From internal pipelines, drains are transported by external ...

In this article, concepts related to threaded connections, such as metric and inch thread. To understand the intricacies associated with a threaded connection, you need to consider the following concepts:
The rod itself, applied to it tapered thread represents a cone. Moreover, according to international rules, taper should be 1 to 16, that is, for every 16 units (millimeters or inches) with increasing distance from the starting point, the diameter increases by one unit the corresponding measurement. It turns out that the axis around which the thread is applied and the conditional straight line drawn from the beginning of the thread to its end along the shortest path are not parallel, but are located at a certain angle to each other. If it is even easier to explain, if we had a length of a threaded connection of 16 centimeters, and the diameter of the rod at its starting point would be 4 centimeters, then at the point where the thread ends, its diameter would already be 5 centimeters.
Rod with cylindrical thread is a cylinder, respectively, there is no taper.
 The thread pitch can be large (or main) and small. Under thread pitch the distance between the threads from the top of the turn to the top of the next turn is understood. It can be measured even with a caliper (although there are special meters). This is done as follows - the distance between several vertices of the turns is measured, and then the resulting number is divided by their number. You can check the accuracy of the measurement in the table for the corresponding step.
The thread pitch can be large (or main) and small. Under thread pitch the distance between the threads from the top of the turn to the top of the next turn is understood. It can be measured even with a caliper (although there are special meters). This is done as follows - the distance between several vertices of the turns is measured, and then the resulting number is divided by their number. You can check the accuracy of the measurement in the table for the corresponding step.
| Pipe threads cylindrical according to GOST 6357-52 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | The number of threads N on 1 " |
Thread pitch S mm |
Outside diameter thread mm |
Average diameter thread mm |
Inner diameter thread mm |
| G1 / 8 " | 28 | 0,907 | 9,729 | 9,148 | 8,567 |
| G1 / 4 " | 19 | 1,337 | 13,158 | 12,302 | 11,446 |
| G3 / 8 " | 19 | 1,337 | 16,663 | 15,807 | 14,951 |
| G1 / 2 " | 14 | 1,814 | 20,956 | 19,754 | 18,632 |
| G3 / 4 " | 14 | 1,814 | 26,442 | 25,281 | 24,119 |
| G7 / 8 " | 14 | 1,814 | 30,202 | 29,040 | 27,878 |
| G1 " | 11 | 2,309 | 33,250 | 31,771 | 30,292 |
The marking is typically present nominal diameter, which in most cases is the outer diameter of the thread. If the thread is metric, then a standard vernier caliper with scales in millimeters can be used for measurement. Also, the diameter, as well as the thread pitch, can be viewed according to special tables.
 Metric thread - has a designation of the main parameters in millimeters. For example, consider a corner fitting with an external cylindrical thread EPL 6-GM5. In this case, the EPL says that the fitting is angled, 6 is 6 mm - the outer diameter of the tube connected to the fitting. Litter "G" in its labeling informs that the cylindrical thread. "M" indicates that the metric thread, and the numeral "5" indicates the nominal diameter of the thread equal to 5 millimeters. Fittings (of those that we have on sale) with the letter “G” are also equipped with a rubber sealing ring, and therefore do not require a fum tape. The thread pitch in this case is equal to - 0.8 millimeters.
Metric thread - has a designation of the main parameters in millimeters. For example, consider a corner fitting with an external cylindrical thread EPL 6-GM5. In this case, the EPL says that the fitting is angled, 6 is 6 mm - the outer diameter of the tube connected to the fitting. Litter "G" in its labeling informs that the cylindrical thread. "M" indicates that the metric thread, and the numeral "5" indicates the nominal diameter of the thread equal to 5 millimeters. Fittings (of those that we have on sale) with the letter “G” are also equipped with a rubber sealing ring, and therefore do not require a fum tape. The thread pitch in this case is equal to - 0.8 millimeters.
main parameters inch threadThus the name - specified in inches. This thread can be 1/8, 1/4, 3/8 and 1/2 inch, etc. For example, consider fitting EPKB 8-02. EPKB - a kind of fitting (in this case the splitter). Conical thread, although this and there is no reference to using letters "R", it would be clever. 8-ka - indicates that the external diameter of the connected tube is 8 millimeters. A 02 - that the connecting thread on the fitting 1/4 inch. According to the table, the thread pitch is 1.337 mm. The nominal diameter of the thread is 13.157 mm.
The profiles of tapered and cylindrical threads are the same, which allows you to screw together fittings with tapered threads and cylindrical.
Inch pipe thread is used in metal pipelines and plastic and metal fittings of collapsible type. What parameters it is characterized by, how it is measured on the inner and outer surfaces of structures and how it differs from the metric version of a threaded connection, this article will tell.
All threads are characterized by the following parameters:
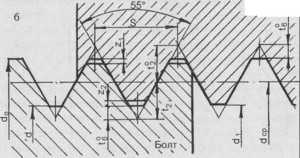
According to GOST 6357, the profile of the inch inch pipe represents an equilateral triangle with an angle at the apex of 55 ° (Vitvor thread) or 60 ° (American standards UNC and UN). The outer diameter here is measured not in millimeters, but in inches. The main characteristic is the number of turns located on one inch dimension. The American system uses two types of steps - large (UNC) and small (UNF).
Note! The turns should have the same step size. If the distance between them is different, it is impossible to select the appropriate bolt or nut to the threaded connection.

An ordinary inch (indicated by a dash "), which is equal to 25.4 mm, measures the internal diameter of the cut. It is noteworthy that in this situation they resort to a unique unit of measurement - a tube inch of 33.249 mm. Here, in addition to the internal diameter, the thickness of two profile walls is included in the dimensions of the inch pipe thread.
For example, in a steel pipeline with a diameter of 5 inches, the cut value is 127 mm from the inside and 166.245 mm from the outside.
On a note! An exception is a 1/2 inch cylindrical pipe thread with an outer diameter of 21.25 mm.
In addition to the inch measurement used in pipelines, there is a metric thread that is used in other areas of life. It is also characterized by diameter and pitch. Such a cut has a profile in the form of an equilateral triangle, the angle at the apex of which is 60 °. The application of threads is done in large and small steps. The first is marked with the letter M with a number indicating the nominal diameter (for example, M20). With fine slicing, a step is added, so the designation has the following form - M20x1.5.
The difference between an inch thread and a metric pipe is as follows.
This also applies to the thread pitch, which in the inch version is characterized by the number of grooves that fit on one inch section of the profile. For example, in a water supply system, only two versions of a threaded “pitch” are used - for 11 threads (equal to a metric pitch of 2.31 mm) and 14 turns (equal to a metric pitch of approximately 1.8 mm).
Note! To measure the thread pitch use a special tool - a thread gauge. If necessary, it is replaced with an ordinary ruler or other available measuring device.
To simplify the determination of the ratios of these two measurements, normative documents provide tables of inch and metric pipe threads for common sizes.
The difference in these differing systems for calculating the screw cutting parameters makes it difficult to determine some quantities, but with careful study, they can be understood. We hope for a positive result!
The quality of the cutting that is performed on the pipeline, its compliance with the diameter of the pipe product - all this is of great importance when installing a plumbing or heating system. Cutting an inch thread with a die is not very convenient. It is much easier to use a special machine tool.
Slicing is a screw recess with an invariable thread pitch and cross-section. It is carried out on products having the shape of a cone, cylinder (bolt, screw elements), on parts that are connected to similar products (nuts).
In everyday life, people are usually found with cylindrical threaded joints on pipes. In addition to thread, the pitch of which is measured in millimeters, inch thread is common in the Russian Federation.
The key parameters of metric cutting are the step (the distance between the recesses or combs, which is measured longitudinally to the product axis) and the diameter.
Inch thread is characterized by a diameter that is measured in inches, the number of curls per 1 inch. How is thread size translated in mm from inches? For such a translation, you need to multiply the size of the inch thread by 25.4.
![]()
How else does an inch threaded connection differ from a metric? The differences are that the inch thread has:
In domestic conditions, pipe products with these types of cuts are most often used:
To establish the appearance and pitch of an inch thread, an object called a thread gauge is used. In addition, it is possible to use an ordinary ruler, vernier caliper.
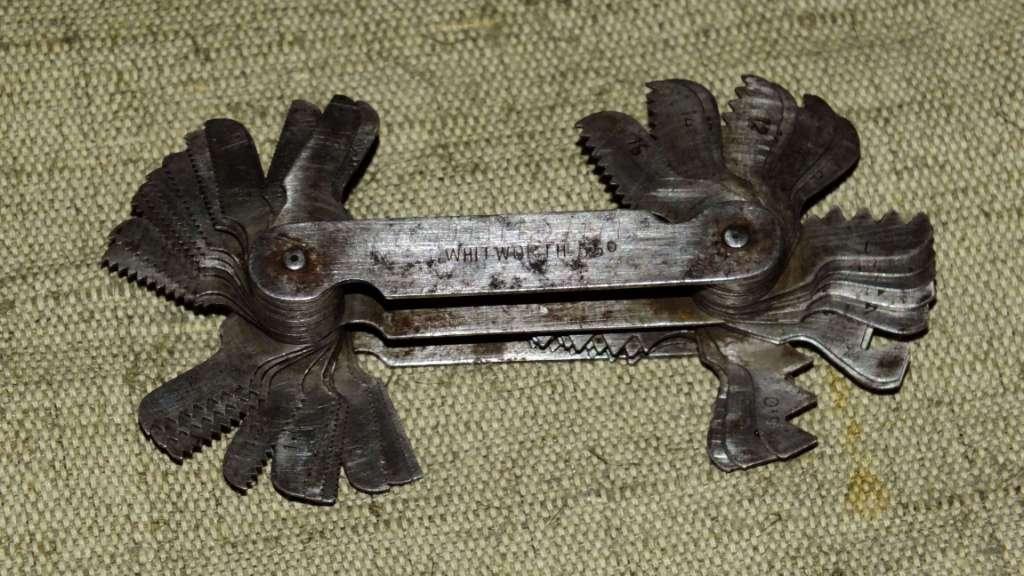

A coupling element can serve as a calibration element. It should be cut, having a size that corresponds to the diameter of an inch thread. The item is screwed into a threaded connection. If no difficulties arose, she firmly stuck in the tubular product, which means that the measurement can be completed. Otherwise, repeat the procedure with another calibration part.
With a thread gauge is still easier. Its measuring plates resemble a set of files. These files need to be pressed to the cut made on the product or inside it. If the profile of the plate coincides with the pipe, this means that the size of the inch thread is the same as that of the file.
With a caliper, it is possible to measure only the outer size of the cut. In view of this, calibration details, thread gauges are considered the best devices for establishing the pitch and size of the cut.
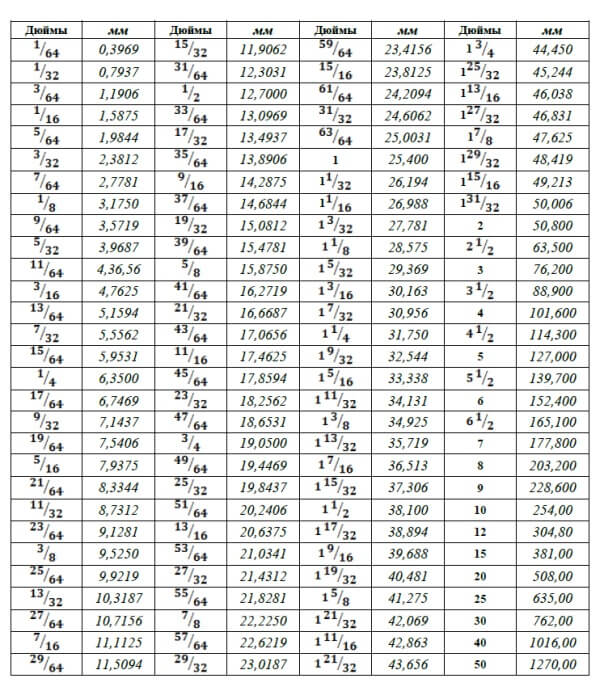 In reality, of course, few can achieve impeccably accurate compliance with thread sizes. However, you can count on creating high-quality slices if you are guided by at least one character in the fractional part of the number.
In reality, of course, few can achieve impeccably accurate compliance with thread sizes. However, you can count on creating high-quality slices if you are guided by at least one character in the fractional part of the number.
If cutting is carried out manually, and not using a machine tool, this can cause certain difficulties, especially when the outer diameter of the thread exceeds 1 inch.
It is best to use a special device to create a threaded connection. It is called "klupp". Klupp includes a body with a pair of handles. It houses mobile combs that can be adjusted. By means of combs, a gradual deepening of the die is performed.
In addition, it is possible to use interchangeable flanges with a full / incomplete threaded profile. They are not too cheap, because not everyone can buy them. You can use the usual die, through which slicing is created.
When the plate holder is twisted clockwise, it is screwed onto the thread that is on the sleeve element. The sleeve is fixed on the tubular with 3 bolt elements. This device has an indisputable plus: you do not need to focus on the tubular product at the beginning of cutting.
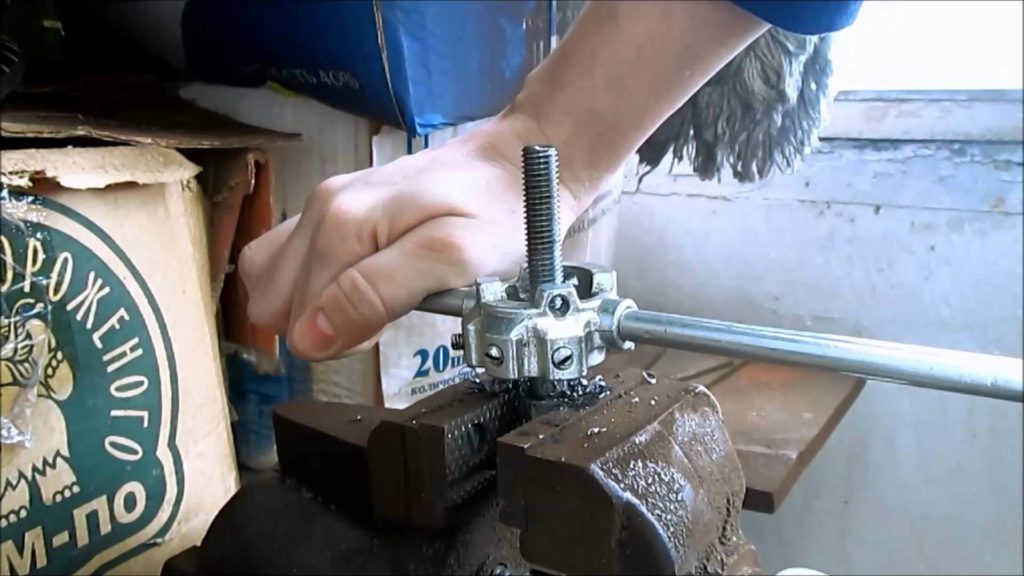

Manual slicing takes place like this:
Of course, the creation of slices outside and inside does not take place in parallel, but alternately.
Cutting using a machine tool is as follows:
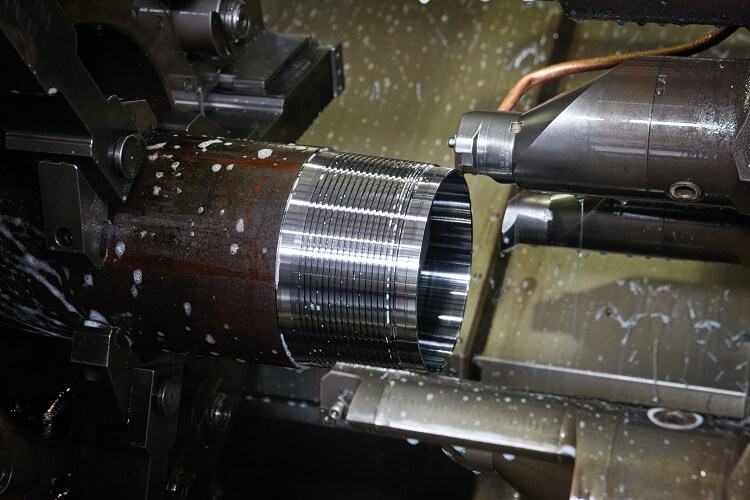

Of course, both the die and the tap can be used on the machine tool, fixing them in the front / rear headstock. However, it is worth considering the fact that the parameters of the inch thread created by the cutting tool will be more accurate.
For fastening the material, refer to the inch thread size chart. It contains GOST data (GOST is the standard adopted in Russia). Remember that not all cuts are common in Russia. For example, UNC and UNF are commonly used in the United States, Canada.
Do not forget that sometimes you need to translate sizes from one unit to another. To convert millimeters to inches, you need to cut the size, for example, divide UNF (UNF - Unified Fine Thread) by 25.4.
It's okay if you make a mistake by making a threaded connection at home. This is for workers in the production to comply with GOST. You are free to practice cutting on unnecessary parts.
The thread is a spiral, which is formed on the surface in the form of a cone / cylinder along a helical line with an invariable pitch. It is considered a key component of a threaded connection. Slicing is divided into categories by:
Pipe thread is designed to connect pipes, fittings, structural parts. Do not equate it to an inch mounting. The dimensions of the pipe thread are not real cutting diameters, but conventional numbers that characterize the bore diameter of a conventional pipe product.
The main difference between metric and pipe cutting is the type of ridge and recesses. The metric profile is a triangle with equal sides. In view of this, all angles in the metric cut are the same, equal to sixty degrees. Metric cutting is measured in millimeters, pipe - in inches. In addition, when creating pipe cutting, the thickness of the pipe walls must be taken into account. In different products, it can be different, since it depends on the compression for which the pipes were calculated in the production.
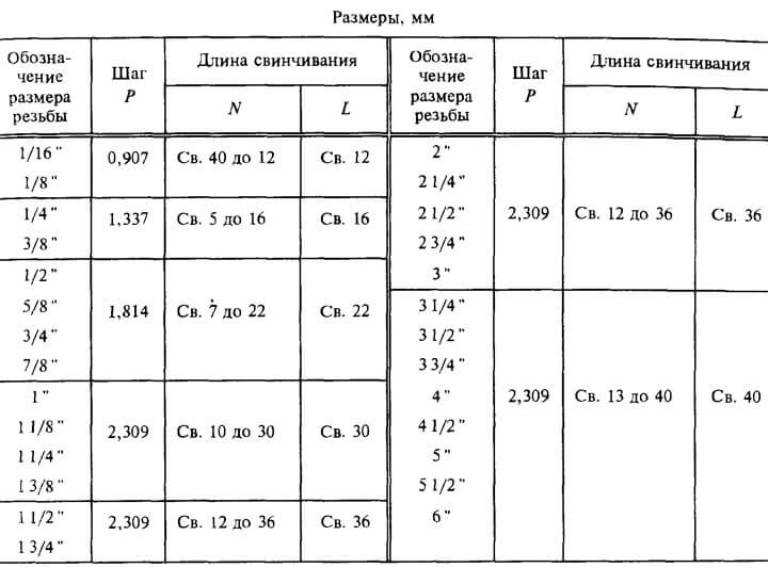
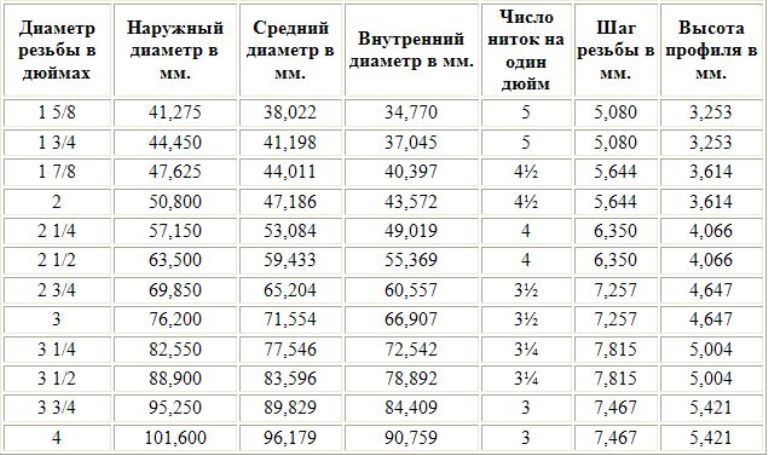


Each cut has the following key characteristics:
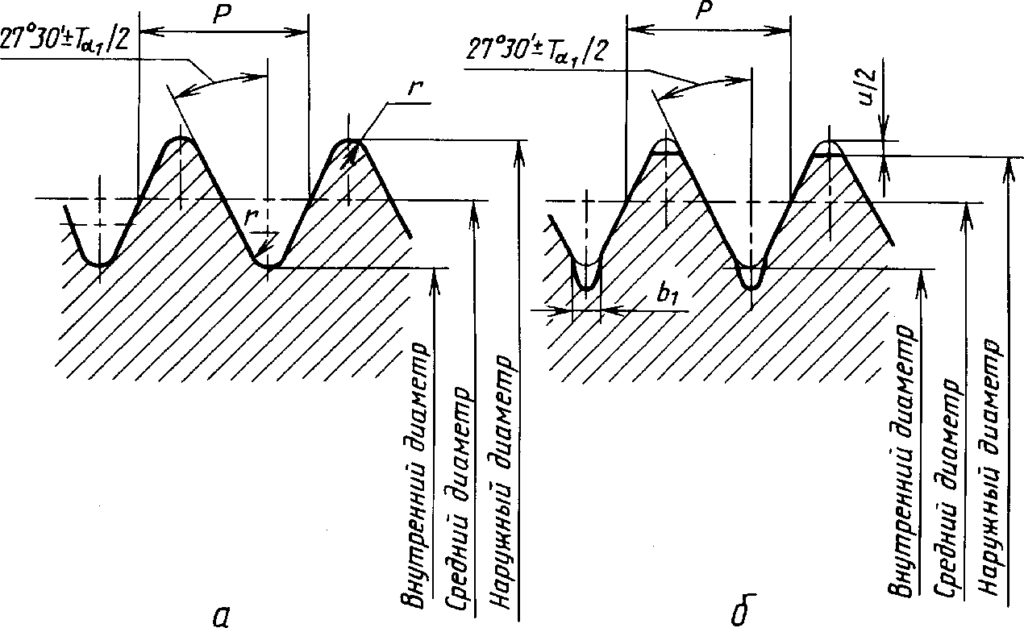
The pipe thread table is used in their work by specialists performing work related to plumbing. This type of slicing is divided into several types.
Another name is slicing Whitward. This type of pipe thread is used to create cylindrical joints. Its characteristics are as follows:
To combine tubular products with a larger radius, welding is required.
Similar pipe threads are used in tapered joints. In addition, with their help, the inner cylindrical and external conical cutting are joined. The seal itself is the thread itself. For combination, a sealing agent is required.
The conical pipe thread has the following parameters:
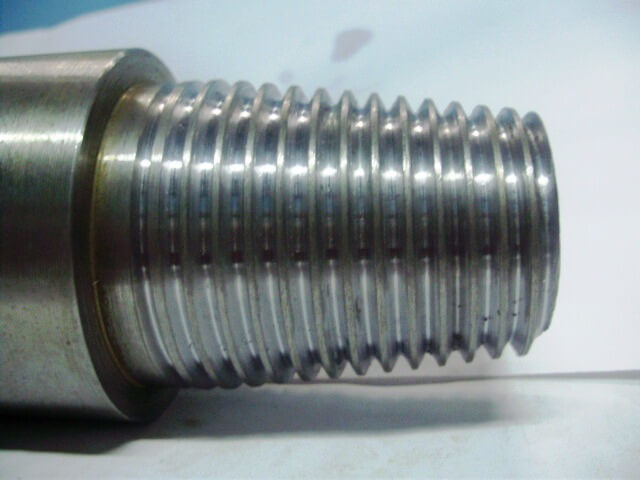

Round pipe threads are used to equip detachable connections. Its design provides a long operational period and greater resistance to severe loads. A similar pipe thread is used in such components:
This type of cutting can be used in conditions of increased pollution.
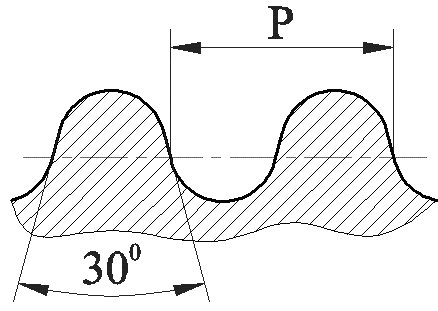
Decryption NPSM - "national pipe thread". This type is considered to be an inch cylindrical (a triangular profile, the angle is sixty degrees). For such pipe threads, the diameter is in the range of one sixteenth to twenty-four inches.
It should not be confused with NPT, which is conical and used to create reliable joints in conditions of high compression.
Characteristics can be set using the following methods:
1. The use of calibers. Special gauges make it possible to determine the pitch and diameter of the thread located both inside and outside. In order to measure the cut inside, you need to use a gauge in the shape of a cylinder having a thread on the outside. It must be screwed into the pipe. If you have chosen the right gauge, screwing will be easy. If there are the slightest differences, then the caliber will not work out to the end.
For pipe threads, the outer pitch size is set similarly. Used caliber with thread inside. It is screwed onto the pipe.
The disadvantage of this method is that it may take a lot of time to select the desired caliber. Today, there are one hundred and twenty such devices. Instead, you can use a fitting / coupling element.
2. Thread gauges. This method is simpler and faster, but it does not always provide the correct result. In view of this, professionals practically do not use it. A plate with a threaded profile is pressed against the thread. Between the ridges and the template, which is selected correctly, there should be no gaps.
In addition, such devices as calipers, micrometers are used to determine the cutting step.
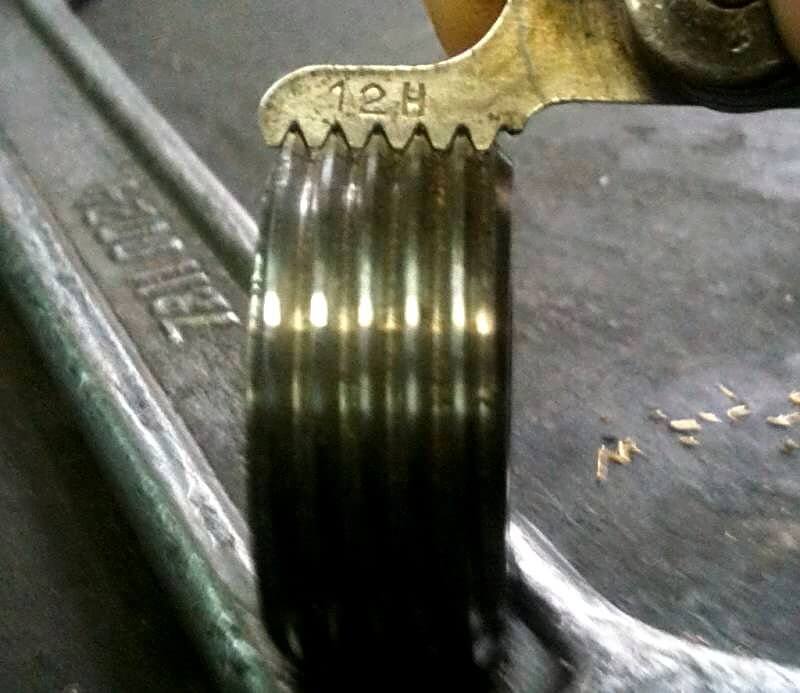

Pipe thread is created using one of the following methods:
A tap is used to create slices inside. The tap shank is fixed in the holder. After this, a slow screwing into the tube cavity is performed. This method requires great physical effort.
To cut a die, fix it in a clamping element with a pair of handles. The die is screwed onto the pipe section (clockwise).
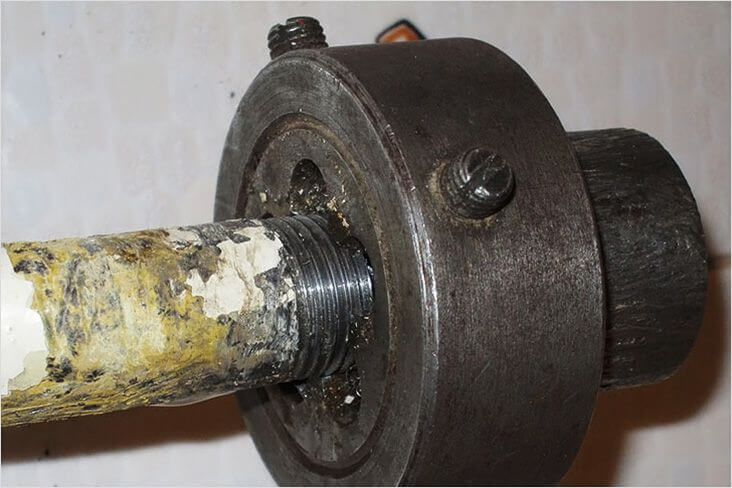

The above cutting methods do not require high qualifications. Creating a thread using a die / tap is a fairly simple operation that any plumber is capable of performing. To understand the designations of threaded connections is also not too difficult. Freshmen master them in one lecture on engineering graphics. The main thing is to correctly determine the size of the necessary slices. Otherwise, you will only waste your time and effort in creating the wrong thread. Do not forget the wise proverb: "Measure seven times, cut once."
Any plumber specialist should be familiar with the varieties of pipe thread. Standard are presented in a special table. must be guided by established standards. Otherwise, a poor-quality transition will result, which will lead to problems in the pipeline.
When performing plumbing work, it is necessary to pay attention to the type of pipe thread
A threaded notch is a sequence of depressions located helically.A screw relief is applied to any cylindrical elements or conical surfaces. Throughout their length, the spiral grooves have the same cross-sectional pitch and the length of the cross-section. Such a relief is used to create helical transitions. It is used in automotive and engineering communications.
Screw fastenings are of two main types:
Pipe notch stands out in a separate category. It can be applied to pipes made of various materials (plastic, metal, plastic, etc.). It is used to assemble a collapsible type pipeline most often in everyday life (water supply, heating).
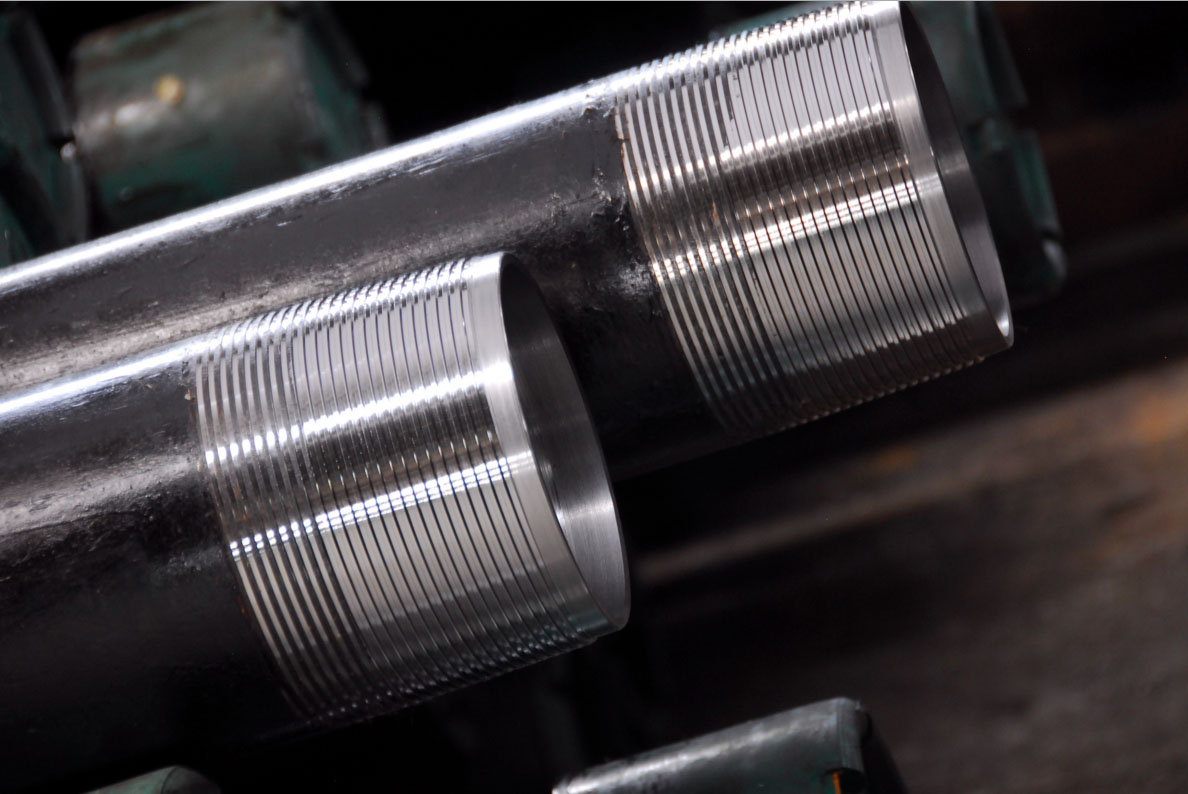

There are various pipe thread options.
The main parameters of the thread:
Visually determining the type and size of the thread is difficult. It is determined by measuring it with a caliper and comparing the obtained parameters.
The dimensions of the inch pipe thread are different from the metric. The main parameter that defines it is the cross section. In this case, the metric relief is determined by the diametrical diameter and pitch. An important characteristic of inch slicing is the number of turns per inch or fraction of an inch. The standard inch is 2.54 cm. The pipe inch differs from the usual one and is 3.324 cm.
The inch pipe thread differs from the metric in its configuration: the recesses are more pointed, and the convex parts of the thread are rounded. Determine the pitch of inch and metric twisting in different ways. For an inch notch, it is enough to calculate the number of turns in one inch. For metric cutting, they take a certain interval, calculate the number of turns in it, and then divide this distance by the number of turns. The accuracy of the calculation should be at least one digit after the decimal point, otherwise it will not work to create a notch of acceptable quality.
There are only 3 ways of applying a notch: at the time of manufacture of the pipe by the coast; cutting on a special lathe; hand tapping and die.
Joining elements by twisting is considered one of the most durable and reliable joints. Using this method is very simple. The disadvantage of this method is only that in some cases, to achieve maximum strength, the use of tow for additional sealing is required.
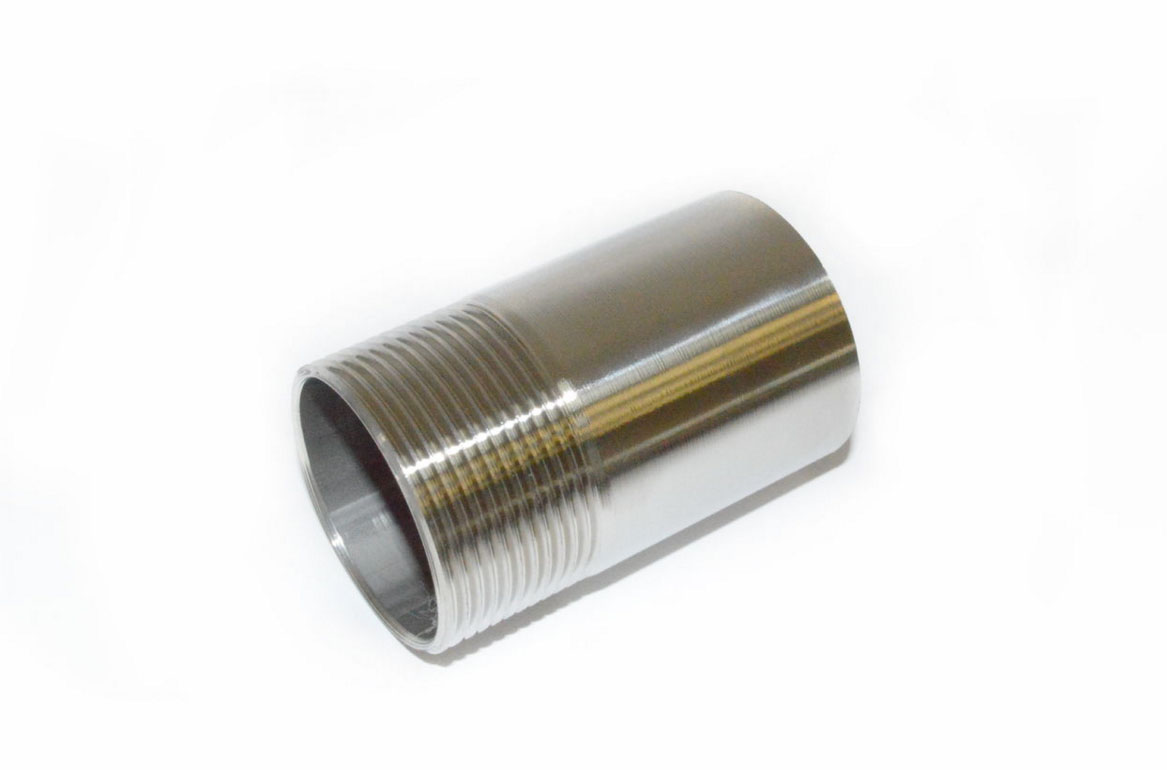

Twisting is one of the most reliable connection methods.
Pipe thread is used for tight twisting of pipes and other thin-walled structures of cylindrical shape. A sectional screw notch forms an isosceles triangle with an upper angle of 55 °. The main parameter of a cylindrical screw notch is the nominal diameter. The external and internal diameter is important when applying a screw notch, while the conditional one is used for reliable installation of plumbing.
Pipes for hot and cold water are often coated with steel threads. The pipes themselves can be made of cast iron and other materials. This is due to the fact that cast iron, for example, is distinguished by brittleness, and steel - by strength, due to which the quality of fasteners is increased. Cylindrical notches are applied to pipes with a size from 1/16 to 6 inches across.
Conical inch thread is used for elements that require increased strength. For example, when assembling pipes through which liquid or gas passes under high pressure. Conical notches are used for the installation of a steel pipe passing underground at a shallow depth. Mandatory transitions are sealed with sealant. The conical helical relief is indicated by the symbols R (external thread) and Rc (internal thread). This type of joining is applied to the conical profiles. In other words, the diameter decreases from the beginning to the end of the pipe. At the time of twisting, the coils have the property of deforming, which creates a strong metal joining of the surfaces.
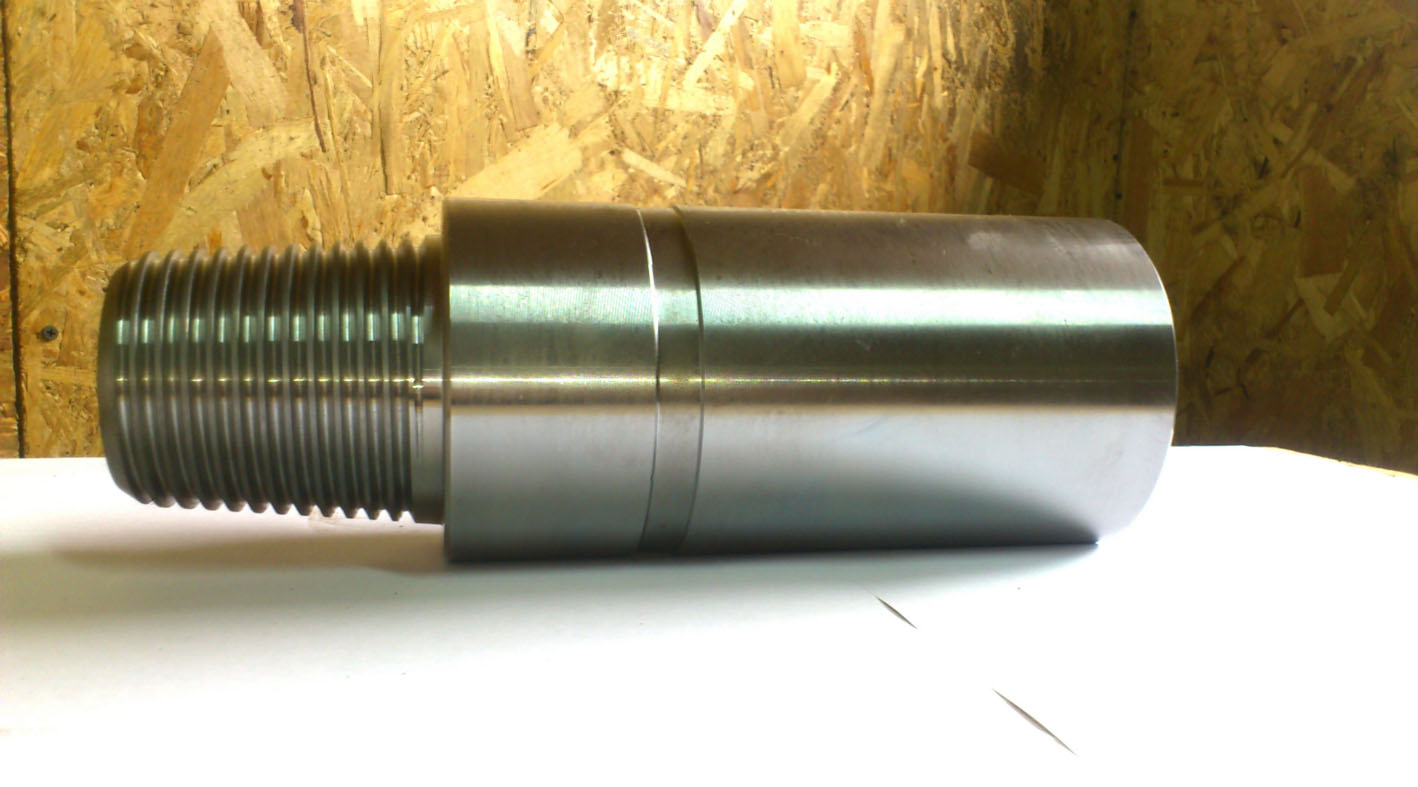

Tapered thread used for increased bond strength
The disadvantage of this connection is that strong tight twisting can be obtained only once. When the elements are separated, the distorted grooves will no longer be able to create a reliable impervious connection.
One of the areas of application of the conical connection is an emergency on the pipeline. In the event that the screw mount is damaged or torn, a larger diameter conical connection is used. This method can solve the problem for a while by sealing the elements.
It is used in the installation of water, gas, fuel pipelines. Today, metric conical relief is gaining ground. Its difference from the first type is the ability to create a dock with an external conical and internal cylindrical screw notch.
Round thread is applied to glass, ceramics, tin. This type of docking is able to withstand significant loads, it is adapted for frequent disconnection. Elements are easily twisted and disconnected. The scope of this type of mount is not so much. These are mainly various valves, taps and mixers, elements with stamped relief. This type of twisting is used in the socles of electric lamps.
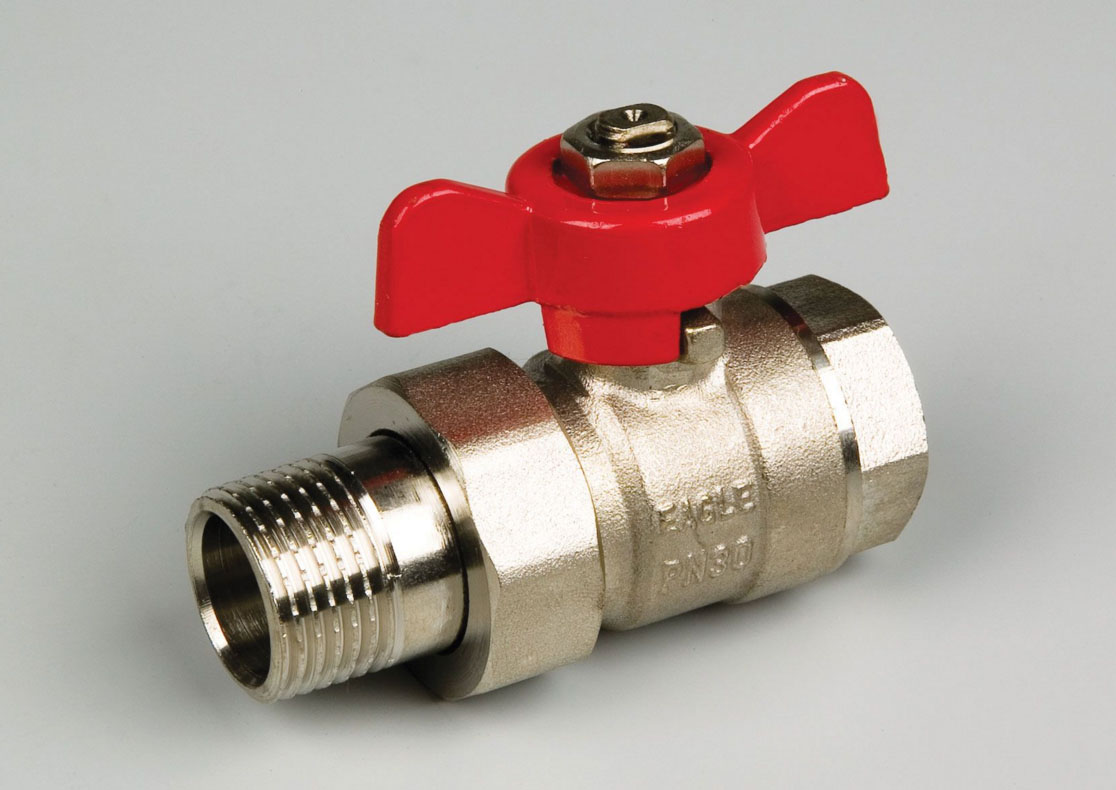

For frequent disconnection of elements, a round thread is used.
A connection of this type is distinguished by endurance in contaminated conditions of use, for example, when coupling cars. It withstands shock and shock.
NPSM is an inch cylindrical American thread. The sectional spiral notch is a triangle with an upper angle of 60 °. Such compounds are available in a wide range: from 1/16 to 24 inches. In fact, this is a type of ordinary cylindrical mount. Such a notch can only be created at the factory.
Inch threads in millimeters are convenient for inexperienced craftsmen who are often confused in units of measurement. In addition, to apply a screw notch to the element, you need to properly drill a hole. The diameters of the holes for the thread are calculated based on such parameters as the pitch and the length of the diameter of the helical groove.
The table of metric and inch threads is as follows:
| Threaded notch (dm) | Diameter (mm) | Radius (mm) | Pitch (mm) | Profile Height (mm) | The number of turns per 1 dm | The number of turns per 127 mm | ||
| outer | average | interior | ||||||
| 0,125 | 9,732 | 9,149 | 8,568 | 0,124 | 0,906 | 0,582 | 29 | 140 |
| 0,25 | 13,162 | 12,305 | 11,448 | 0,185 | 1,336 | 0,857 | 18 | 96 |
| 0,375 | 16,666 | 15,808 | 14,953 | |||||
| 0,5 | 20,958 | 19,795 | 18,633 | 0,250 | 1,812 | 1,161 | 13 | 71 |
| 0,625 | 22,914 | 21,752 | 20,587 | |||||
| 0,75 | 26,444 | 25,283 | 24,118 | |||||
| 0,875 | 30,204 | 29,042 | 27,879 | |||||
| 1 | 33,252 | 31,773 | 30,294 | 0,315 | 2,303 | 1,473 | 12 | 53 |
| 1,125 | 37,898 | 36,422 | 34,943 | |||||
| 1,25 | 41,914 | 40,435 | 38,955 | |||||
| 1,375 | 44,327 | 42,848 | 41,368 | |||||
| 1,5 | 47,808 | 46,328 | 44,819 | |||||
| 1,75 | 53,749 | 52,272 | 50,793 | |||||
| 2 | 59,617 | 58,139 | 56,657 | |||||
| 2,25 | 65,713 | 64,236 | 62,756 | |||||
| 2,5 | 75,188 | 73,709 | 72,232 | |||||
| 2,75 | 81,538 | 80,059 | 78,582 | |||||
| 3 | 87,889 | 86,408 | 84,932 | |||||
| 3,25 | 93,985 | 92,507 | 91,028 | |||||
| 3,5 | 100,335 | 98,857 | 97,378 | |||||
| 3,75 | 106,686 | 105,207 | 103,729 | |||||
| 4 | 113,035 | 111,558 | 110,079 | |||||
| 4,5 | 125,737 | 124,258 | 122,779 | |||||
| 5 | 138,437 | 136,958 | 135,479 | |||||
| 5,5 | 151,138 | 149,658 | 148,179 | |||||
| 6 | 163,838 | 162,358 | 160,877 | |||||
We hope you find the table useful!