Of the many questions and topics that are asked to tarot cards, not a small one ...


"Basic characteristics of stars" - The angle at which the radius of the earth's orbit is visible from the star. Like the Sun, the stars illuminate the Earth. Distance to the star. Distances to the stars. Spectral classification of stars. Masses of stars. Star speeds. Distance from the Sun to the nearest star. The parallax method is on this moment in the most accurate way.
"Structure and evolution of stars" - Nuclear reactions in stars. Burning of C and O in the late stages of evolution. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Scheme of the evolution of a single star. Mass-luminosity relation. Sun model. Pressure of an electron degenerate gas. NASA animation. Sirius V. Hydrostatic balance. The opacity of matter in the interiors of stars.
"Distances to the stars" - Distances to the stars. Hipparchus. Even with the naked eye you can see that the world around us is extremely diverse. Supergiant in the constellation Scorpio - Antares. Distances to the stars. The brightest stars in ancient times were called stars of the first magnitude. Stars differ in color and brilliance.
"Black holes" - Away from the hole, the rays bend slightly. Singularity - all the matter of a black hole, collected in an infinitesimal point. After all the reserves of nuclear fuel are used up and the reactions stop, the star dies. Astronomer Karl Schwarzschild in the last years of his life calculated the gravitational field around a mass of zero volume.
"Starry Sky" - Northern Hemisphere. Celestial sphere. Johann Bayer. Bucket of the Big Dipper. Area of the celestial sphere. Bright stars. Stars. constellation images. Bright stars. The stars were the main landmarks. Winter triangle. Starry sky. Letters of the Greek alphabet. Astronomers of antiquity. Constellation Ursa Major.
"The structure of the stars" - Yellow - white. Canopus. Shaved. Mass. Color. Building. Dimensions. One. Temperature (color). White. The physical nature of the stars. effective temperature K. Class. Orange. Rigel. Crossbar white-blue, White-blue. Age. The luminosity of the stars. Red. The stars have a variety of colors. Yellow. Star radii.
In total there are 17 presentations in the topic

What is astronomy??? Studies the structure of the universe, movement, physical nature, the origin and evolution of celestial bodies and the systems formed by them. Based primarily on observations. Almost all information about celestial bodies is brought to us by electromagnetic radiation. Only in the last 40 years have individual worlds been studied directly: by probing the atmospheres of planets, by studying the lunar and Martian soil.

The word astronomy comes from two Greek words: astron - star, nomos - law. The practical need to study the starry sky led to the birth of science, which later received in Ancient Greece around 4th century BC name of astronomy. But the name itself does not at all serve as proof of the origin and development of astronomy only in ancient Greece. Astronomy arose and independently developed literally among all peoples, but the degree of its development, of course, was in direct proportion to the level of productive forces and culture of peoples.

Applicability Astronomy is closely related to other sciences, primarily physics and mathematics. But astronomy is also an indispensable testing ground. Space is the only place where matter exists at temperatures of hundreds of millions of degrees and near absolute zero, in the void of vacuum and in neutron stars. Now it is no longer necessary to determine the course of the ship by the stars, to predict the flood of the Nile, or to count the time by hourglass: technical means have replaced astronomy here. But astronomy and astronautics are still indispensable in communication systems and television, in observing the Earth from space. Astronomy studies the fundamental laws of nature and the evolution of our world. Therefore, its philosophical significance is especially great. In fact, it determines the worldview of people.

Astronomy The scale of the observable universe is huge and the usual units of measurement of distances - meters and kilometers - are of little use here. The astronomical unit is used in the study of the solar system. This is the size of the semi-major axis of the Earth's orbit: 1 AU. e. = 150 million kilometers.

Calendar Everything repeats itself in the sky above us: every night the stars rise and set, change lunar phases The sun finds its way between the stars. Thanks to astronomy, people have a calendar and timekeeping. The counting system for long periods of time is called a calendar. Over the centuries of human history, many different calendar systems have been developed (and used). But all calendars can be divided into three main types: solar, lunar and lunisolar. The solar calendars are based on the length of the tropical year. lunar calendars- the length of the lunar or synodic month, lunisolar calendars are based on both of these periods. The modern calendar adopted in most countries is the solar calendar.

Borders in the sky Already in ancient times, our ancestors divided the starry sky into clearly distinguishable combinations of stars, which they called constellations. Astronomy arose before all other sciences - noticing patterns in the movement of stars, our ancestors learned to measure time, created the first prototypes of the calendar, and learned to navigate the terrain. The names of the constellations were associated with myths, the names of gods, the names of instruments and mechanisms. Knowing the constellations is the ABC of astronomy. How to navigate in this huge and beautiful world, in this stellar placer? A constellation is a section of the celestial sphere, the boundaries of which are determined by a special decision of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). In total, there are 88 constellations in the celestial sphere. The boundaries between these strictly defined areas of the sky are arbitrary, they have no physical meaning .. 88 constellations

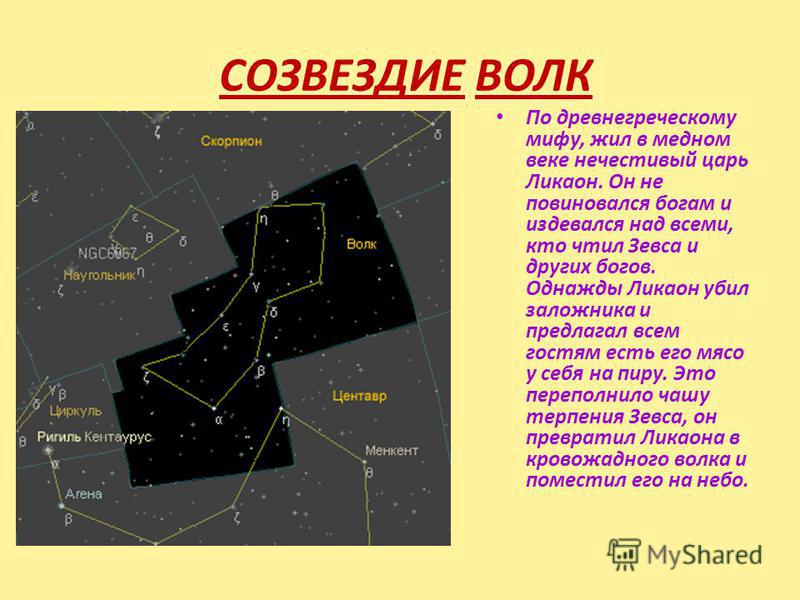
CONSTELLATION WOLF According to ancient Greek myth, the wicked king Lycaon lived in the Copper Age. He disobeyed the gods and mocked everyone who honored Zeus and other gods. One day, Lycaon killed a hostage and invited all the guests to eat his meat at his feast. This overflowed the patience of Zeus, he turned Lycaon into a bloodthirsty wolf and placed him in the sky.


Interesting objects. The most interesting object in this constellation is the Large Magellanic Cloud. This is a distant galaxy, visible in the southern hemisphere with the naked eye as a hazy cloud. It was named so by Antonio Pifanett in 1521 during the journey of Magellan. The Large Magellanic Cloud is one of the closest galaxies, only 200,000 light-years away. It is an irregular, ragged galaxy in which a large amount of interstellar gas has been found. In the sky, it occupies 5 °, which is ten times the apparent diameter of the moon. irregular galaxy

FISH Origin of the name. Drawing Constellation Pisces on vintage engravings. Drawing Constellation Pisces on vintage engravings. The ancient drawings of this constellation depict two fish tied with a ribbon. According to ancient Greek legend, Akis fell in love with the beautiful daughter of the sea god Nereus Galatea. Galatea also answered him with love. But not only Akida fell in love with Galatea. The huge Cyclops Polyphemus once saw Galatea and was also inflamed with passion for her. But suddenly he saw Polyphemus Galatea and Akis in a cool grotto on the seashore. Mad with jealousy, the mighty Cyclops began to destroy everything around. Frightened, Galatea threw herself into the stormy sea in horror, fleeing from the angry Cyclops, so that her father Nereus would protect her. And the enamored Akid rushed into the sea for his beloved. They turned into fish, tied with a long and wide ribbon. In honor of such a great love, the gods raised these fish to heaven. According to another legend, Pisces is Aphrodite and Eros fleeing the terrible Typhon.

Origin of name. The ancient drawings of this constellation depict two fish tied with a ribbon. According to ancient Greek legend, Akis fell in love with the beautiful daughter of the sea god Nereus Galatea. Galatea also answered him with love. But not only Akida fell in love with Galatea. The huge Cyclops Polyphemus once saw Galatea and was also inflamed with passion for her. But suddenly he saw Polyphemus Galatea and Akis in a cool grotto on the seashore. Mad with jealousy, the mighty Cyclops began to destroy everything around. Frightened, Galatea threw herself into the stormy sea in horror, fleeing from the angry Cyclops, so that her father Nereus would protect her. And the enamored Akid rushed into the sea for his beloved. They turned into fish, tied with a long and wide ribbon. In honor of such a great love, the gods raised these fish to heaven. Constellation Pisces on vintage engraving.
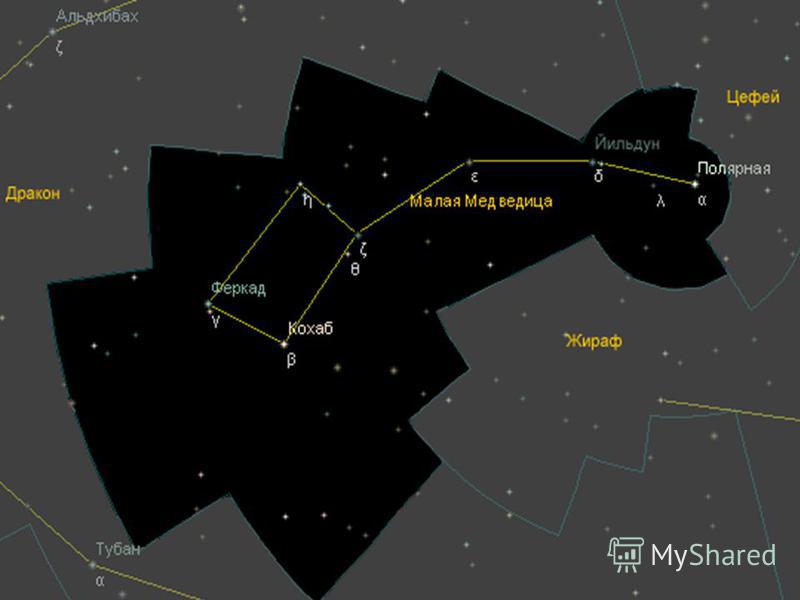

Interesting objects In this constellation is located α Ursa Minor - the North Star. It is a very important star due to its special location - it is currently less than a degree from the north pole. The whole vault of heaven, as it were, revolves around her, and she herself remains in place. It is the only practically fixed star in the sky to the naked eye. The main stars of Ursa Minor form a well-known asterism called the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the tip of the "tail" of Ursa Minor. The two stars that form the bottom of the "Small Dipper" are also called the guardians of the pole. Near the Polar at a distance of 18 "you can see its satellite with a telescope, the apparent magnitude of which is 9m. The origin of the name. Drawing Ursa Minor in the atlas of Hevelius. Atlas of Hevelius. This is one of the most ancient constellations. On old maps of the starry sky, Ursa Minor revolves around its long, bear-like tail. Such a long tail was invented for heavenly bears by the Greeks, who did not know what these northern animals looked like. The end of the tail of Ursa Minor Ursa Minor almost coincides with the north pole of the world, so from the outside it seems that the sky is spinning the tail of a poor animal.About three millennia ago, the star β Ursa Minor, which has its own name Kohab, was the closest to the North Pole of the world. Shemali means the star of the north, in China this star is called the regal star, it is believed that this constellation was formed by Thales of Miletus ; he also recommended using the bright star of this constellation for orientation in the sea. Thales of Miletus

Origin of the name This is one of the most ancient constellations. On old maps of the starry sky, Ursa Minor revolves around its long, bear-like tail. Such a long tail was invented for heavenly bears by the Greeks, who did not know what these northern animals looked like. The end of the tail of Ursa Minor almost coincides with the north pole of the world, so from the side it seems that the sky is spinning the poor animal by the tail. About three thousand years ago, the closest star to the North Pole of the world was the star β Ursa Minor, which has its own name Kokhab. Translated from Arabic, Kohab el-Shemali means the star of the north. In China, this star is called regal. It is believed that this constellation was formed by Thales of Miletus; he also recommended using the bright star of this constellation for orientation in the sea. Thales of Miletus

The starry sky above us ... In the middle latitudes, about 80% of the celestial sphere is available for observation. Let's start our acquaintance with the constellations from the summer sky. In the northern part, Ursa Major and Cassiopeia are visible. In the south, the summer-autumn triangle shines - Vega, Deneb and Altair. The huge Cygnus cross is easy to spot against the backdrop of the Milky Way. Closer to the horizon, you can see the brightest star of Scorpio - Antares. To the west of the triangle are Hercules, Northern Crown and Bootes. Ursa Major Cassiopeia Cygnus Scorpio Hercules Northern Crown Bootes
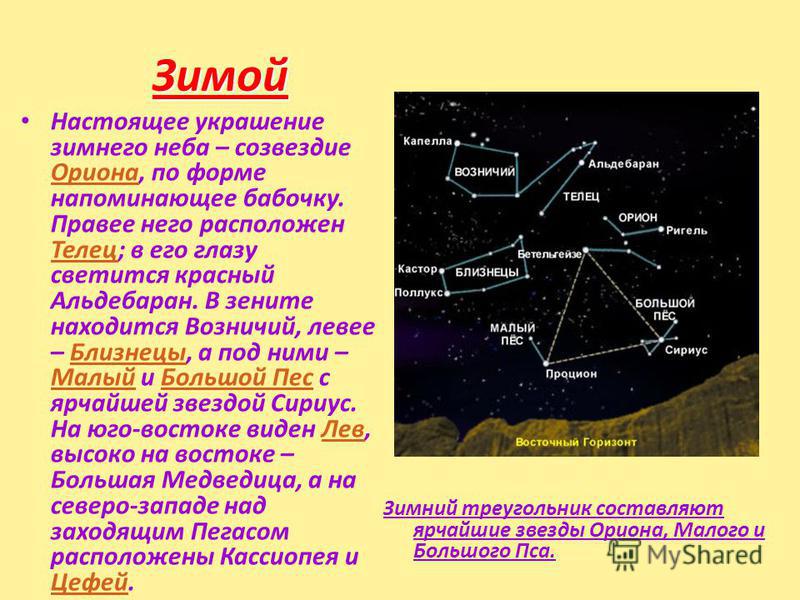
In winter The real decoration of the winter sky is the constellation Orion, shaped like a butterfly. To the right of it is Taurus; red Aldebaran glows in his eye. At the zenith is the Charioteer, to the left - Gemini, and below them - the Lesser and Greater Dog with the brightest star Sirius. Leo is visible in the southeast, Ursa Major is visible high in the east, and Cassiopeia and Cepheus are located in the northwest above the setting Pegasus. Orion Taurus Gemini Canis Minor Leo Cepheus The winter triangle is made up of the brightest stars of Orion, Canis Minor and Major.
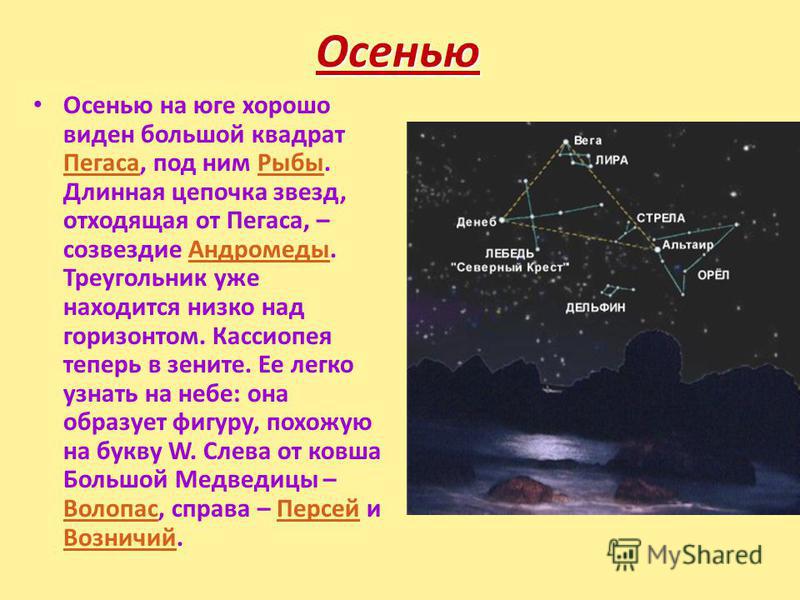
Autumn In autumn, a large Pegasus square is clearly visible in the south, Pisces below it. The long chain of stars extending from Pegasus is the constellation Andromeda. The triangle is already low on the horizon. Cassiopeia is now at its zenith. It is easy to recognize in the sky: it forms a figure similar to the letter W. To the left of the Ursa Major bucket is Bootes, to the right are Perseus and Charioteer. Pegasus Pisces Andromeda Bootes Perseus Charioteer

In spring, the sky is dark: there are few bright stars in it and the Milky Way is not visible. In the north hangs an inverted bucket of the Big Dipper. The handle of the bucket points to the orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern sky. On the continuation of this arc, you can find Spica - α Virgo. High in the south lay Leo, between him and Bootes is the constellation Coma Berenices. In the west, the Pleiades and Orion enter. Virgin Hair of Veronica Before the invention of the compass, the stars were the main landmarks: it was through them that the ancient sailors and travelers found the right direction. Astronavigation - orientation by the stars - has retained its significance in our age of satellites and atomic energy. It is necessary for navigators and astronauts, captains and pilots. The 25 brightest stars are called navigation stars, with the help of which the location of the ship is determined.


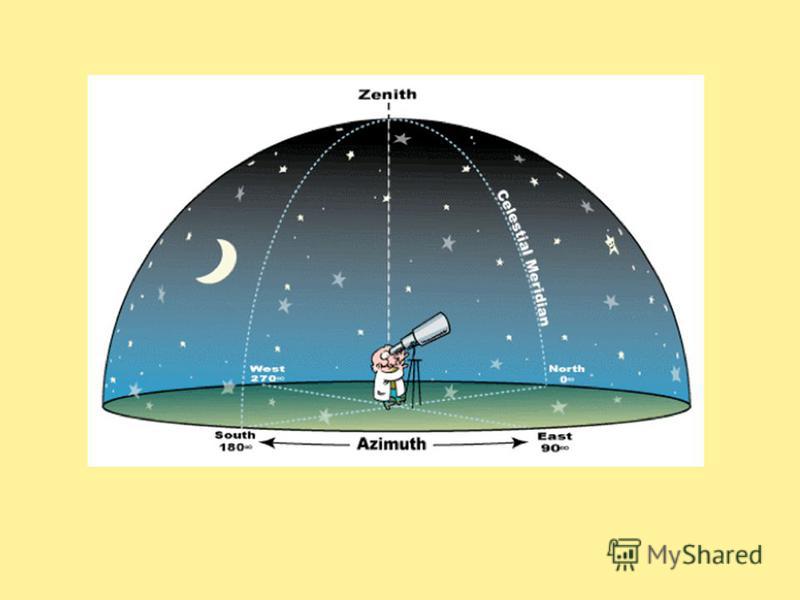

With the naked eye, you can see about 6,000 stars in the entire sky, but we see only half of them, because the Earth closes the other half of the starry sky from us. Due to its rotation, the appearance of the starry sky changes. Some stars are just emerging from the horizon (rising) in its eastern part, others are high above their heads at this time, and still others are already hiding behind the horizon in the western side (setting). At the same time, it seems to us that the starry sky rotates as a whole. Now everyone is well aware that the rotation of the sky is an apparent phenomenon caused by the rotation of the Earth. The picture of what happens to the starry sky as a result of the daily rotation of the Earth, allows you to capture the camera. If it were possible to photograph the paths of the stars in the sky for a whole day, then the photograph would turn out to be full circles - 360 °. After all, a day is the period of a complete revolution of the Earth around its axis. In an hour, the Earth will turn 1/24 of the circle, i.e., 15 °. Consequently, the length of the arc that the star will describe during this time will be 15 °, and in half an hour - 7.5 °. To indicate the position of the luminaries in the sky, a coordinate system is used similar to that used in geography - the equatorial coordinate system. As you know, the position of any point on the globe can be indicated using geographic coordinates - latitude and longitude.

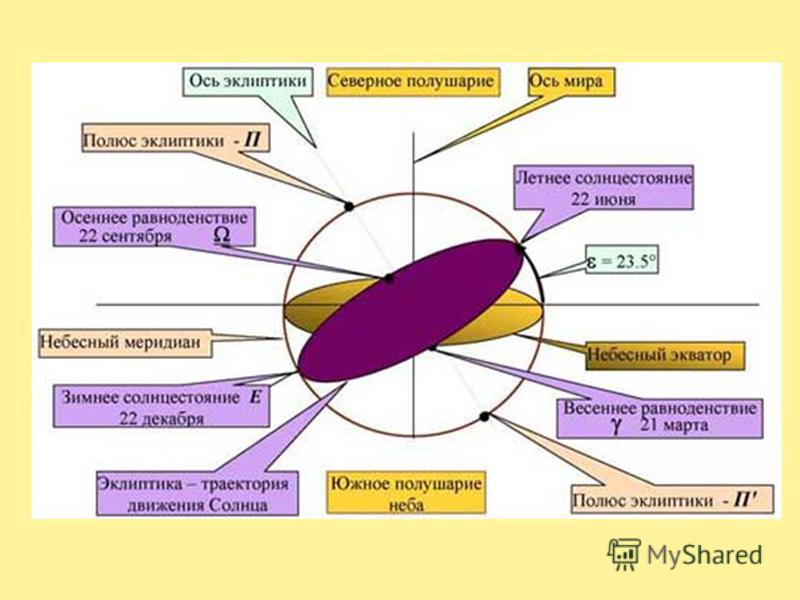
Let's introduce a system of equatorial coordinates, which indicates the position of the stars on the celestial sphere relative to each other. Let us draw a line through the center of the celestial sphere parallel to the axis of rotation of the Earth - the axis of the world. It will cross the celestial sphere at two diametrically opposite points, which are called the poles of the world - P and P. "The North Pole of the world is called the one near which the Polar Star is located. The plane passing through the center of the sphere parallel to the plane of the Earth's equator forms a circle in cross section with the sphere, called the celestial equator. The celestial equator (like the earth's) divides the celestial sphere into two hemispheres: Northern and Southern. The angular distance of the luminary from the celestial equator is called the declination, which is indicated by the Greek letter "delta". The declination is counted in a circle drawn through the luminary and the poles of the world, it is analogous to geographic latitude.The second coordinate, which indicates the position of the star in the sky, is similar to geographic longitude.This coordinate is called right ascension and is denoted by the Greek letter alpha.Right ascension is measured along the celestial equator from the vernal equinox point, at which the Sun annually occurs on March 21 (per day weight its equinox). In astronomy, it is customary to express right ascension not in degrees, but in hours. You remember that due to the rotation of the Earth, 15° corresponds to 1 hour, and 1° to 4 minutes. Therefore, a right ascension equal, for example, to 12 hours is 180°, and 7 hours and 40 minutes corresponds to 115°.
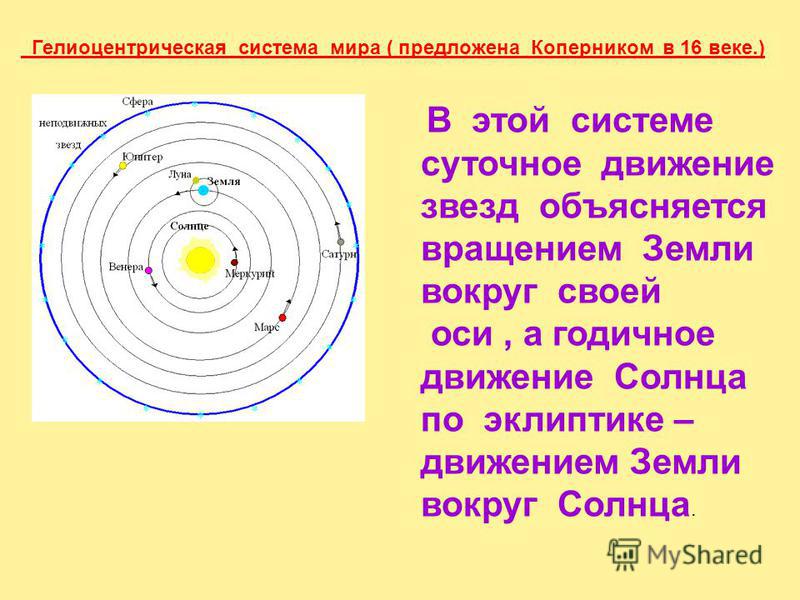


Observations are carried out with the help of astronomical observatories. The first observatory was established in 4000 BC. e. in the town of Stonehenge (England). The most famous observatories of the Russian Federation: Main Astronomical Observatory Russian Academy Sciences - Pulkovo (in St. Petersburg); Special Astrophysical Observatory (in the North Caucasus); State Astronomical Institute. PC. Sternberg (in Moscow).

Telescopes are very different: - optical (general astrophysical purpose, coronographs, telescopes for observing satellites); - radio telescopes; - infrared; - neutrino; - X-ray. With all their diversity, all telescopes that receive electromagnetic radiation solve two main tasks: to create the sharpest possible image and, in visual observations, to increase the angular distances between objects (stars, galaxies, etc.); collect as much radiation energy as possible, increase the illumination of the image of objects.

The first telescope was built in 1609 by the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. The telescope had modest dimensions (tube length 1245 mm, objective diameter 53 mm, eyepiece 25 diopters), an imperfect optical scheme and a 30x magnification. He made it possible to make a whole series of remarkable discoveries (phases of Venus, mountains on the Moon, satellites of Jupiter, spots on the Sun, stars in the Milky Way). The very poor image quality in the first telescopes forced opticians to look for ways to solve this problem. It turned out that increasing the focal length of the lens significantly improves image quality. Telescopes of Galileo (Museum of the History of Science, Florence). Two telescopes are mounted on a museum stand. In the center of the vignette is a broken lens from Galileo's first telescope Galileo's telescopes (Museum of the History of Science, Florence). Two telescopes are mounted on a museum stand. In the center of the vignette is a broken lens from Galileo's first telescope.

The telescope of Hevelius had a length of 50 m and was suspended by a system of ropes on a pole. The Ozu telescope was 98 meters long. At the same time, he did not have a tube, the lens was located on a pole at a distance of almost 100 meters from the eyepiece, which the observer held in his hands (the so-called air telescope). It was very inconvenient to observe with such a telescope. Ozu did not make a single discovery. Telescope Hevelius and Ozu

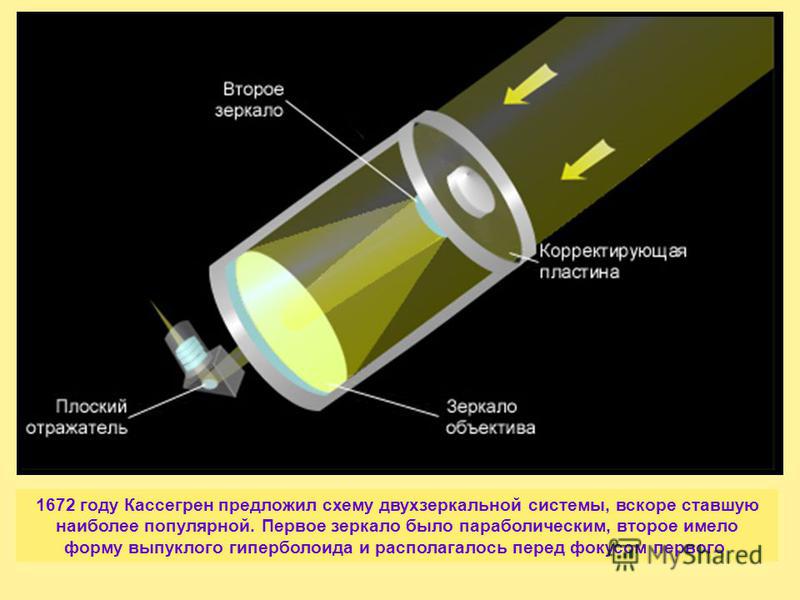
In 1663, Gregory created a new design for a reflecting telescope. Gregory was the first to suggest using a mirror instead of a lens in a telescope. The first reflecting telescope was built by Isaac Newton in 1668. The scheme by which it was built was called "Newton's scheme". The length of the telescope was 15 cm.
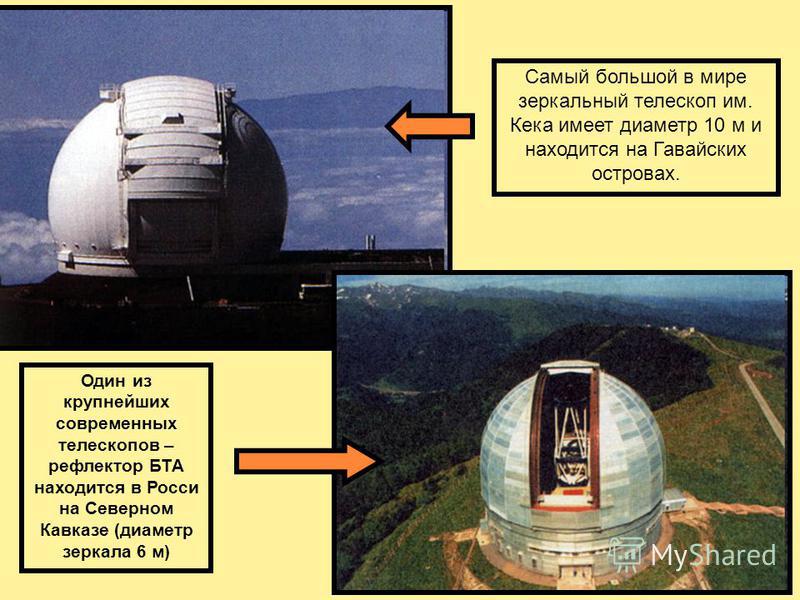
 In 1963, a 300-meter radio telescope with a spherical antenna began to operate in Arecibo on the island of Puerto Rico, installed in a huge natural pit in the mountains. In 1976, the 600-meter RATAN-600 radio telescope began to operate in the North Caucasus in Russia. The angular resolution of the radio telescope at a wavelength of 3 cm is 10".
In 1963, a 300-meter radio telescope with a spherical antenna began to operate in Arecibo on the island of Puerto Rico, installed in a huge natural pit in the mountains. In 1976, the 600-meter RATAN-600 radio telescope began to operate in the North Caucasus in Russia. The angular resolution of the radio telescope at a wavelength of 3 cm is 10".
Presentation on the topic "Starry sky" in astronomy in powerpoint format. Beautifully illustrated and filled interesting facts about stars and constellations. Presentation authors: Roman Erofeev and Vladimir Boryushkin, 11th grade students.
On a cloudless and moonless night away from settlements about 3000 stars can be distinguished. The entire celestial sphere contains about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye.
The most famous group of stars in the northern hemisphere is Bucket Ursa Major.
Astronomers of antiquity divided the starry sky into constellations. Most of the constellations named in the time of Hipparchus and Ptolemy have the names of animals or heroes of myths.
Thousands of years ago, bright stars were conditionally connected into figures that were called constellations.
In 1603, Johann Bayer began to designate the bright stars of each constellation with the letters of the Greek alphabet (α alpha), (β beta), (γ gamma), (ε delta) and so on, in descending order of their brightness. These designations are still in use today.
A constellation is a section of the celestial sphere, the boundaries of which are determined by a special decision of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). In total, there are 88 constellations in the celestial sphere.
The brightest stars have their own names.
The constellation Ursa Major can serve as a good helper for remembering the brightest stars in the Northern Hemisphere.
From the bucket of the Big Dipper it is easy to determine the northern direction.
Before the invention of the compass, the stars were the main landmarks: it was through them that the ancient sailors and travelers found the right direction. Astronavigation (orientation by the stars) has retained its importance in our age of satellites and atomic energy. It is necessary for navigators and astronauts, captains and pilots. Navigation is called the 25 brightest stars, with which they determine the location of the ship.
Constellations of the starry sky
Astronomy presentation
Made by physics teacher Pronkina V.S.




Ursa Minor
Next to the Big Dipper, a smaller seven-star bucket shines - this is the constellation Ursa Minor. According to legend, Zeus turned Arkad, the son of Callisto, into Ursa Minor.

constellation dragon
The long constellation Draco seems to wrap around the North Pole, surrounding Ursa Minor on three sides. The Greeks associate it with the myth of the battle of the gods and the titans. During the battle, one of the titans threw the dragon at the goddess of wisdom, Athena, but she grabbed the snake by the tail and threw it into the sky. The wriggling dragon flew to the very celestial pole and there it froze to the sky.
Constellation Andromeda
The huge constellation Andromeda represents a girl with outstretched arms. The wrists were chained to the rock. This is how Perseus saw her. He fell in love with a girl and decided to save her. The king and queen promised Perseus that they would give Andromeda in marriage to him if he protected the girl from the whale. Here the waves foamed, and the sea monster surfaced. The whale was ready to pounce on Perseus, but the young man showed him the head of Medusa. Under the gaze of even a dead Medusa, the whale turned into a huge rock. Perseus freed the rescued Andromeda from the shackles. Lovers shone in the sky with constellations


Inserting a picture
Constellation Cassiopeia
The easiest way to find it is in the sky. It shines in the sky like a giant "M"