For digital control of voltage and current in the power supply, it is not necessary to ...


Ventilation in a private house is an indispensable component for maintaining a comfortable microclimate in residential premises. However, along with its positive properties, it is often the main source of heat loss. How to insulate a ventilation pipe in a private house, and what is the best way to use it?
During operation, a small layer of ice can often be observed on the surface of the ventilation pipe. Its appearance is due to the temperature difference between the material of manufacture and the air leaving the residential building. This results in the formation of moisture and the appearance of frost and ice.
Vent pipe icing
If this process is left to chance, then a number of negative factors may appear as a result. They will directly affect not only the integrity and functionality, but can also affect the performance of the entire building. The reason for this is the condensate that forms on the inner wall of the pipe. Its constant presence can lead to the following consequences:
The issue of insulation of the ventilation pipe is recommended to be addressed at the stage of building construction. However, this is not always possible. It is often necessary to install a thermal insulation layer on an already functioning system.

Insulation for ventilation
First of all, it is necessary to choose the right thermal insulation. It should have a number of properties that will subsequently affect the performance of the ventilation system. You also need to take into account the cost of materials and the complexity of installation.
The priority when choosing is the degree of thermal insulation. The main purpose of the insulation is to bring the temperature on the surface of the pipe as close as possible to the degree of heating of the warm air leaving the house. This is the only way to get rid of the appearance of condensate. To do this, you can use a number of materials:

One of the parameters for choosing a certain type of heat insulator is the thickness of the material. For medium-sized regions of Russia, it is enough to install thermal insulation with a thickness of 20 to 50 mm. The lower the temperature in winter, the greater the layer of insulation must be mounted on the ventilation system.
The method of installation of insulation directly depends on the selected material. Scotch tape is used to fasten basalt wool. When installing a ready-made foam shell, special attention is paid to sealing the connecting seams.

It is not necessary to mount a heat insulator on the entire ventilation system. It is important to ensure the proper level of protection against the effects of negative temperatures in certain sections of the pipeline:
In all other cases, the installation of insulation is not required. It is important to periodically check the possible presence of condensation on the inner surface. If it appears even after sealing the air ducts, an additional layer of insulation will be needed.
Few people doubt the need for installation of ventilation systems. But many young owners are perplexed why it is necessary to insulate ventilation pipes in the attic or in other unheated rooms, because this is not plumbing or heating, there seems to be nothing to freeze there.
However, if you leave this issue without due attention, serious problems may “emerge” over time. In this material, I will try to explain the meaning of such insulation and tell you how and with what you can insulate ventilation ducts with your own hands, without the involvement of specialists.
The main enemy of any ventilation system is condensate, which is actively formed when warm and cold flows collide. In addition to the competent layout of the system itself, insulated pipes for ventilation are one of the main means of preventing moisture loss. And what is terrible about this very condensate in the ventilation system, I will tell further.
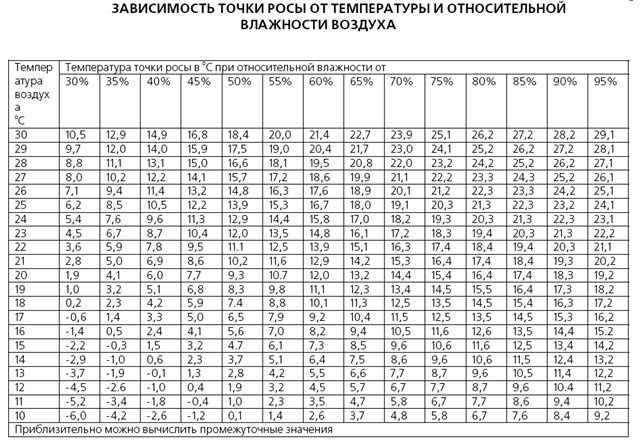
Actually, the insulation itself is necessary to prevent the conditions for the occurrence of the so-called dew point. According to the building code SP-50.1333-2012, this term refers to the temperature at which the water vapor contained in the air falls out in the form of water on surrounding objects, that is, it condenses. Naturally, the dew point directly depends on the humidity of the air, the higher it is, the closer the dew point is to the ambient temperature.


Now weigh the pros and cons and decide for yourself whether it is necessary to insulate the ventilation pipes in your house. I think the answer is obvious and further we will dwell in detail on common materials and methods for their installation.
Installation of a ventilation pipe through a side wall is not so common and in most cases it is not pure domestic ventilation, but a chimney for a heating boiler, but in any case, thermal insulation on such air ducts is equipped, starting from a warm room or boiler and up to a deflector at the end of the pipe .
As a rule, this is a heat-resistant cocoon made in the factory. As for the arrangement of ventilation insulation with your own hands, this type of work is more relevant for attic spaces.
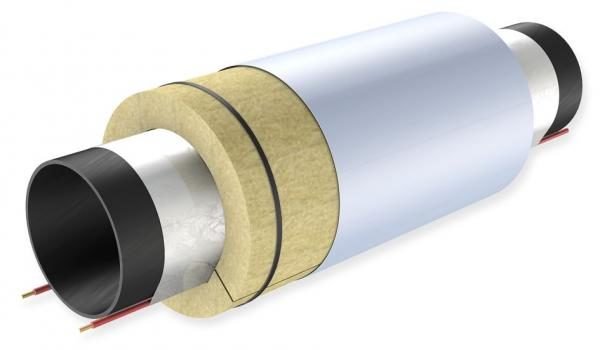
From the mass of various modern thermal insulation materials, I have chosen several of the most common options. In general, when choosing, you need to be guided by three main criteria:
Glass wool can be safely called the patriarch of domestic insulation. There are no complaints about the level of thermal insulation here. As for fire safety, even the most meticulous inspector will not be able to find fault with it. The price of this material will also please you, it is one of the lowest among competitors. On the market, this material is presented in the form of soft mats of various types.


With mineral wool, not everything is so sad, it is a newer and more perfect representative of this direction. Such mats are dense, durable and resistant to external influences.
They combined everything positive characteristics glass wool. It is easier to work with mineral wool, overalls are no longer needed here. Although this material is still afraid of moisture.
Thermal insulation of high-temperature surfaces (for example, chimneys) is carried out just with the help of heaters from the line of mineral materials.

Now let's move on to the question of installation. As I said, this is not particularly difficult. Soft glass wool is more suitable for curved and round surfaces. This "blanket" wraps the ventilation pipe. But you can’t leave glass wool like that, you need to additionally wrap it with a layer of technical foil or, in extreme cases, roofing material.
And in order for this whole “pie” to hold securely, it must be fixed from above with some kind of bandage. As a bandage, you can use a metal or synthetic packing tape, but it is cheaper and easiest to fix such a cocoon with annealed steel wire, which is used for knitting reinforcement.

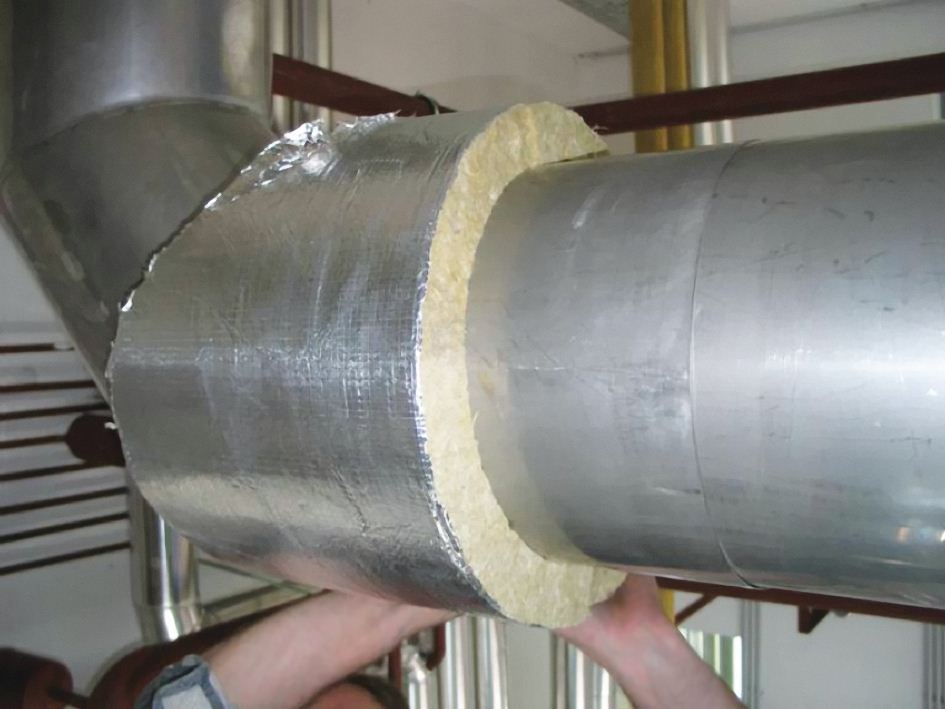
Mineral wool boards are denser than glass wool and are more suitable for insulating straight and flat surfaces. This is an almost ideal option for arranging thermal insulation of rectangular and square ventilation ducts.
You just need to cut such a regular plate into segments of the desired size, cover the box with them, then wrap it with foil and fix it with bandages. It will be easier to work if you first degrease the pipe with an alcohol-containing solution and plant mineral plates on liquid nails.
These two types of insulation have fairly high thermal insulation characteristics. They are durable and absolutely not afraid of moisture. But both of these materials are rigid, you can’t wrap anything with them. Therefore, for complex surfaces this option hardly suitable.
In terms of fire safety, they are exactly the same. Both polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene melt easily and burn well, and during combustion they release harmful and toxic compounds. So it is impossible to mount them in fire hazardous places or on hot pipes.
As for the differences between polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam, both of these heaters have the same basis. But Styrofoam is less dense, therefore, not as strong and rigid as Styrofoam. Although polystyrene has one indisputable and important advantage, its price is an order of magnitude lower than that of a competitor.
I believe that if you need inexpensive insulation for attic ventilation pipes, then foam is a decent and quite acceptable option. Expanded polystyrene is certainly strong, but in the attic this strength does not play any role, and why pay more if there is practically no point in it.

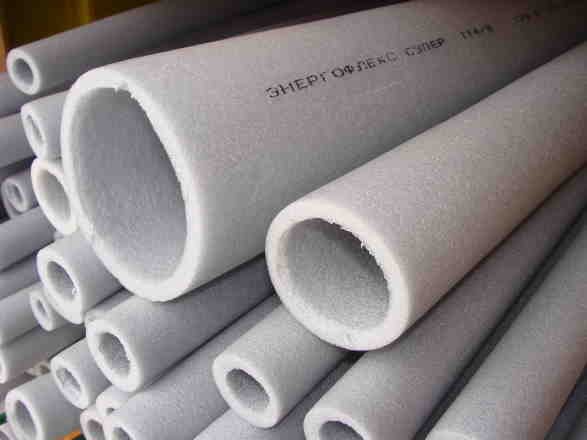
Do-it-yourself foam insulation of a pipe for ventilation is even easier to equip. For round pipes, ready-made cocoons are sold. These segments consist of two or four semicircular sectors, which are interconnected according to the tenon-groove principle. They can be covered with foil or go without it; in a dry attic, this does not really matter. The segments on the pipe are stacked with a shift according to the principle of brickwork.
You only need to tightly connect them together and tighten with a bandage. Although in this case I prefer to use liquid nails or any other glue for mounting. Styrofoam insulation of square and rectangular ventilation ducts is carried out according to the same scheme as the installation of mineral mats.
If you are looking for the easiest and cheap way ventilation insulation, then polyethylene foam is just for you, in some sources this material is called penofol. In appearance, it is similar to ordinary foam rubber, but with a larger structure. On the market, you have probably seen such gray foam tubes of different diameters, so this is one of the options for such a heater.

You select a "wrap" of the appropriate diameter for your pipe. Each such braid is already cut along, so it will be easy to put it on the pipe. In order for the penofol to hold, it needs to be wrapped with tape in several places and that's it.
In addition, penofol is sold in the form of a wide canvas up to 10 mm thick. Such a “blanket” can wrap any non-standard part of the ventilation duct and fix it with construction or ordinary tape at the end. The same canvas can be covered with foil. This material is more expensive, but the thermal insulation effect is much higher.

Recently, another model of polyethylene foam has appeared on the market. It works well for ventilation.
Such a canvas differs from existing options by the presence of a self-adhesive surface on one of the sides. The instruction is elementary, I removed the protective film and pasted it on the ventilation pipe or box. If a thick coating is required, penofol is wrapped in several layers.
On the this moment insulation of attic floors with the help of special construction foam is widespread. Pleasure is certainly not cheap, but the effect is very worthy. It is possible to insulate ventilation pipes in this way, but it is better to entrust it to professionals. Because there, in addition to the foam itself, special equipment is needed, plus strict adherence to technology.

And you don’t need to try to “blow out” the surface of the duct with ordinary mounting foam, apart from the high cost of this project, polyurethane foam in the open air will stand for a maximum of a year, after which it will begin to crumble. After all, this convenient building material is intended for several other purposes.
And it’s absolutely not worth wrapping the ventilation pipes with old rags and cotton mattresses. Ordinary fabric or cotton wool will gradually be saturated with moisture and there will be practically no sense from this undertaking, except that the external condensate will be absorbed into these rags.
As you can see, self-insulation of ventilation pipes, both in the attic and in any other room, is not something transcendental. And if desired, a good owner will be able to cope with this task. The photo and video in this article shows the installation options for such insulation. If you have something to add or have questions, write in the comments, I will try to help.

If you want to express gratitude, add a clarification or objection, ask the author something - add a comment or say thanks!
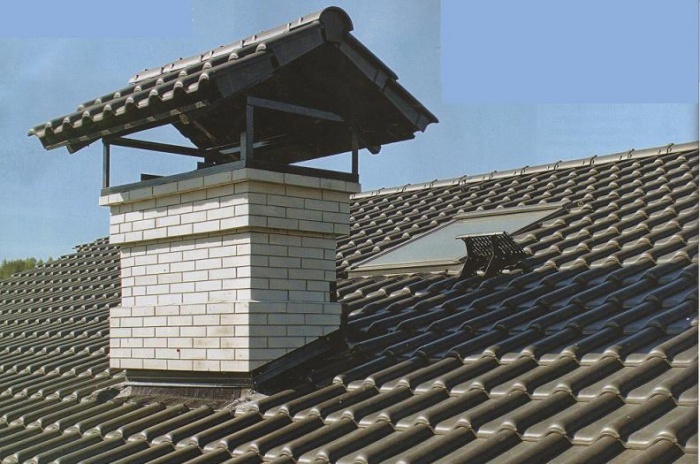
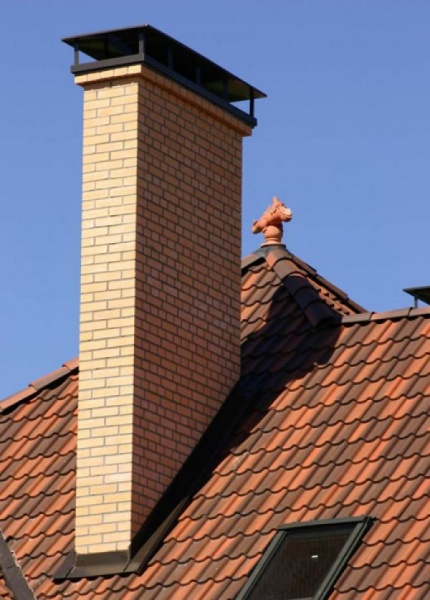
Special attention is paid to the arrangement of high-quality thermal insulation of external and internal surfaces of residential buildings. At the same time, thermal insulation of ventilation pipes and chimneys is carried out only in exceptional cases. Do I need to insulate the ventilation pipe on the roof? This question is of interest to the owners of private households, where an autonomous heating system for the house is provided, there is a chimney and forced ventilation.
Professional builders claim that as a result of a decrease in the thermal conductivity of chimneys, ventilation pipes significantly increase their lifespan. It will not be difficult to carry out all the construction processes associated with the insulation of chimney ventilation pipes on your own. This does not require any special knowledge of skills, it is enough just to choose the right quality material, make a little effort.
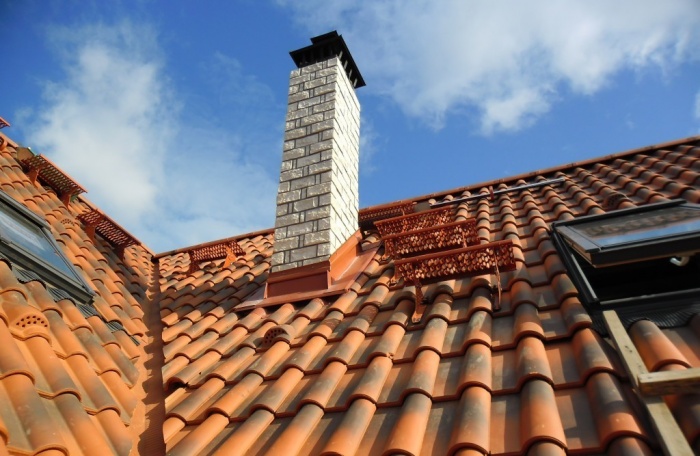

The main negative factors that affect the life of a brick chimney pipe are smoke or moisture. This is especially evident in the cold period of time, when there is a sharp drop in temperature regimes.
The condensate that protrudes on the walls of the pipe tightly clogs all the surfaces of the brick chimney that have small cracks. The consequence of a sharp drop in temperature is the freezing of moisture, the formation of ice. As you know, water expands when freezing, so there is pressure from the inside on the structural material of the masonry. Experiencing a constant negative impact, the chimney collapses.
In addition, there is another danger. The consequence of fuel combustion is a number of oxides, on their basis solutions of sulfuric or carbonic acid are obtained. Combustion waste, together with condensate, settles on the walls of the chimney pipe, destroying bricks and metal surfaces.
Benefits of an insulated chimney:
Do I need to insulate the ventilation pipe? Definitely needed! The design insulated with a special material looks more attractive, it is easier to care for it.

Manufacturers offer a wide range of thermal insulation materials for ventilation pipes. Each type has certain features and advantages. When choosing the most suitable thermal insulation option, the following conditions must be taken into account:
The most commonly used are broken bricks, glass wool, fibrous insulation, cinder block slabs.
Fiberglass and mineral wool are fireproof. This quality completely eliminates the possibility of self-ignition of the material. In addition, the thermal insulation does not emit substances harmful to human life, perfectly tolerates the aggressive influence of the atmospheric environment.
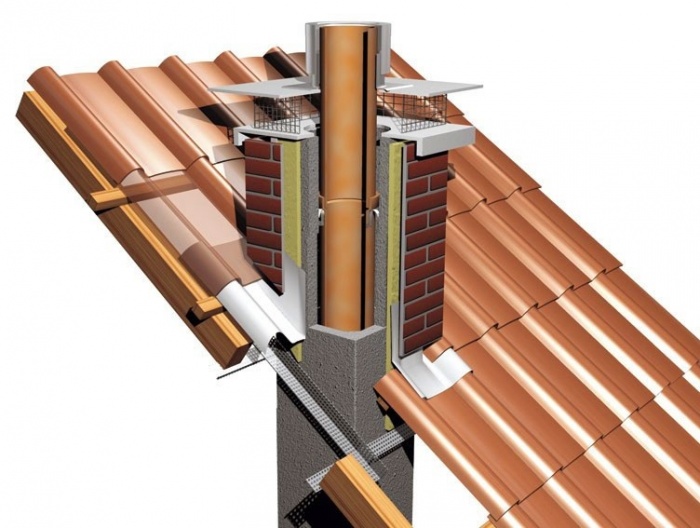

Today, there are several options for insulating a pipe on a roof.
The most common method of arranging a chimney is carried out using glass wool or mineral wool, preference should be given to materials produced in the form of plates. In the process of work, the high vapor permeability of thermal insulation should be taken into account. Pipe insulation based on fibrous materials has a limited service life, it is necessary to equip a protective hydrocoating.
If the chimney to be insulated is made of brick, the pipe surfaces can be plastered. For this, a special slag-lime mixture is used. In the process of further operation, it is necessary to regularly inspect, if necessary, repair the plastered surfaces of the pipe. Otherwise, burning soot can get into the formed depressions or cracks from the chimney. From this, ceilings and roofs will suffer. One of the main advantages of this method is the relatively low cost of insulation material, ease of installation.
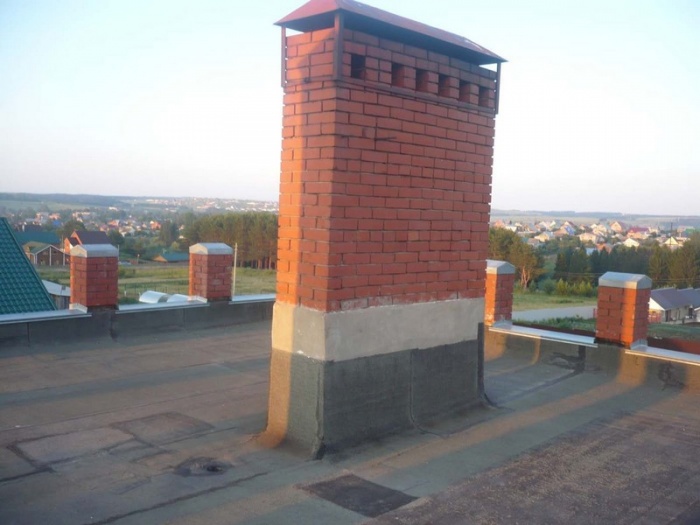

How to insulate an asbestos pipe on a roof? One of the most reliable methods of thermal insulation is the use of broken brick chips or granular backfill. The created layer retains heat well, prevents the formation of condensate products. The material is inexpensive, but additional waterproofing is needed. In addition, you will need to create a solid frame.
After a suitable insulation material has been selected, you can begin to carry out work on the thermal insulation of the chimney.
Attention! Any type of chimney insulation must be carried out taking into account all building codes and requirements.
When creating thermal insulation of the pipe, the necessary indentation (about 5 cm) should be left between the brick chimney and the insulating material. The segment of insulation material must be laid so that it takes about 40 cm on the roof of the attic. Care should be taken to ensure that all existing joints are tightly sealed. For insulation work, special adhesives with refractory properties, adhesive tape are used.
![]()
High-quality insulation of the outer surfaces of a brick chimney is carried out according to a certain scheme:
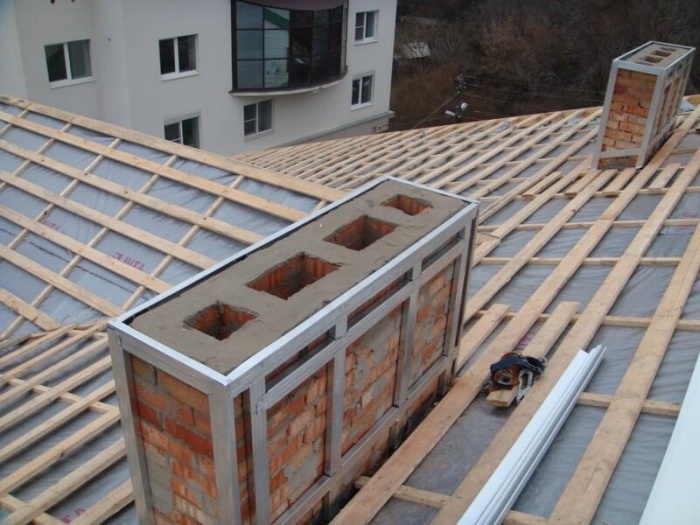

Upon completion of all construction work, the thermal insulation cake is decorated with a facing material, which is both protection from external negative influences and an excellent decorative element.

It should be noted that in the absence of the necessary experience, it is better to entrust all work related to the insulation of chimneys and ventilation pipes to professionals. But if you are completely confident in your abilities, then you can carry out the insulation yourself. The main thing is to do everything carefully, do not leave gaps on the pipe, otherwise all the work will be in vain. It is from the consistent and correct implementation of all processes that the life and quality of the chimney depends.
It happens that a newly created ventilation system in a private house in the summer works flawlessly, pleases with efficiency and presentability. However, with the advent of winter, the homeowner suddenly discovers that a small amount of frost appears on the outside of the air duct. It is not difficult to guess that this is a signal for action, otherwise, after a relatively short period of time, the pipe will begin to collapse. As a result, it will take serious material resource. And, if you react in time, then you just need to buy a heater for ventilation, which you can fix without much effort yourself.
The appearance of frost and ice on the outer surfaces of the ventilation pipe indicates that condensate accumulates inside the duct, which is fraught with:
In a word, the poor state of ventilation in winter will lead to wear and tear the entire building. Moisture on the walls of the ventilation passages will form the more, the greater the difference between the temperature indicators of the air flows moving through the pipes and the air outside (on the street). Hence the positive answer to the question, is it necessary to insulate the ventilation exhaust pipe in a private house?
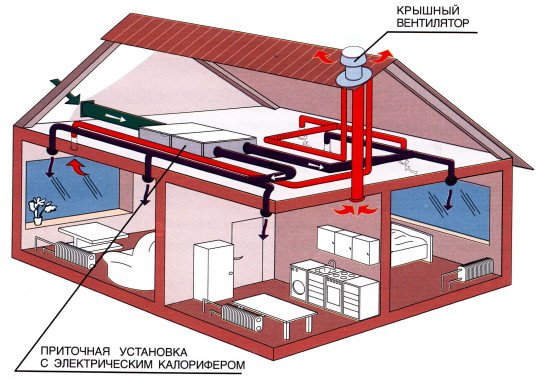
The ventilation “set” includes a list of equipment for supplying and removing air flows that maintain the required microclimate characteristics inside the premises. This also includes air ducts: transport air "arteries" passing from the side of the street and indoors.
In order for the air channels to have the necessary strength indicator, the necessary cross-country ability, their proper insulation is required. For this, norms are adopted that ensure sanitary and epidemiological stability in residential buildings. Do not neglect the requirements of building rules and regulations in terms of heating, organization of ventilation and air conditioning, as well as the use of thermal insulation and protection of buildings from heat losses.
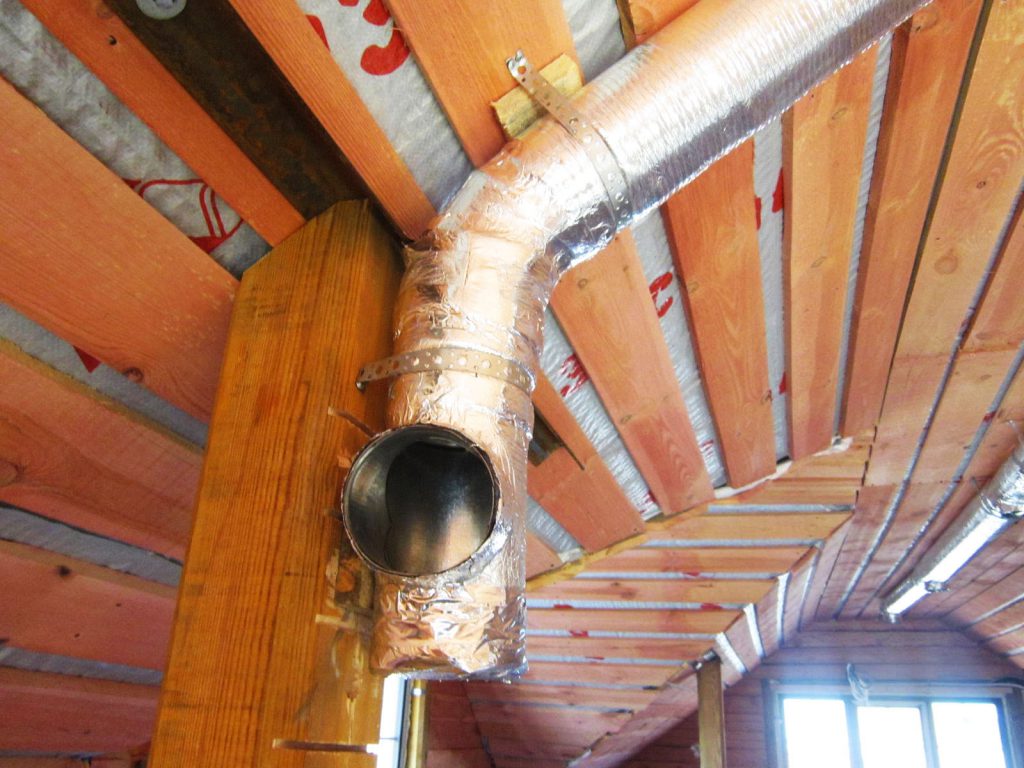

Insulation of ventilation in a private house solves the following tasks in a complex:
You need to know how and how to insulate pipes for ventilation. When choosing, the advantage is given to the thermal resistance of the material. The main role of the insulation is to bring the temperature on the surface of the pipe to the maximum amount of air leaving it. In this way, condensation can be avoided. For this purpose, materials based on mineral fiber (stone and mineral wool, fiberglass), foam elastomers, and polyacrylates are used: polystyrene - a product of styrene polymerization, polyurethane, etc.
Insulation based on metal and glass threads obtained from inorganic components is supplied to the trade network in the form of plates or rigid (semi-rigid) rolled materials. The choice is simplified by a wide range of heaters with different densities, prices and thermal insulation characteristics. The indisputable advantage of mineral wool insulation is its resistance to decay and fire resistance.
Attention! If you do not know how to insulate the ventilation pipe in the attic, especially if it is not heated, use special sections of mineral wool for external cladding specifically for pipes. At the same time, the inner surfaces of the sleeves are insulated with fiberglass treated with a special impregnation.
Insulated pipes for ventilation are either lining from the inside or external insulation. Each method is characterized ambiguously.

Interior finish:
External pipe protection is easier to install, but also only in a vapor-tight version. At the same time, it is necessary to foresee how to insulate the ventilation exhaust pipe that rises above the living space, and what kind of hydraulic barrier to make. The outer protective shell should protect the exhaust structures from mechanical damage. An important requirement for insulation is incombustibility, because. when an open flame appears and contact with atmospheric oxygen, the degree of ignition of the insulation increases significantly. External insulation does not affect the size of the internal section of the ventilation duct and does not require its expansion. And pathogenic organisms (viruses, bacteria), which often occupy inside the walls of air ducts and, being in isolation, are protected from adverse conditions, do not take root in the insulation layer from the outside.
When isolating ventilation with a polystyrene shell, the following is carried out:
The structure (shell) is easily installed and dismantled in case of work with the pipe.

Works on insulation with foamed polyethylene in the form of a finished shell of a ventilation pipe are as follows:
Protection from fire-resistant polypropylene or polyurethane foam is performed as follows:
If the ventilation opening in the house is in the shape of a rectangle:
Thermal insulation for ventilation by any of these methods, with all the positive aspects, has one weak point - "cold bridges". It is important to prevent violations of the work technology and the prerequisites for their formation during the installation process. To do this, the joints between the ventilation ducts and the structures of the house are especially carefully isolated, otherwise the effect expected from the insulation will decrease.
Why is ventilation pipes insulated in the attic or above the roof level? What insulation for ventilation is better to use? Is it difficult to do this work with your own hands?
Let's try to figure it out.
The key word is condensation. Without insulation, it will inevitably form on the inner surface of the ventilation duct and flow down the inner walls, flowing through leaky joints into the main walls and ceilings. The consequences are obvious: dampness of walls and ceilings, the appearance of mold and their gradual destruction.
The effect of condensate on the ventilation duct itself depends on what material it is made of:
Another trouble associated with moisture condensation is the gradual freezing of frost on the inner walls of the ventilation duct outside a warm room. Within a few weeks of operation very coldy the pipe clearance can decrease from 100 - 150 millimeters to zero.
Where does the condensate come from?
There are two reasons for its appearance.
However: in industrial premises this item is relevant to a much lesser extent, however, insulation of exhaust ventilation is still required. Cause? See point number two.
In production, there is often a need for forced ventilation with a high air flow rate. In particular, to remove harmful volatile products of production, sawdust, shavings, etc.
The noise of the air and what it carries becomes a serious problem in some cases. In factory premises, ventilation insulation often aims not so much to combat condensate as to simply soundproof. The methods, however, apply the same.
Where exactly do you need insulation for ventilation pipes?
The simple answer to this question is obvious: where a sharp and significant cooling of the air flow is possible.
Ventilation is of particular note. Here, the possibility of moisture condensation on the outer walls of the supply ventilation duct depends on its length and location.
If necessary, these pipes can be insulated in the same way as exhaust pipes, however, the influx of cold air itself can create some discomfort; adjustable dampers for fresh air ventilation can even freeze.
One solution to this problem is an insulated valve for ventilation. Probably, a ventilation grill with a layer of thermal insulation arose in the reader's imagination? It wasn't there.
The insulated ventilation damper is a solution for large premises, primarily for offices, warehouses and production facilities. It really is an adjustable louvre that allows you to limit the air flow and ... if necessary, heat it up with tubular heaters.
Adjustment can be carried out manually - a system of traction and lever, or using a simple electric drive. The open area of the valve in a fully open state can be up to 3.5 m2, the power of heating elements is up to 8 kW.
The function of heating elements, however, is not to supply warm air into the room. With a valve area of 3.5 m2, 8 kilowatts of thermal energy is a drop in the ocean. Heating elements only warm up the valve flaps before changing their position in order to avoid icing and breakage.
In some cases, an accurate calculation is desirable: with a long ventilation length, the cost of insulation will be significant, and it is better to be sure of their necessity.
The key concept is the dew point. This is the temperature at which condensation begins to form in air with a certain relative humidity.
A simple measurement of the relative humidity of the air in the room and the surface temperature in different parts of the ventilation duct will give the exact boundaries of the zone that needs to be insulated.
Please note: it is still better to slightly shift the border of insulation towards a warm room.
Just in case of extremely strong and prolonged frosts.
And, finally, the cherished question: how to insulate the ventilation pipe? Let's arrange a short review of modern heaters that can be successfully used for ventilation ducts.
Let's start by formulating our wishes.
Disclaimer: we will leave outside of our attention the insulation of ventilation ducts from the inside.
The instruction for its use implies the complete dismantling of the ventilation duct, which is not always realistic; in addition, the effective ventilation cross section will be noticeably reduced.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
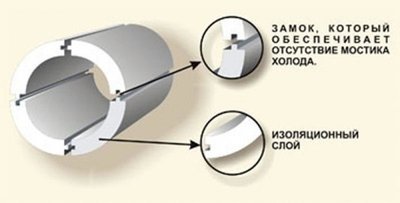
Some of the shortcomings are devoid of a ready-made solution based on mineral wool - an insulated corrugation for ventilation, which is a two-layer sleeve made of aluminum foil with steel wire reinforcement. However, it involves laying ventilation from scratch.
A ready-made detachable shell made of dense foam (polystyrene foam) is more convenient in many respects.
Advantages:
Useful: with a long length of the insulated ventilation duct, the shell halves are placed with mutual displacement, connecting with the next section of insulation.
Disadvantages:
The shell can be made not only from foam. The other two foamed plastics are similar in application to foam insulation.
Shell made of polyurethane foam.
On sale, this material can be found in the form of split tubes of various diameters. They are put on the ventilation pipe - and, in fact, the thermal insulation work is completed.
The material is cheap and is not afraid of moisture, moderate mechanical stress and rodents.
However, in cases where it is necessary to insulate ventilation in a cold climate zone, you can pay attention to two other types of insulation based on polyethylene foam.
The material is very convenient for the insulation of square or rectangular pipes.
The thickness of the insulation can reach 10 millimeters; if necessary, it can be laid on ventilation pipes in several layers.
Warm" width="640" height="360" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen">
Which insulation to choose - you decide. The author's sympathies are given to foil materials based on polyethylene foam, but this is more a matter of habit. In the presented video in this article you will find additional information on this topic.