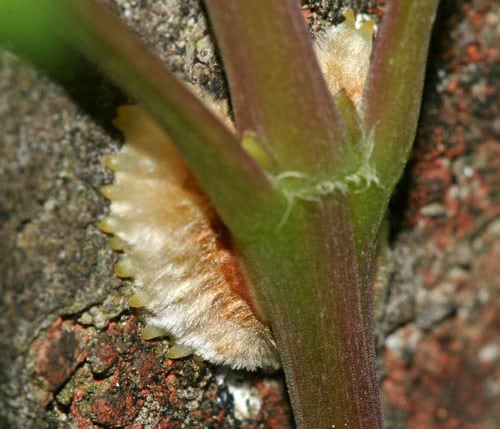

Aerial roots of the campis root
Along the entire length of the trunk, cirrus leaves 10-30 cm in length grow oppositely, which cover the vine with a dense bright green veil. They consist of 7-15 oval leaflets with serrated edges 2-6 cm long, dark green and bare above, lighter and diffusely hairy below, often only along the middle vein
Bright brushes from yellow-orange to red shade of funnel-shaped flowers appear in mid-summer (earlier - in the southern regions) and consistently bloom until early autumn. Thus, the buds, tubular flowers, and then the seed boxes are on the vine simultaneously.
The following cultivars of the rooted kampsis are widely popular in culture:
![]()
Campsis rooted
K. large-flowered or Chinese (lat. C. grandiflora) is a highly decorative species that grows in nature in the eastern and southeastern parts of China and Japan. As a rule, lianas of this species reach 10 m and have attractive, large-toothed, composed of small leaves, cirrus, medium to dark green leaves. Aerial roots are rare for plants of this species, more often the ends of the shoots cover the support for growing up.
Against the dense background of dark foliage during flowering, campsis literally flares up with a carpet of large (up to 8 cm) reddish-orange flowers with a hint of yellow and salmon. Flowering lasts a month, then a small number of flowers remain on the vine and oblong seed bolls are formed, which split when ripened in half and release numerous winged seeds downwind.

Campsis large-flowered, or Chinese (C. grandiflora)
K. hybrid or Taglibuan (Latin C. x hybrida \u003d C. tagliabuana) - interspecific hybrid of C. radians x C. grandiflora, bred in the middle of the 19th century. Shrub liana with funnel-shaped orange, salmon or red large (up to 7 cm) flowers, collected in loose panicles and blooming almost throughout the summer, has aerial roots, with which it clings to the surface. They grow quickly and reach up to 7-8 meters. It blooms later than other species - starting in August.
Campsis is photophilous, although it also tolerates partial shade. In the middle zone of the country, it is best to plant it on the south side of buildings, this will provide not only the desired illumination, but also the maximum possible air temperature for full development.
Important. Planting the campusis too close to the house can lead to damage to the foundation by creeping roots, so it is important to maintain a certain distance from the building.

Campsis hybrid (C. tagliabuana)
A trellis, fence or gazebo are great as a support structure for growing campsite and caring for it, and trees can be strangled with a vine. For young plants, it is recommended to use removable supports made of synthetic ropes or wire, so that in winter they can be laid on the ground under cover with a vine, without tearing off the roots.
The campsis plant is able to adapt to any soil, but prefers drained, does not tolerate waterlogging and stagnation of water.

Camppsis can also be grown as a standard tree
When growing campsis, an important factor is the containment of fast-growing shoots. To initially form a plant, before the growing season, all shoots should be broken off from the already rooted cuttings, except for the 2-4 strongest ones, which will subsequently become woody and form the basis of the campsis. After landing in open ground, this skeleton, having reached about 3 meters, will confidently winter, even if the annual shoots are frozen. Since flowers are formed on the shoots of the current year, this will not hinder flowering, just like forming pruning in early spring.
If the vine is grown over a sufficiently large area where aerial roots are available for regular pruning, it can be grown without support and shaped like a bush.
Campsis grows very energetically, watering and top dressing is required only when necessary, fertile soil leads to a strong growth of an already energetic plant.
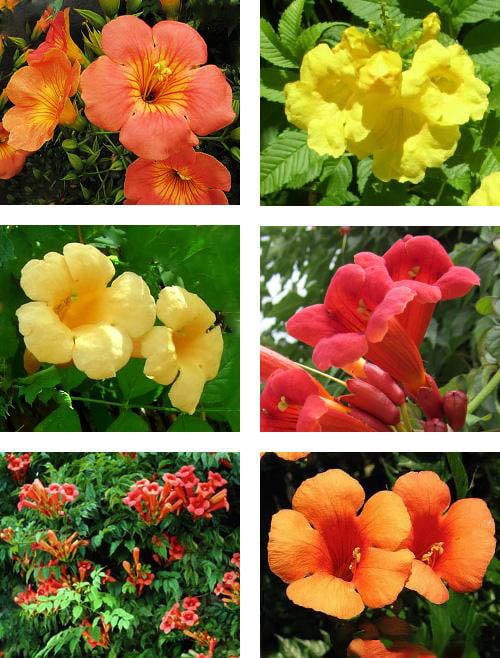

Various colors of campsite flowers
Campsis propagation easily occurs by cuttings or layering, flowering in these cases occurs for 2-3 years. Kampsis cultivation from seeds is less effective, seedlings bloom only after 6-7 years.
Campsis is resistant to disease, rarely damaged by pests. Sometimes he is worried about a typical thunderstorm of gardens - aphids, at the first signs of damage, insecticides should be treated.

Campsis on decorative vertical supports
Spectacular creepers with cirrus leaves giving the plant a general openwork look and bright exotic flowers will be an adornment to decorate the walls of houses, terraces, hedges. They do not require special supports and confidently climb on any surface, clinging to it with air roots. Without support, they grow on the ground and can be used as ground cover plants.
Campsis should not be used for landscaping painted arbors, because aerial roots secrete an adhesive substance that can almost certainly spoil the paint.

Campsis in the landscape
Unusual flowers are used for cutting, but it should be remembered that they are attractive to many insects that can hide in the depths of the flower tube.
Campsis is an undeservedly rare guest in the gardens, although due to long flowering and fairly simple maintenance, it is quite capable of taking a leading position in vertical gardening.
A large, abundantly flowering bush in a garden of amazing beauty is the campsis ( Campsis) We will consider landing and caring for this marvelous giant with elegant spreading branches reaching 15 m in support in this article.
The choice of place. The plant gained popularity due to splendor and unpretentiousness. Any kind of soil is suitable for it, but it will grow better in loose, fertile, non-moistened soils with a neutral pH level. Campsis is a southern plant that requires a sunny spot on the south side of the site. Over time, it develops powerful roots, from which multiple shoots grow.
So that the bush does not capture more than the territory allotted for it, plant it on an asphalt plot, in a specially designated place for plants or protect the rhizome with metal sheets to a depth of 80 cm.Do not place it near the window because insects are actively flying to the campsis.
Landing In the spring, after all the frosts, seedlings with sprouted buds can be planted in the ground. It is advisable to prepare a hole for planting 50 × 60 cm in size from the fall, add phosphorus and potassium fertilizers in an amount of 500 g and compost 5 to 10 kg. At the bottom of the pit, pour sand and gravel 15 - 20 cm for drainage, and pour soil on top of the hill. Place a seedling in the pit, straighten the roots, cover with earth and condense. After that, pour and mulch peat. Initially, seedlings need tying and support.
Campsis can be grown from seeds. Sowing of seeds is carried out at the beginning of March in boxes with loose earth 3-4 mm deep. The soil in the box is watered as the surface dries. When the seeds sprout, rearrange the box on the windowsill on the sunny side. In a phase of 5-6 leaves, seedlings are planted in the ground. However, flowering will occur only at 7 - 8 year.
If severe winters prevent the bush from growing on the street, then with the help of forming pruning it can grow in a house or apartment in the form of a houseplant.

Campsis radicans "Atropurpurea"
Watering. Drought-resistant, but in order for the plant to maintain its decorativeness and abundant flowering, regular watering is required. Next to it, you can plant perennial bushes to preserve soil moisture and shelter bare vines below.
The plant does not tolerate excessive watering - the roots begin to rot and it dies.
Campsis can withstand only short-term adverse conditions.
Pruning. Vines quickly grow and stretch in height along the support. You can control their growth using pruning, which is carried out at the end of the growing season and is necessary to enhance flowering in the next year.
For the formation of the skeleton, 2 to 3 of the tallest shoots are selected, the rest are removed. During the growing season they are sent along trellises, tied up. The actions are repeated until the shoots close the entire surface allocated to them. The formation of the skeletal system takes at least three years.
Strong pruning of the formed plant is done every year. Only lignified skeletal branches are left, formed from perennial shoots and 3-4 new shoots cut to 2-3 buds.
To maintain an elegant look throughout the season, wilted inflorescences remove and shorten faded shoots by 3-4 buds.
Extra shoots near the bush are dug up or cut off with a reinforced secateurs.
To stimulate the growth of new strong shoots, rejuvenation is performed. For this, all shoots are cut to 30 cm above the ground.
Top dressing. Liana grows excellently and without fertilizing. The introduction of nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizers enhance the duration of rich flowering.
Pests and diseases. Campsis is very resistant to disease. But, in moments of drought and prolonged heat, aphids can attack him. To combat aphids, spray the foliage with a solution of laundry soap.
Shelter for the winter. The plant is thermophilic, and we often have severe winters with severe frosts.
Harboring campsis for the winter is a must!
They remove the creeper, cover it with fir spruce branches, cover it with dry foliage, cover it with polyethylene. In winter, a large snowdrift is made at the shelter site.
Some gardeners lay lianas between sheets of polystyrene foam and wrap dense acrylic on top.
Without shelter, the plant can withstand only a short-term frost up to -20С, but, as a rule, it freezes.
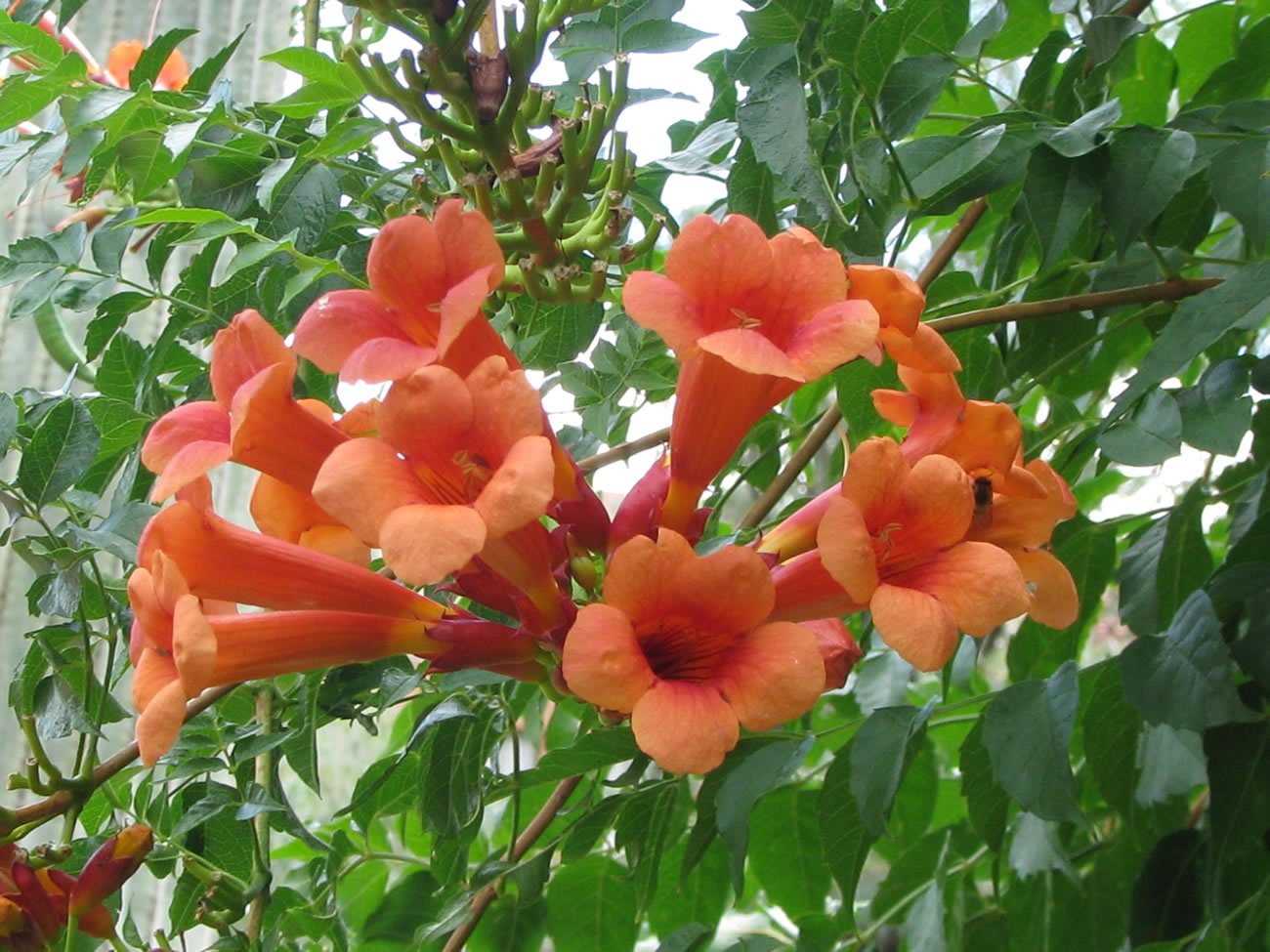

Campsis is used as a living, green hedge when decorating trellised fences, walls of houses and arbors. Lianas gracefully encircle pergolas and long arches that adorn the entrance to the garden or make a passage between the buildings in the courtyard, and if you put a bench under such an arch, you will get a cozy place to relax.
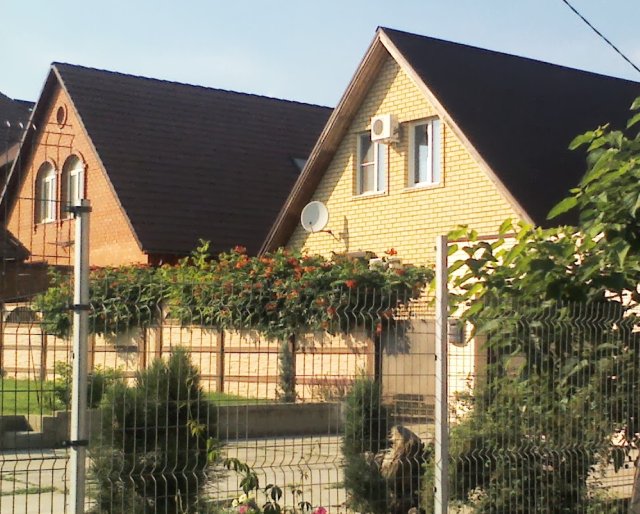

With the help of a competent forming haircut, they get a small flowering tree in the form of a ball, a pyramid or a bizarre shape.
Campsis is a magnificent garden decoration that creates a pleasant cool shadow. All summer until late autumn, it will delight with splendor and flowering, without requiring special labor in return.
Tatyana Salomatina
2014,. All rights reserved.