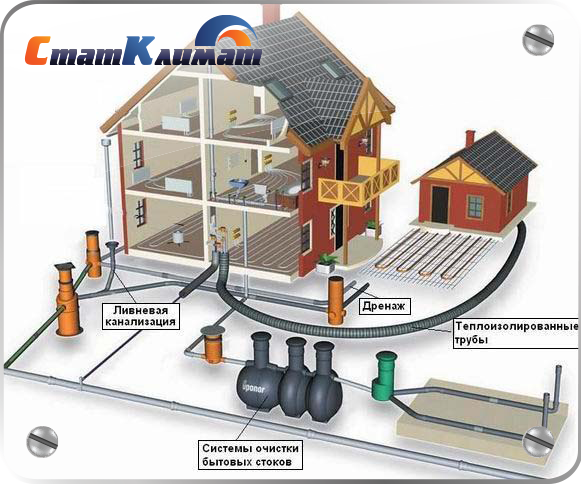
From internal pipelines, drains are transported by external ...
Grounding devices are now called devices that could be used to create a reliable current path through the earth. In the overwhelming majority of cases, such a need arises when consumers need to ensure the operation of the electrical installation in working or emergency operation modes. A striking example of working grounding is the deliberate connection to the earth of all kinds of arresters, transformers, or generators, in extreme cases.
The connection of lightning rods to the grounding, the presence of which is determined by the need to protect the electrical installation from induced overvoltages, as well as from direct lightning strikes, is often also perceived as a working grounding. The type of grounding that is performed to ensure the safety of people is called protective. 
A distinctive feature of this type of grounding is that it is subject to absolutely all metal parts of the body, frames, frames, corresponding fencing, and so on. As for the so-called grounding device, it is customary to call them already the combination of the ground electrode and grounding conductors.
At the present time, it is customary to distinguish also such a concept as an artificial ground electrode system. In its quality, there is a ground electrode, the electrically conductive parts of the communication of which are in contact with the ground. Grounding conductor is called grounding parts that connect to the ground electrode. 
The parts that are subject to not only grounding, but also to grounding include the following:
Generally speaking, it should be noted such distinctive features of protective and working grounding:
Protective grounding, at the moment, is called deliberate electrical connection to ground, or its equivalent, which, by the way, can also be metal non-conductive parts. The latter, often under voltage, which occurs as a result of a short to the housing or for some other reason. The main purpose of protective grounding is to eliminate electric shock in the event that a consumer accidentally touches the housing of the electrical installation, as well as any other, non-conductive metal parts that turned out to be voltage due to a short to the housing, for example
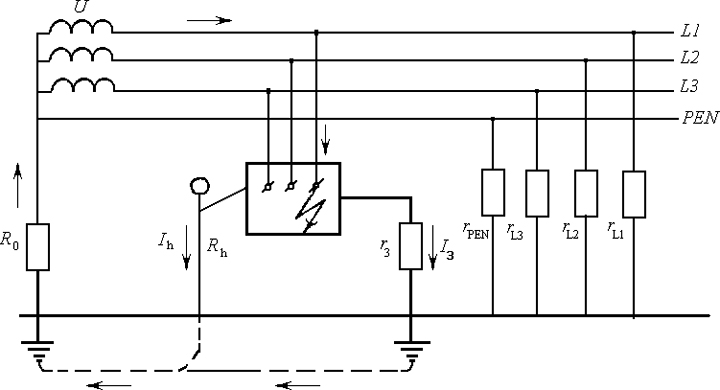
Working grounding, in turn, is deliberate connection to the ground at the same time of several separate points of the electrical circuit. They can be neutral points of the windings of generators, as well as a variety of measuring transformers. Unlike protective grounding, the working one is designed to ensure the correct operation of electrical installations, regardless of the conditions under which the latter will work: in normal or emergency. This type of grounding is carried out directly - that is, by connecting the grounded parts together with the so-called ground electrode system.
Speaking of what is called protective grounding, it should be noted that this term refers to the deliberate electrical connection of a separate part of the electrical installation (most often, the housing) with a special grounding device, which is carried out to ensure electrical safety. This measure should protect a person touching the housing or any other part of the electrical installation.
It is important to note that the smaller the value of the grounding device used, the better it can cope with its task - this can be seen on any example. And you can take advantage of all the features of this technology if you purchase outlets equipped with a grounding contact. However, even such devices should be chosen carefully, and therefore, everyone who deals with electrical installations should be aware of what the protective grounding of electrical installations is and how to organize it.
In the event that a breakdown of insulation occurs between the active phase and the casing of the electrical installation, the latter may be energized. And of course, if a person touches the device at this time, it can have sad consequences for him. And grounding and protective electrical safety measures prevent electric shock. Moreover, such a system will consist directly of grounding conductors and special conductors.

If we consider the grounding device, it is important to note that grounding conductors can be both natural (metal structures of buildings and structures that are connected to the ground), and artificial (steel pipes, corners and rods). Well, depending on the type of conductors used, a protective circuit and a working ground circuit can be created.
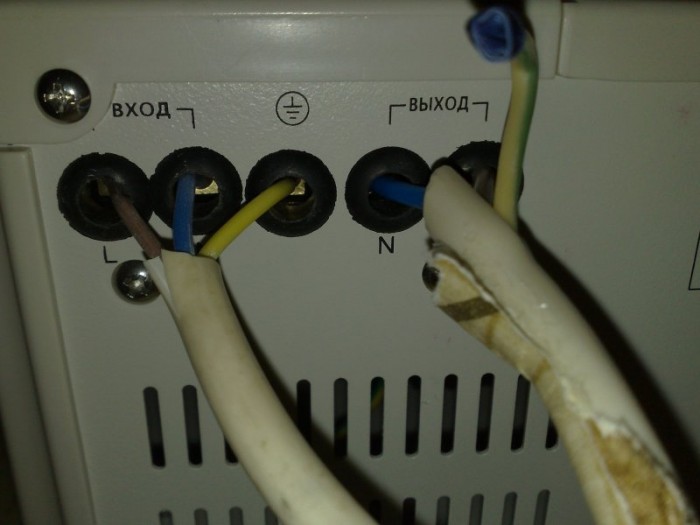

The working neutral conductor is designed to power electrical installations, and therefore its cross section reaches such values \u200b\u200bthat the passage of the operating current is possible. And the protective conductor allows you to create short-term short-circuit current, providing quick disconnection of electrical installations, the operation of which was disrupted, from the power supply. That is, the purpose of protective grounding is precisely to ensure human safety. And it is precisely this that is gaining the greatest distribution today.
Since most specialists use a variety of mobile conductors (steel pipes, neutral wires, devoid of switches and fuses, etc.), they create a portable protective ground. Moreover, the calculation of the system in question will directly depend on what materials were used in the process of its creation, and to ensure the safety of work, which installation it is used.

Special protective grounding can be used in a residential building or in a summer cottage, in a workroom or in a workplace. Moreover, it is necessary to understand its principle of action not only for specialists directly involved in performing work in this area, but also for ordinary people. Note that the purpose of using the system in question is to reduce step and touch stresses to safe values. Moreover, the touch of voltage and step in this case can be due to both a short to the case and other reasons. And they make the installation in such a way as to effectively reduce the potential of a particular equipment or to align the potentials of the equipment and the foundation on which the person is at the moment of contact.

There are certain rules for protective grounding, on which its effectiveness directly depends. Experts are well aware of such rules and try to strictly abide by them. Therefore, it is very important that portable protective earths of all kinds are mounted exclusively by people with the appropriate qualifications. Only in this case can it be guaranteed that the process will be carried out correctly, in compliance with all requirements and norms, and that the final result will be able to demonstrate high efficiency.
Working ground - deliberate connection to the ground of individual points of the electrical circuit, for example, neutral points of the windings of generators, power and measuring transformers, arc suppression devices, transverse compensation reactors in distant power lines, as well as the phase when using the earth as a phase or return wire. Working grounding is designed to ensure the proper operation of the electrical installation in normal or emergency conditions and is carried out directly (i.e., by connecting the grounded parts to the grounding conductor) or through special devices - breakdown fuses, arresters, resistors, etc.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
working ground - In the Electrical Installation Rules, the term "working grounding" is widely used. However, in the International Electrotechnical Dictionary (MES) and other standards of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), this term does not ... ...
Working ground - Grounding of live parts of the electrical installation necessary to ensure the operation of the electrical installation Source: RM 4 249 91: Automation systems for technological processes. Grounding network device. Allowance for the BCH 205 84 / MMSS ... Glossary of terms of normative and technical documentation
WORKING GROUNDING - grounding, designed to improve the functioning of the quality of the product ...
working ground (maintenance-free amplification [regeneration] point) - Earthing, providing remote power transmission according to the “wire-ground” scheme of amplifiers [regenerators], as well as the inclusion of a single metal cable sheath, NUP [NRP] tank, housings and screens in the system ... ... Technical Translator Reference
GROUNDING, electrical connection of the elements of electrical machines, apparatus, appliances, etc. with earth in order to protect people from electric shock (protective grounding) or use the earth as a conductor (working ... ... Modern Encyclopedia
Grounding - deliberate electrical connection what l. points of an electrical network, electrical installation or equipment with a grounding device, i.e. with a combination of a grounding conductor and grounding conductors. The grounding conductor (or group of conductors) is located ... Russian encyclopedia on labor protection
GROUNDING - an electrical connection with the earth or its equivalent in metal cases of electric power, telephone, telegraph, television, radio engineering, electromedical, electrometric, gas and other installations or devices. Depending ... ... Big Polytechnical Encyclopedia
The article is not a normative document. Warning: the article is purely informative in nature and is not a normative document. When performing work related to electricity, you should be guided ... Wikipedia
Working (functional) grounding - 1.7.30. A working (functional) grounding grounding of a point or points of current-carrying parts of an electrical installation, performed to ensure the operation of the electrical installation (not for electrical safety) ...