DEGREES OF COMPARISON OF ADJECTIVES In English, as in Russian, ...


Twisted pair refers to cable systems with its own structure, used to transfer information in telecommunications networks. Connection to network devices is made by 8P8C connector. Consider the technical data of a twisted pair, taken into account in the formation of computer networks.
The great popularity of using twisted pair is due to the fact that it is combined with different types equipment, easy to install, low cost for networking. Crimping is done with special crimping pliers.
Twisting wires is done for a specific purpose. The interlacing of wires with a certain weaving pitch forms a pair of wires, with the help of which the communication quality is improved. Interference from electromagnetic waves have a uniform effect on the wires in a pair, reduce mutual interference during signal transmission, external factors during operation.
Twisted pair has different technical data. It depends on the category. It consists of many copper conductors that form a pair. Conductors can be insulated with PVC or polypropylene. High quality cables are equipped with Teflon or polyethylene insulation. Such insulation provides a guarantee of low dielectric losses, protects conductors from increased heating. Conductors can be from one or more strands that make up the bundle.
To make it convenient to cut the cable, the sheath provides kapron thread for a break. The outer shell is made of polyvinyl chloride, as well as fire-resistant polymers.
ng(A)—HF; ng(B)—HF; ng, HF; ng(D)—HF;
The outer shell is made of hydrophobic polyethylene. It is applied over the PVC sheath. The empty area in the cable is filled with hydrophobic helium, and can also be equipped with armor with a special tape.
The use of different colors is used to identify and designate the cable sheath. The black color indicates that the cable is protected from moisture, the orange cable has fire resistance. The light gray network cable is used inside offices, residential buildings.
Communication cables are multi-core and single-core, as well as with a shielded sheath and without a screen.
The single core network cable is used to run the line in the wall, it is not connected directly to the devices. Terminal equipment is connected to the cable, for example, a socket (termination). Such a cable has easily broken cores.
A twisted-pair cable with multiple cores is used for switching digital devices. Such a cable is suitable for bends, it has thin cores. A multi-core cable has a significant attenuation signal, so its maximum length should not exceed 100 m.

UTP- no screen.
FTP- foil screen.
STR– the screen of each pair and the common grid.
S/FTP– foil screen for couples and outer screen.
U/STR- there is no common screen, each pair with a screen.
SF/UTR– two external screens.
Twisted pair categories are divided into categories based on the frequency interval of the signal transmission. This is achieved by the number of turns. The higher the transmission frequency and the number of turns, the higher the category.
There has been a lot of progress in science lately, but many inventions were made as early as the 19th century. This can be attributed to twisted pair as well. Today, such a cable is widely used:
If we compare a coaxial cable and a twisted pair, then the twisted pair has the best protection of the data stream from interference, due to its structural features. This is especially noticeable at a distance of about 2 kilometers. The signal is crisp and clear, especially if a grounded wire with a shield is used. Such a wire is relevant in places with high electromagnetic radiation.
The line can simultaneously transmit several signals: sound, video, telemetry data. There is one limitation: the number of pairs in the cable. To avoid the influence of these pairs on each other in the cable, the stranding steps are made different. The more accurate the balancing is, the lower the negative impact of the pairs on each other will be.
The cost of installing and connecting a local area network of computers or video surveillance with different monitors and cameras is reduced, as less cable length is required. If the cable is laid over a distance of more than two kilometers, then the signal frequency is noticeably attenuated. Therefore, the network cable is more often used in short networks. It is better to choose a twisted-pair cable made of copper strands, rather than copper-clad steel.
Let's figure out how to crimp the twisted pair cable needed to connect computers to each other on a local network, or connect a TV to a hub, or another media device.
We have the cable, connectors and crimping tool you need to crimp the twisted pair itself. Consider how two different connectors are crimped. One is two-component, the other is single-component. The two-component connector consists of two parts, has an additional insert, which supposedly makes it easier to assemble the wires in the connector. The one-piece connector does not have any inserts.
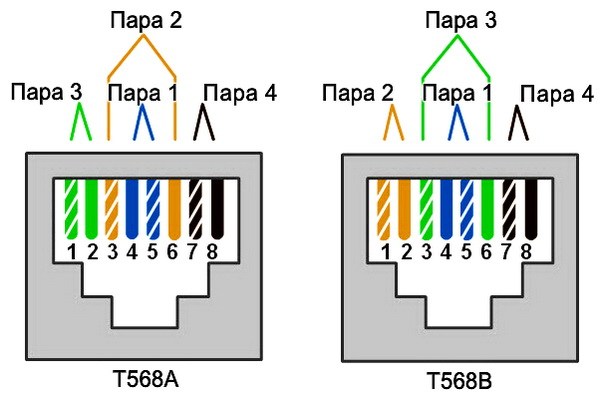
A twisted pair has four twisted pairs of eight conductors. This means that there are eight wires divided by color. Of these, every two wires are twisted together, thereby forming a twisted pair.
Category 5E cable is suitable for a home network. It is designed for indoor installation. There is a cheaper version of the cable, where instead of eight conductors there are only four wires. That is, there are only two twisted pairs in the cable.
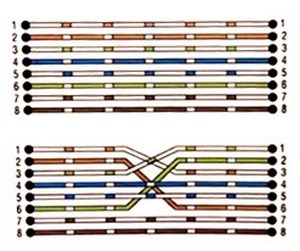
A direct connection is used to connect the computer to the hub and connect other devices to the hub. The second is used to connect two computers, or to connect a computer to a hub. It is recommended to crimp the cable according to the second option. If you connect a computer to a hub, then you can connect two computers with the same cable. You do not have to pinch the cable that was crimped in the first option.
The figure shows that some of the wires are crossed. This means that on one connector there is one numbering, on the second connector there will be a completely different numbering of the same wires.
There are standards for crimping wires by color. Only four wires are used for data transmission. These are 1, 2, 3, and 6 conductors. They are the most important wires. They cross as follows: the first - the third, the second - the sixth. The rest of the wires run in parallel.
Consider how the connector according to the second scheme. First we need to cut the end of the wire with a pair of pliers. For this they have a special knife.


We straighten the wires, and unwind the pairs, straighten the conductors. We distribute them by color, as shown in the figure. We level them so that they fit snugly against each other.

Once again, check the arrangement by color. Now we take crimping pliers and with the knife that they have, we cut off the conductors 1.5 cm long from the edge of the outer insulation.

After trimming, there is a smooth, neat edge. Now we take the connector. If the connector is turned towards you, then the first contact will be located on the right, and the eighth on the left. Now insert the conductors into the connector. At the same time we press them to the plane of the comb and to the lower wall of the connector.

There are special guides, each wire has its own guide channel. Insert to the end. Each posting should shine. This suggests that he rested against the plastic case and is inserted to the end.


Thus, the comb of contacts on the wires is clamped, and on the other hand, the insulation is clamped. This is a properly crimped RJ-45 connector, done right. Now it is almost impossible to remove it.

Now consider how a two-piece connector is crimped. We also clean the insulation, straighten the wires, straighten them. If the nylon thread, which is in isolation, interferes, then it can be cut off.
The first wire should not be white-orange, but white-green. All wire colors are dialed according to the above scheme. All operations are the same, just different colors. Another difference is that to facilitate the crimping of contacts, there is a plastic insert. She has a small ledge, which we place up. We cut exactly the wires, insert the wires into this insert.
The peculiarity of this connector is that there are difficulties with inserting wires into the insert. But it is convenient in that it holds the wire, keeps the order and numbering of the wires. Now we cut the wires again, make a smooth edge at a distance of 5 mm from the insert.

Now we also put on the connector, only it is not necessary to press the plastic.

We insert the wires with the insert to the end. Now we insert the connector with wires into the crimping pliers and also clamp.
![]()
Our connector is crimped. We received a small patch cord to connect two computers, or connect a computer to a hub.
Twisted pair (network cable) Definition of twisted pair, types of cables, description of design and categories, crimping schemes, installation. http://www.site/lan/vitaya-para-setevoi-kabel http://www.site/@@site-logo/logo.png
Definition of twisted pair, types of cables, description of design and categories, crimping schemes, installation.
Content
twisted pair (twisted pair) - a type of communication cable, is one or more pairs of insulated conductors twisted together (with a small number of turns per unit length), covered with a plastic sheath. The twisting of conductors is carried out in order to increase the connection of the conductors of one pair (electromagnetic interference equally affects both wires of the pair) and the subsequent reduction of electromagnetic interference from external sources, as well as mutual interference during the transmission of differential signals. To reduce the coupling of individual cable pairs (periodic convergence of conductors of different pairs), in UTP cables of category 5 and above, the wires of the pair are twisted with different pitches. Twisted pair is one of the components of modern structured cabling systems. Used in telecommunications and computer networks as a network carrier in many technologies such as Ethernet, ARCNet and Token ring. Currently, due to its low cost and ease of installation, it is the most common solution for building local networks.
The cable connects to network devices using an 8P8C connector (often erroneously referred to as RJ45 or RJ-45), slightly larger than an RJ11 telephone connector.
Depending on the presence of protection - electrically grounded copper braid or aluminum foil around twisted pairs, the types of this technology are determined:
Shielding provides better protection against electromagnetic interference, both external and internal, etc. The shield is connected along its entire length to an uninsulated drain wire, which consolidates the shield in case of division into sections due to excessive bending or stretching of the cable.
Depending on the structure of the conductors, the cable is used single-core and multi-core. In the first case, each wire consists of one copper core, and in the second - of several.
A single-core cable does not imply direct contacts with connected peripherals. That is, as a rule, it is used for laying in boxes, walls, etc., followed by termination with rosettes. This is due to the fact that copper conductors are quite thick and break quickly with frequent bends. However, for "cutting" into the connectors of the socket panels, such cores are the best suited.
In turn, a stranded cable does not tolerate “cutting” into socket panel connectors (thin cores are cut), but it behaves remarkably when bending and twisting. In addition, stranded wire has greater signal attenuation. Therefore, multi-core cable is mainly used for the manufacture of patch cords ( patch cord) connecting the periphery with sockets.
The cable usually consists of four pairs. Conductors in pairs are made of solid copper wire 0.5-0.65 mm thick. In addition to the metric system, the AWG system is used, in which these values are 24 or 22, respectively. The thickness of the insulation is about 0.2 mm, the material is usually polyvinyl chloride (English abbreviation PVC), for higher quality samples of category 5 - polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE). Particularly high-quality cables are insulated with expanded (cellular) polyethylene, which ensures low dielectric losses, or Teflon, which ensures a high operating temperature range.
Also inside the cable there is a so-called “breaking thread” (usually kapron), which is used to facilitate cutting the outer sheath - when pulled, it makes a longitudinal cut on the sheath, which opens access to the cable core, without damaging the insulation of the conductors. Also, the tear thread, due to its high tensile strength, performs a protective function.
The outer shell has a thickness of 0.5-0.6 mm and is usually made of the usual polyvinyl chloride with the addition of chalk, which increases fragility. This is necessary for an accurate break at the place of the incision with the blade of the cutting tool. In addition, so-called “young polymers” are beginning to be used, which do not support combustion and do not emit halogens when heated (such cables are labeled as LSZH - Low Smoke Zero Halogen and usually have a bright outer sheath color).
The most common shell color is grey. An orange coloration generally indicates a non-combustible sheath material that allows lines to be laid in enclosed areas. In general, colors do not indicate special properties, but their use makes it easy to distinguish communications with different functional purposes, both during installation and maintenance.
Separately, it is necessary to note the marking. In addition to information about the manufacturer and type of cable, it necessarily includes meter or foot marks.
The shape of the outer shell can also be different. More often than others, the simplest one is used - round. Only for laying under the floor, for obvious reasons, a flat cable is used.
Cables for outdoor laying they must have a moisture-resistant polyethylene sheath, which is applied (as a rule) with a second layer over the usual, polyvinyl chloride. In addition, it is possible to fill voids in the cable with water-repellent gel and armor with corrugated tape or steel wire.
There are several categories of twisted pair cable, which are numbered from CAT1 to CAT7 and determine the effective frequency range to pass. Higher category cable usually contains more pairs of wires and each pair has more turns per unit length. Categories of unshielded twisted pair are described in the standard EIA/TIA 568(American standard for wiring in commercial buildings).
 |
| Category 7 twisted pair |
Each individual twisted pair that is part of a cable intended for data transmission must have a characteristic impedance of 120 ohms, otherwise the shape of the electrical signal will be irreversibly distorted and data transmission will become impossible. The reason for this can be not only poor quality cable, but also the presence of "twists" in the cable and the use of sockets of a lower category than the cable.
These twisted-pair crimping diagrams are for Category 5 cable (4 pairs of conductors). Crimped with 8P8C connector.
There are 2 cable crimping schemes: straight cable and crossover (cross-over) cable. The first scheme is used to connect a computer to a switch / hub, the second one is used to connect 2 computers directly and to connect some old models of hubs / switches (uplink port).
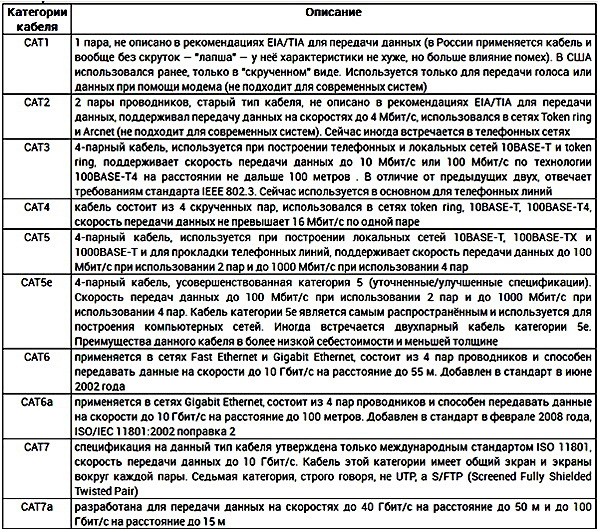
EIA/TIA-568A option:
| 1 | = = = = | = = = = | 1 green-white | |||
| 2 | ==== | ==== | 2 green | |||
| 3 | = = = = | = = = = | 3 orange-white | |||
| 4 | ==== | ==== | 4 blue | |||
| 5 | = = = = | = = = = | 5 blue-white | |||
| 6 | ==== | ==== | 6 orange | |||
| 7 | = = = = | = = = = | 7 brown white | |||
| 8 | ==== | ==== | 8 brown |
And according to the EIA/TIA-568B standard:
| 1 | = = = = | = = = = | 1 orange white | |||
| 2 | ==== | ==== | 2 orange | |||
| 3 | = = = = | = = = = | 3 green-white | |||
| 4 | ==== | ==== | 4 blue | |||
| 5 | = = = = | = = = = | 5 blue-white | |||
| 6 | ==== | ==== | 6 green | |||
| 7 | = = = = | = = = = | 7 brown white | |||
| 8 | ==== | ==== | 8 brown |
Crossover cable for connecting two network cards directly at a speed of 100 Mbps (Crossover)
10base-T/100base-TX crossover (T568B)
Pin no. - core color - pin no. at the other end of the cable
| 1 | = = = = | = = = = | 1 | |||
| 2 | ==== | ==== | 2 | |||
| 3 | = = = = | = = = = | 3 | |||
| 4 | ==== | ==== | 4 | |||
| 5 | = = = = | = = = = | 5 | |||
| 6 | ==== | ==== | 6 | |||
| 7 | = = = = | = = = = | 7 | |||
| 8 | ==== | ==== | 8 |
Crossover cable for connecting two network cards directly at a speed of 1 Gigabit / s (Crossover)
10base-T/100base-TX/1000base-TX/T4 crossover (T568B)
Pin no. - core color - pin no. at the other end of the cable
| 1 | = = = = | = = = = | 1 | |||
| 2 | ==== | ==== | 2 | |||
| 3 | = = = = | = = = = | 3 | |||
| 4 | ==== | = = = = | 4 | |||
| 5 | = = = = | ==== | 5 | |||
| 6 | ==== | ==== | 6 | |||
| 7 | = = = = | ==== | 7 | |||
| 8 | ==== | = = = = | 8 |
|
|
| Crimping tool (crimper) |
The white-orange core changes from white-green, orange to green (for a 100-megabit connection); the blue core changes from white-brown, white-blue to brown (for a gigabit connection, for 100 megabits they can be crimped in any order or not crimped at all).
Using a cable that is not crimped according to the standard can lead to the fact that the cable will not work, or there will be a very large percentage of losses (depending on the length of the cable), as well as situations of a complete cable check to determine the purpose of certain pairs.
To check the correct crimping of the cable, in addition to visual control, there are special devices - LAN testers. Such a device consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter in turn sends a signal to each of the eight cable cores, duplicating this transmission by lighting one of the eight LEDs, and on the receiver connected to the other end of the line, one of the eight LEDs lights up accordingly. If the LEDs on the transmission and reception light up in a row, it means that the cable is crimped without error. More expensive models of LAN testers may have a built-in intercom, a break indicator indicating the distance to the break, etc.
These crimping schemes are suitable for both 100 Mbit and Gigabit connections. When using a 100 megabit connection, only 2 out of 4 pairs are used, namely orange and green. The blue and brown pairs can then be used to connect a second computer over the same cable. Each end of the cable is split into two, two pairs each, and two cables are obtained, as it were, but under one insulation. However, this connection scheme can reduce the speed and quality of information transfer. When using a gigabit connection, 4 pairs of conductors are used.
There are also restrictions on the choice of cross-wiring scheme imposed by the Power-Over-Ethernet (POE) standard, but this standard has not yet been fully approved. With a direct connection of the cores in the cable ("one to one"), this standard will work automatically.
When installing a twisted pair cable, the specified curvature at the bends must be maintained. Exceeding may lead to a decrease in the resistance to pickups or to the destruction of the cable.
When installing a shielded twisted pair, it is necessary to monitor the integrity of the shield along the entire length of the cable. Stretching or bending leads to the destruction of the screen, which leads to a decrease in resistance to pickups. The drain wire must be connected to the connector shield.
twisted-pair crimping for LAN needs on
Indoor unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable, 2 pairs (solid), category 5, used in subscriber wiring to provide access to data network services.
|
|
1 - Outer shell
2 — Twisted pair solid
Unshielded 4-pair category 5e cable with solid copper conductors and designed for use in applications with bandwidth up to 1Gb.
|
|
|
1 - Outer shell
2 — Twisted pair solid
| Conductor: | |
| Insulation: | |
| Wire diameter | 0.9±0.02mm |
| Twisted pair color: | |
| 4 twisted pairs covered with PVC sheath | minimum sheath thickness 0.4 mm |
| Cable outer diameter | 5.1±0.2mm |
| Cable bending radius: | |
| Working temperature: | -20°C – +75°C |
| Fire resistance: | CM |
| Standards: |
FTP cable (foiled twisted pair - twisted pair with an overall foil shield and a copper conductor to drain induced currents) for outdoor installation, 4 pairs (solid), category 5e.
|
|
|
1 - Outer shell
2 - Screen - foil
3 - Drain wire
4 - Protective film
5 — Twisted pair solid
| Conductor: | bare copper wire Ø0.51±0.01 mm, 24 AWG |
| Insulation: | high density polyethylene, minimum thickness 0.18 mm |
| Wire diameter | 0.9±0.02mm |
| Twisted pair color: | blue-white/blue, orange-white/orange, green-white/green, brown-white/brown |
| 0.025mm x 20mm | |
| Ø0.5 mm | |
| Cable outer diameter | 7.0±0.2mm |
| Cable bending radius: | 8xØ during installation, 6xØ with vertical cabling, 4xØ with horizontal cabling |
| Working temperature: | -40°C – +60°C |
| Fire resistance: | CMX |
| Standards: | UL444/UL1581, TIA/EIA 568B.2. |
FTP cable (foiled twisted pair - twisted pair with an overall foil shield and a copper conductor to drain induced currents) for external installation with a cable, 4 pairs (solid), category 5e.
|
|
|
1 - Outer shell
2 - Screen - foil
3 - Drain wire
4 - Protective film
5 — Twisted pair solid
6 - Metal cable
| Conductor: | bare copper wire Ø0.51±0.01 mm, 24 AWG |
| Insulation: | high density polyethylene, minimum thickness 0.18 mm |
| Sheathed conductor diameter: | 0.92±0.02mm |
| Twisted pair color: | blue-white/blue, orange-white/orange, green-white/green, brown-white/brown |
| 4 twisted pairs shielded with aluminum foil tape | 0.025mm x 20mm |
| The cable has a drain wire | Ø0.5 mm |
| The cable is sheathed in polyethylene | minimum sheath thickness 0.65 mm |
| Cable outer diameter: | 7.0±0.2mm |
| Carrying rope: | Cink Steel |
| Rope sheath thickness: | 0.6±0.05mm |
| Rope diameter: | 2.0±0.1mm |
| Cable bending radius: | 8xØ during installation, 6xØ with vertical cabling, 4xØ with horizontal cabling |
| Working temperature: | -40°C – +60°C |
| Fire resistance: | CMX |
| Standards: | UL444/UL1581, TIA/EIA 568B.2. |
Shielded copper cable, 10 pairs, HDPE insulation, UV resistant polyethylene sheath. The cable is designed for outdoor installation, category 5e.
With the development of information technology and the Internet, a cable for creating data transmission networks has become the most demanded product. Computer networks surround us everywhere: at work and at home, in educational institutions and clinics, in shops and banks. The reliability and quality of communication in the network largely depend on the type of cable used.
For example, you decided to save money and laid a utp 2 or utp 4 cable between buildings, designed for indoor use only. As a result, you will get constant network freezes and data loss. At the same time, using a 25-pair ftp cable for external installation is a waste of money in the case of creating a home network for a couple of computers.
Unshielded twisted pair - this is the name of the cable marked from UTP 2 TO UTP 10. Most often, this type of cable is used to create indoor home and office networks. UTP 2, consisting of two pairs of wires twisted together, will handle small amounts of data just fine. Category UTP 4 to UTP 50 category cables are suitable for high bandwidth networks.
UTP cable consists of several twisted copper pairs with a PVC outer sheath.
Typically, UTP series cables are used indoors, but there are models for outdoor installation, for example, UTP PE 25 pair cat 5 cable.
The disadvantages of the UTP cable, first of all, include its poor protection against external induced currents, which are both outdoors and indoors. In this regard, the UTP cable is suitable for use with minor external electromagnetic interference, types UTP 2 - UTP 10 are laid at relatively short distances between the nodes of the data transmission network.
To organize a reliable network, it is better to use an FTP cable instead of a 25-pair UTP cable with more noise protection.
A cable marked FTP, that is, shielded twisted pair, is better protected from the effects of external induced currents and interference in general. FTP 4/8/10/16 cables have the number of twisted pairs corresponding to the marking and are equipped with a shielding foil sheath. The FTP cable contains in its configuration a draining copper wire without insulation, connecting disparate sections of the foil, damaged during installation or operation.
A larger number of twisted pairs in a cable, on the one hand, increases its bandwidth, but at the same time, the effect of internal interference is more noticeable. FTP 10 pairs with a different turn pitch in each pair partially solves this problem. This approach allows to significantly increase the distance between the nodes of different parts of the data network. That is why FTP cable is often used for network communications between buildings. The most popular type of cable for outdoor networking can be called external FTP 5e. A metal cable on certain types of FTP 4 and FTP 10 cables allows for aerial laying of the network without the use of additional suspension systems. The PE outer FTP 5e jacket makes it more UV resistant.
Even the highest quality and most expensive FTP 4 cable of the 5e series will quickly become unusable if it is installed incorrectly or the rules for operating the cable network are systematically violated. The network cable will not withstand a bending radius that exceeds more than 8 diameters of the cable itself. Too much bending will damage the inner foil shield, and this, in turn, will noticeably degrade the quality of the cable and reduce the speed of communication within the network.
UTP FTP twisted pair cable types of its varieties